Write The Prime Factorization Of 27
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
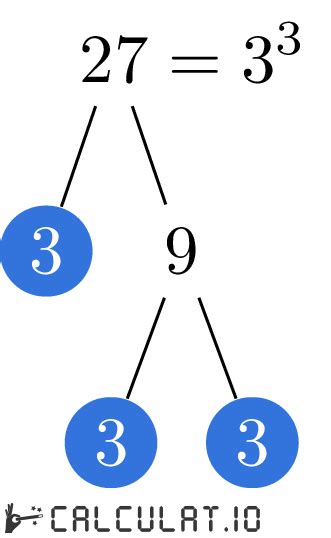
Table of Contents
The Prime Factorization of 27: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization of 27?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory. While the answer itself is straightforward, understanding the process and its implications unveils fundamental concepts crucial to mathematics and computer science. This article delves into the prime factorization of 27, exploring the underlying principles and expanding on their broader significance.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before tackling the factorization of 27, let's solidify our understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. These numbers are the building blocks of all other natural numbers.
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic: This theorem states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers, disregarding the order of the factors. This uniqueness is what makes prime factorization so powerful. It's like a unique fingerprint for each number.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 27
Now, let's find the prime factorization of 27. We can use a method called the factor tree. This involves repeatedly dividing the number by the smallest prime number that divides it evenly until we are left with only prime numbers.
-
Start with 27: Since 27 is an odd number, it's not divisible by 2. The next smallest prime number is 3.
-
Divide by 3: 27 divided by 3 is 9. So we have 27 = 3 x 9.
-
Continue Factoring: Now we need to factor 9. 9 is also divisible by 3, giving us 9 = 3 x 3.
-
Prime Factorization: Combining these steps, we get 27 = 3 x 3 x 3. We can also write this as 3³. This is the prime factorization of 27. All the factors (3) are prime numbers.
Visual Representation (Factor Tree):
27
/ \
3 9
/ \
3 3
Significance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple act of finding the prime factorization of 27 has far-reaching implications across various fields:
1. Cryptography: The Foundation of Secure Communication
Prime numbers play a crucial role in modern cryptography, particularly in public-key cryptography. Algorithms like RSA rely on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime components. The security of online transactions, secure communication protocols (like HTTPS), and digital signatures all depend on this computational challenge. Even factoring a relatively small number like 27 is a simple illustration of the underlying principle.
2. Number Theory: Unraveling the Mysteries of Numbers
Prime factorization is fundamental to number theory. It helps us understand the properties of numbers, solve Diophantine equations (equations with integer solutions), and explore relationships between different numbers. The study of prime numbers and their distribution is an active area of research, with unsolved problems like the Riemann Hypothesis still captivating mathematicians.
3. Computer Science: Algorithms and Efficiency
Finding efficient algorithms for prime factorization is a major challenge in computer science. The complexity of these algorithms directly impacts the security of cryptographic systems. The development of faster factorization algorithms would have significant implications for data security and potentially break widely used encryption methods.
4. Other Applications: Beyond Cryptography and Number Theory
Prime factorization also finds applications in other areas, including:
- Coding Theory: Error detection and correction codes often rely on prime numbers for their construction.
- Data Structures: Some data structures utilize prime numbers for efficient hashing and indexing.
- Random Number Generation: Prime numbers are used in the generation of pseudo-random numbers.
Exploring Related Concepts
Let's delve deeper into related number theory concepts that are illuminated by understanding the prime factorization of 27:
1. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD):
The GCD of two numbers is the largest number that divides both without leaving a remainder. Knowing the prime factorization makes finding the GCD significantly easier. For instance, finding the GCD of 27 and another number requires only examining the prime factors.
2. Least Common Multiple (LCM):
The LCM of two numbers is the smallest number that is a multiple of both. Again, prime factorization simplifies this calculation. It involves identifying the highest power of each prime factor present in either number.
3. Perfect Numbers:
Perfect numbers are numbers that are equal to the sum of their proper divisors (excluding the number itself). Understanding prime factorization is crucial in investigating and identifying perfect numbers.
4. Mersenne Primes:
Mersenne primes are prime numbers that are one less than a power of two (2<sup>p</sup> - 1, where p is a prime). The search for Mersenne primes is an ongoing quest, driven by both mathematical curiosity and the potential for discoveries related to prime number distribution.
Advanced Concepts: Beyond the Basics
While the prime factorization of 27 is simple, the field of prime numbers and factorization extends to significantly more complex scenarios:
-
Factoring Large Numbers: As mentioned earlier, factoring very large numbers is computationally intensive. This complexity is the foundation of the security of many cryptographic systems. Algorithms like the General Number Field Sieve are used to factor these large numbers, but even these algorithms are limited in their ability to tackle extremely large numbers efficiently.
-
The Riemann Hypothesis: One of the most significant unsolved problems in mathematics is the Riemann Hypothesis, which relates to the distribution of prime numbers. Its solution would have profound implications for our understanding of prime numbers and their properties.
-
Distribution of Prime Numbers: The study of how prime numbers are distributed amongst the natural numbers is another area of active research. While there are patterns and formulas that help predict the approximate number of primes within a given range, a precise formula remains elusive.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple prime factorization of 27 – 3³ – serves as a gateway to a vast and intricate world of mathematics. Its significance extends far beyond a basic arithmetic exercise. From underpinning the security of our digital world to driving research in number theory, the principles illustrated by this simple factorization remain crucial to our understanding of numbers and their applications in various fields. The quest to unravel the mysteries of prime numbers continues, shaping both theoretical mathematics and practical technological advancements. The journey from a seemingly simple question to the complex world of prime numbers and their applications highlights the profound depth and continuous evolution of mathematical understanding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Does A Circle Have A Corner
Mar 18, 2025
-
Why Do We Look Like Our Parents
Mar 18, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 27 And 45
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Do You Turn Gas Into A Liquid
Mar 18, 2025
-
A Push Or Pull Is Called
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Write The Prime Factorization Of 27 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
