How Are Cellular Respiration And Photosynthesis Related
Juapaving
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
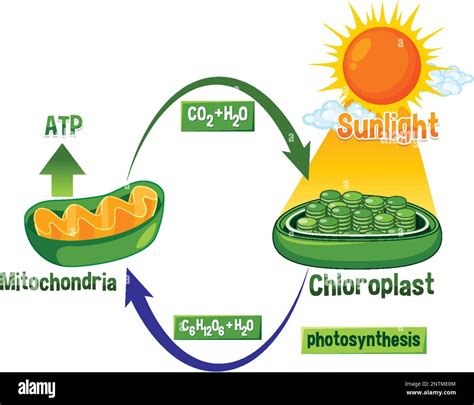
Table of Contents
How Are Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Related? A Deep Dive into Earth's Energy Cycle
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two fundamental processes that underpin the survival of almost all life on Earth. While seemingly disparate, they are intricately linked in a cyclical dance of energy transfer, forming the cornerstone of Earth's biogeochemical cycles. This article delves into the intimate relationship between these processes, exploring their similarities, differences, and the crucial role they play in maintaining the balance of life on our planet.
The Yin and Yang of Energy Transfer: A Comparative Overview
At first glance, photosynthesis and cellular respiration might seem like opposing processes. However, a closer examination reveals their complementary nature – one producing the fuel the other consumes.
Photosynthesis, the process primarily carried out by plants, algae, and some bacteria, converts light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose (a sugar). This process occurs in chloroplasts, specialized organelles within plant cells containing chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for absorbing light energy. The overall equation for photosynthesis is:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Light Energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
This equation demonstrates that photosynthesis takes in carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O) and, using light energy, produces glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) and oxygen (O₂). The glucose serves as the primary energy source for the plant, while the oxygen is released as a byproduct.
Cellular respiration, on the other hand, is a process that occurs in nearly all living organisms, including plants and animals. It breaks down glucose to release the stored energy for cellular activities. This process takes place in the mitochondria, the "powerhouses" of the cell. The overall equation for cellular respiration is:
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + ATP
This equation shows that cellular respiration uses glucose and oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell's primary energy currency. The energy released during this process is harnessed to power various cellular functions, including growth, movement, and reproduction.
Key Similarities:
- Energy Transformation: Both processes involve the transformation of energy from one form to another. Photosynthesis converts light energy into chemical energy, while cellular respiration converts chemical energy into a usable form (ATP).
- Use of Water: Both processes utilize water, though in different ways. Photosynthesis uses water as a reactant, while cellular respiration produces water as a byproduct.
- Involvement of Gases: Both processes involve the exchange of gases with the environment. Photosynthesis takes in CO₂ and releases O₂, while cellular respiration takes in O₂ and releases CO₂.
- Metabolic Pathways: Both processes are complex metabolic pathways involving multiple steps and enzymes. While the specific steps differ significantly, both involve a series of oxidation-reduction reactions.
Key Differences:
| Feature | Photosynthesis | Cellular Respiration |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Chloroplasts (in plants and algae) | Mitochondria (in almost all cells) |
| Energy Source | Light energy | Chemical energy (glucose) |
| Reactants | Carbon dioxide, water, light energy | Glucose, oxygen |
| Products | Glucose, oxygen | Carbon dioxide, water, ATP |
| Process | Anabolic (builds complex molecules) | Catabolic (breaks down complex molecules) |
The Interdependence: A Cyclical Relationship
The crucial relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration lies in their cyclical nature. The products of one process become the reactants of the other, creating a continuous flow of energy through ecosystems.
- Oxygen Production and Consumption: Photosynthesis produces the oxygen that is essential for cellular respiration in most organisms. Plants, through photosynthesis, release oxygen into the atmosphere, which is then inhaled by animals and used in cellular respiration.
- Carbon Dioxide Exchange: Cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide, a byproduct that is crucial for photosynthesis. The CO₂ released by animals and other organisms is then taken in by plants for photosynthesis.
- Glucose Production and Utilization: Photosynthesis produces glucose, the primary energy source used in cellular respiration. Plants produce glucose through photosynthesis, and this glucose serves as the fuel for both plant cells and the organisms that consume them.
The Carbon Cycle: A Manifestation of the Interdependence
The interdependence between photosynthesis and cellular respiration is vividly illustrated by the carbon cycle. This cycle shows the continuous movement of carbon atoms between the atmosphere, organisms, and the environment.
Plants absorb CO₂ from the atmosphere during photosynthesis, incorporating carbon atoms into glucose molecules. These carbon atoms are then passed on to animals through the food chain. During cellular respiration, the carbon atoms in glucose are released back into the atmosphere as CO₂, completing the cycle. This continuous cycling of carbon is vital for maintaining the balance of atmospheric CO₂ and for sustaining life on Earth.
Beyond the Basics: Variations and Adaptations
While the basic principles of photosynthesis and cellular respiration remain consistent, variations and adaptations exist across different organisms and environments.
Variations in Photosynthesis:
- C3, C4, and CAM Plants: Plants have evolved different photosynthetic pathways to adapt to varying environmental conditions. C3 plants use the standard Calvin cycle, while C4 and CAM plants have evolved mechanisms to minimize water loss and photorespiration in hot, dry climates.
- Photosynthetic Pigments: Different organisms possess various photosynthetic pigments that absorb different wavelengths of light, allowing them to thrive in diverse light conditions.
Variations in Cellular Respiration:
- Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration: While most organisms rely on aerobic respiration (requiring oxygen), some organisms can perform anaerobic respiration (without oxygen), such as fermentation in yeast and muscle cells during intense exercise.
- Metabolic Pathways: Different organisms may utilize slightly different metabolic pathways within cellular respiration, resulting in variations in ATP production efficiency.
The Importance of Understanding the Interplay
Understanding the intricate relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration is critical for comprehending various ecological and environmental phenomena.
- Climate Change: The balance between photosynthesis and cellular respiration plays a crucial role in regulating atmospheric CO₂ levels. Human activities, such as deforestation and the burning of fossil fuels, disrupt this balance, leading to increased CO₂ levels and contributing to climate change.
- Ecosystem Stability: The cyclical exchange of energy and matter between plants and animals through these processes is essential for maintaining ecosystem stability and biodiversity.
- Food Production: Understanding photosynthesis is crucial for improving agricultural practices and increasing food production. Scientists are constantly exploring ways to enhance photosynthesis efficiency in crops to meet the growing global food demands.
Conclusion: A Symbiotic Dance of Life
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are not simply two separate processes; they are inextricably linked in a symbiotic dance of life. One provides the fuel for the other, creating a continuous cycle of energy transfer that supports the intricate web of life on Earth. Understanding their interdependence is essential for appreciating the complexity and fragility of our planet's ecosystems and for addressing the challenges posed by climate change and other environmental issues. Further research and innovation in understanding and manipulating these fundamental processes will be crucial in securing a sustainable future for all life on Earth.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Does A Gas Have A Definite Volume
Apr 02, 2025
-
Which Base Is Found Only In Rna
Apr 02, 2025
-
Difference Between Meiosis 1 And Meiosis 2
Apr 02, 2025
-
Equation Of Circle In Parametric Form
Apr 02, 2025
-
How To Find The Complement Of An Angle
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Are Cellular Respiration And Photosynthesis Related . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
