What Was Darwin Influences On Malthus
Juapaving
Mar 30, 2025 · 6 min read
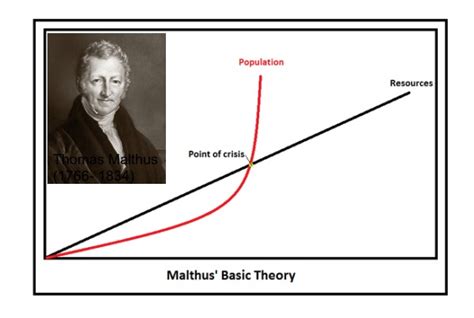
Table of Contents
Darwin's Debt to Malthus: How an Essay on Population Shaped the Theory of Evolution
Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection, a cornerstone of modern biology, owes a significant intellectual debt to the Reverend Thomas Robert Malthus. While Darwin synthesized insights from various sources, Malthus's Essay on the Principle of Population provided a crucial missing piece—a compelling mechanism for explaining how species change over time. This article delves into the profound influence Malthus had on Darwin's thinking, examining the specific aspects of Malthus's work that resonated with Darwin and how they were integrated into the theory of natural selection.
Malthus's Core Argument: A Struggle for Existence
Malthus's Essay, first published in 1798, argued that human populations tend to grow exponentially, while food production increases only linearly. This fundamental imbalance, Malthus asserted, inevitably leads to a "struggle for existence." He detailed the consequences of this imbalance, predicting recurring cycles of famine, disease, and war, which he saw as nature's brutal checks on population growth. While Malthus focused on human populations, the core principle—a relentless struggle for limited resources—had implications far beyond humanity.
The Significance of "Struggle for Existence" for Darwin
Darwin, reading Malthus's Essay in 1838, several years after his voyage on the Beagle, experienced what he later described as a "flash of insight." Malthus's concept of a "struggle for existence" provided the crucial mechanism he'd been seeking to explain the process of natural selection. Darwin recognized that this struggle wasn't limited to humans; it was a universal phenomenon occurring throughout the natural world. Plants compete for sunlight, water, and nutrients. Animals contend for food, mates, and territory. This constant competition, Darwin realized, was the driving force behind the adaptation and diversification of species.
Beyond Population: Malthus's Broader Impact on Darwin's Thinking
While the "struggle for existence" was the most direct influence, Malthus's ideas extended beyond this core concept. Several other aspects of Malthus's work subtly but significantly shaped Darwin's thinking:
1. The Concept of Variation: Seeds of Natural Selection
Although Malthus didn't explicitly address the topic of variation within populations, his focus on the differential success of individuals within a population implicitly acknowledged the existence of individual differences. Darwin, deeply influenced by his observations of diverse species during his voyage, recognized the crucial role of variation. He understood that within any population, individuals vary in their traits. Some of these variations might provide an advantage in the struggle for existence, increasing their chances of survival and reproduction. This understanding laid the foundation for the concept of natural selection.
2. The Role of Environmental Pressures: Shaping Adaptation
Malthus highlighted the role of environmental factors—limited resources, for example—in limiting population growth. Darwin extended this concept to explain the adaptation of species to their environments. He argued that environmental pressures, like scarcity of food or the presence of predators, would favor individuals possessing traits that enhanced their survival and reproduction in those specific conditions. Over time, these advantageous traits would become more common within the population, leading to evolutionary change.
3. Gradualism vs. Catastrophism: A Slow and Steady Process
Malthus's work implicitly supported a gradualist view of change. His model of population growth and resource limitations suggested a slow, ongoing process rather than sudden, catastrophic shifts. Darwin, influenced by the work of geologists like Charles Lyell, embraced this gradualist perspective. He proposed that evolution occurs through the accumulation of small changes over vast periods, a process he termed "descent with modification." This contrasted with the then-prevalent view of catastrophism, which attributed large-scale changes to sudden catastrophic events.
Integrating Malthus into Darwin's Theory: Natural Selection
The synthesis of Malthusian principles with Darwin's own observations formed the core of his theory of natural selection:
- Variation: Individuals within a population exhibit variation in their traits.
- Inheritance: These traits are heritable, passed from parents to offspring.
- Overproduction: Populations produce more offspring than can possibly survive given limited resources.
- Struggle for Existence: This overproduction leads to a struggle for existence, with individuals competing for resources and survival.
- Differential Survival and Reproduction: Individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing those advantageous traits to their offspring.
- Adaptation: Over time, this process leads to the adaptation of populations to their environments and the evolution of new species.
This elegantly simple yet powerfully explanatory theory revolutionized our understanding of the natural world, and Malthus's concept of the "struggle for existence" was the pivotal mechanism that made it work.
Criticisms of Malthus and Their Impact on Darwin's Theory
While Malthus's influence on Darwin was undeniable, it's crucial to acknowledge criticisms of Malthus's work and their implications for Darwin's theory. Malthus's predictions of inevitable population collapse, for example, have been challenged, with advancements in agriculture and technology demonstrating the capacity to increase food production. Furthermore, the simplistic nature of Malthus's model, neglecting factors like technological innovation and social change, led to criticisms regarding its accuracy and applicability.
However, these criticisms don't negate Malthus's profound impact on Darwin. Even if Malthus's specific predictions weren't entirely accurate, the fundamental principle of a "struggle for existence" remains a cornerstone of evolutionary biology. The competition for resources, even if modulated by human intervention or environmental fluctuations, continues to shape the evolution of species.
The Enduring Legacy: Malthus and Evolutionary Biology Today
Despite ongoing debate about specific aspects of Malthus's work, its impact on Darwin and subsequently on evolutionary biology remains profound. The "struggle for existence," though refined and nuanced by subsequent research, continues to be a central concept in our understanding of adaptation, speciation, and the dynamics of populations. Malthus's work highlights the importance of environmental constraints in shaping evolution, a theme that remains central to ecological and evolutionary studies today. The interplay between population growth, resource availability, and the selective pressures these factors impose continues to be a focus of research across diverse biological disciplines.
Conclusion: A Necessary Component
Thomas Robert Malthus’s Essay on the Principle of Population provided a crucial missing link in Darwin's intellectual framework. The concept of the "struggle for existence," central to Malthus's work, provided the mechanism by which Darwin explained the process of natural selection. While criticisms exist regarding the accuracy of some of Malthus's predictions, the fundamental principle of limited resources driving competition within populations remains a cornerstone of modern evolutionary theory. Malthus's influence, therefore, transcends the specific details of his arguments; it represents a crucial conceptual breakthrough that fundamentally shaped our understanding of life on Earth. The enduring legacy of Malthus's work lies in its contribution to one of the most significant scientific revolutions in history: the development and acceptance of the theory of evolution by natural selection.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Where Glucose Gets Broken Into Pyruvate In The Cell
Apr 01, 2025
-
Find The Inverse Of The Relation
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Are Cellular Respiration And Photosynthesis Related
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Many Rna Polymerases Are Found In Prokaryotes
Apr 01, 2025
-
When Two Parallel Lines Are Crossed By A Transversal
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Was Darwin Influences On Malthus . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
