What Kingdom Does Euglena Belong To
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
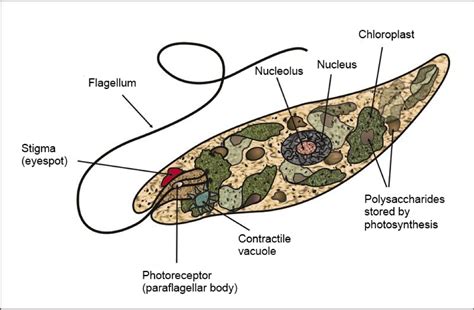
Table of Contents
What Kingdom Does Euglena Belong To? A Deep Dive into the Controversial Classification of Euglena
The question of what kingdom Euglena belongs to is not a straightforward one. Unlike many organisms neatly categorized into the plant, animal, or fungi kingdoms, Euglena presents a fascinating case of evolutionary ambiguity, blurring the lines between traditional classifications. This has led to considerable debate and revisions within the scientific community, making it a compelling topic for biological exploration. This article will delve into the complexities of Euglena classification, exploring its unique characteristics and why its kingdom assignment remains a subject of ongoing discussion.
The Traditional Kingdoms and Their Limitations
For many years, the biological world relied on a five-kingdom system: Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista, and Monera (now divided into Bacteria and Archaea). This system, while useful for introductory purposes, struggled to accommodate organisms exhibiting characteristics of multiple kingdoms. Euglena, with its blend of plant-like and animal-like traits, highlights the inherent limitations of this approach.
Animal-like Characteristics of Euglena
-
Movement: Euglena possesses flagella, whip-like appendages used for locomotion, a characteristic commonly associated with animal cells. This allows them to move freely in their aquatic environment, actively seeking optimal conditions for growth and survival. This active motility distinguishes them from many plant cells, which are typically immobile.
-
Heterotrophic Nutrition: While capable of photosynthesis, Euglena can also obtain nutrients through heterotrophic means. In the absence of sunlight, they can absorb organic molecules from their surroundings, a strategy typical of animals. This adaptability allows them to survive in diverse environments, even when light is limited. This flexibility in nutrient acquisition is a crucial feature distinguishing them from strictly autotrophic plants.
-
Presence of an Eyespot: Euglena possesses a distinctive eyespot (stigma), a light-sensitive organelle that helps them detect light sources. This structure facilitates phototaxis, the movement towards or away from light, a behaviour more commonly associated with organisms capable of responding to environmental stimuli, a hallmark of more complex organisms.
Plant-like Characteristics of Euglena
-
Photosynthesis: Euglena contains chloroplasts, organelles responsible for photosynthesis. These chloroplasts enable them to produce their own food using sunlight, a defining characteristic of plants. The presence of chlorophyll allows them to harness light energy, contributing to their autotrophic lifestyle. This photosynthetic capability is a strong argument for placing Euglena within a plant-related classification.
-
Cell Wall (sometimes): While not always present, some species of Euglena possess a flexible pellicle, a protein layer that provides structural support, somewhat analogous to a cell wall in plants. However, this pellicle is significantly different in structure and composition from the rigid cell walls found in most plants, adding another layer of complexity to its classification.
The Kingdom Protista: A Refuge for the Unclassifiable
The kingdom Protista, often described as a "catch-all" kingdom, provided a temporary home for organisms like Euglena that defied simple categorization. Protista encompasses a vast array of eukaryotic organisms, including algae, protozoa, and slime molds, each with its own unique set of characteristics. This kingdom encompasses a wide range of organisms which share one common trait: they are eukaryotic but not plants, animals, or fungi.
The Limitations of Protista
However, the kingdom Protista itself is becoming increasingly outdated. It's a polyphyletic group, meaning its members do not share a single common ancestor, highlighting its artificial nature. This has led to a growing movement towards a more cladistic approach to classification, based on evolutionary relationships. As our understanding of phylogenetic relationships improves, the kingdom Protista's future is uncertain. It is likely to be further subdivided into more specific, and more reflective classifications.
Modern Classification and Phylogenetic Approaches
Modern biological classification strives for a more natural system, reflecting evolutionary relationships more accurately. Phylogenetic analysis, using molecular data like DNA sequences, is crucial in this endeavor. This method analyzes the genetic relatedness between organisms, providing a more robust basis for establishing evolutionary lineages.
Euglena's Place in the Phylogenetic Tree
Phylogenetic studies have shown that Euglena belongs to a larger group of organisms called the Excavata. This supergroup contains a diverse array of single-celled eukaryotes, many of which are flagellated and exhibit unusual mitochondrial structures. Within the Excavata, Euglena is classified within the Euglenozoa, a clade characterized by unique mitochondrial cristae and a distinctive flagellar apparatus. This phylogenetic placement provides a more precise and biologically meaningful classification than simply placing them in the broad Protista kingdom.
The Significance of Molecular Data
Molecular data, particularly ribosomal RNA sequences, have been instrumental in clarifying the evolutionary history of Euglena and other protists. This information allows scientists to build more accurate phylogenetic trees, reflecting the branching patterns of evolution. The analysis of genetic material provides a more objective and data-driven approach to classification compared to relying solely on morphological characteristics.
The Ongoing Debate: Kingdom or Clade?
The debate regarding Euglena's classification isn't just about which kingdom it belongs to; it's also about the very structure of the biological classification system. The traditional kingdom system is increasingly being superseded by a cladistic approach, focusing on evolutionary relationships and monophyletic groups (groups containing a common ancestor and all of its descendants).
Advantages of Cladistic Classification
Cladistic systems provide a more accurate and informative way to represent the evolutionary history of life. By grouping organisms based on shared derived characteristics (synapomorphies), they avoid the artificial groupings inherent in the older kingdom-based systems. This offers a clearer understanding of evolutionary relationships and helps scientists to comprehend the diversification of life on Earth.
The Future of Euglena Classification
It’s unlikely that the term “kingdom” will persist as a primary descriptor for Euglena in the future. The ongoing refinement of phylogenetic analysis will likely lead to even finer subdivisions within the Excavata supergroup. The focus will shift towards precise clades and sub-clades, reflecting the evolutionary history and relationships more accurately than broad kingdom designations.
Practical Implications of Euglena's Classification
While the finer points of Euglena's classification might seem purely academic, they have practical implications for various fields:
-
Biotechnology: Euglena species are increasingly being explored for their potential in various biotechnological applications, including biofuel production and the synthesis of valuable compounds. A clear understanding of their phylogeny is crucial for identifying species with desirable traits and optimizing cultivation techniques.
-
Environmental Monitoring: Euglena are sensitive to environmental changes, making them useful indicators of water quality. Knowing their taxonomic placement can help refine monitoring strategies and improve the accuracy of environmental assessments.
-
Evolutionary Biology: The study of Euglena continues to provide valuable insights into the evolution of eukaryotic cells and the development of key cellular processes like photosynthesis and motility. Their unique evolutionary history provides a window into the early diversification of life.
Conclusion: A Dynamic and Evolving Understanding
The question of what kingdom Euglena belongs to highlights the dynamic nature of biological classification. While it was once comfortably (though somewhat arbitrarily) placed in the Protista kingdom, modern phylogenetic analyses paint a more nuanced picture. Euglena belongs within the Excavata supergroup, specifically the Euglenozoa clade, reflecting a more accurate representation of its evolutionary history. As our understanding of evolutionary relationships improves through continued molecular studies, further refinements in Euglena's classification are likely. The focus will shift towards a more cladistic approach, abandoning the limitations of the traditional kingdom system in favor of a more precise and biologically meaningful system of classification. The ongoing research into Euglena continues to reveal fascinating aspects of its biology and evolutionary significance, emphasizing the dynamic and ever-evolving nature of biological classification.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Density An Intensive Or Extensive Property
Mar 18, 2025
-
Words That End In The Letter E
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Formula For The Chlorate Ion
Mar 18, 2025
-
Chemical Reaction Of Iron And Water
Mar 18, 2025
-
Write The Prime Factorization Of 27
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Kingdom Does Euglena Belong To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
