What Is The Prime Factorization Of 25
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
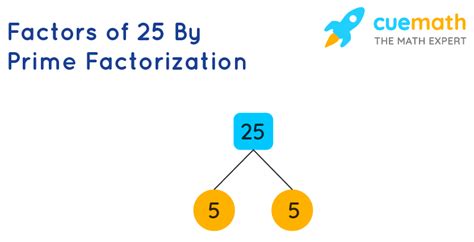
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization of 25? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization of 25?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory. While the answer itself is straightforward, understanding the underlying concepts of prime numbers and factorization provides a solid foundation for more complex mathematical explorations. This comprehensive guide will delve into the prime factorization of 25, exploring the concepts of prime numbers, factorization, and the significance of this seemingly basic mathematical operation.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before tackling the prime factorization of 25, let's define what a prime number is. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself. This means it's not divisible by any other whole number without leaving a remainder. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The number 1 is not considered a prime number.
Prime numbers are the building blocks of all other whole numbers. They are fundamental to many areas of mathematics, including cryptography, computer science, and even the study of the distribution of galaxies in the universe. The study of prime numbers is an ongoing area of research, with many unsolved problems and conjectures, making it a vibrant and exciting field.
Identifying Prime Numbers
Determining whether a number is prime can be straightforward for smaller numbers, but it becomes increasingly complex as the numbers get larger. There are various methods to test for primality, including:
-
Trial Division: This involves testing for divisibility by all prime numbers less than the square root of the number in question. If it's not divisible by any of these primes, it's a prime number. This method is effective for smaller numbers but becomes computationally expensive for larger numbers.
-
Sieve of Eratosthenes: This is a more efficient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer. It involves systematically marking the multiples of each prime number, leaving only the prime numbers unmarked.
-
Probabilistic Tests: For very large numbers, probabilistic tests are used. These tests don't guarantee primality but provide a high probability that a number is prime. These are crucial for applications like cryptography, where very large prime numbers are essential.
Factorization: Breaking Down Numbers
Factorization is the process of expressing a whole number as a product of its factors. Factors are the numbers that divide evenly into the original number without leaving a remainder. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12.
There are different types of factorization, including:
-
Prime Factorization: This is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. This is unique for every number and is often represented using exponents to show repeated factors. For example, the prime factorization of 12 is 2² x 3.
-
Integer Factorization: This involves finding any factors of a number, not necessarily prime ones.
-
Polynomial Factorization: This extends the concept of factorization to polynomials, expressions involving variables and coefficients.
The Prime Factorization of 25
Now, let's address the central question: What is the prime factorization of 25?
The number 25 can be factored as 5 x 5. Since 5 is a prime number (its only divisors are 1 and 5), the prime factorization of 25 is 5². This means 25 is composed of two factors of 5 multiplied together.
Significance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of a number, seemingly a simple concept, holds significant importance in several areas:
-
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM): Prime factorization simplifies the calculation of the GCD and LCM of two or more numbers. This is crucial in various mathematical and computational applications.
-
Cryptography: The security of many cryptographic systems relies on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime factors. RSA encryption, for example, uses this principle to secure online transactions and data transmission.
-
Number Theory: Prime factorization is fundamental to many areas of number theory, including the study of prime number distribution, modular arithmetic, and Diophantine equations.
-
Algebra and Polynomial Factorization: The concept of prime factorization extends to polynomials, offering tools for simplifying algebraic expressions and solving equations.
Applications of Prime Factorization in Real-World Scenarios
The seemingly abstract concept of prime factorization has practical applications in various real-world scenarios. Consider these examples:
-
Simplifying Fractions: When simplifying fractions, finding the prime factorization of the numerator and denominator allows you to cancel out common factors, resulting in a simplified fraction.
-
Solving Problems Involving Ratios and Proportions: Understanding prime factorization can help in solving problems related to ratios and proportions, such as scaling recipes or determining the optimal mix of ingredients.
-
Coding and Algorithms: Prime factorization is essential in designing efficient algorithms for various computational tasks, including cryptography and data compression.
-
Scientific Research: In scientific research, particularly in areas involving pattern recognition and data analysis, prime factorization can aid in identifying patterns and relationships within data sets.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Deeper Concepts
The prime factorization of 25 provides a springboard for delving into more complex mathematical concepts:
-
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic: This theorem states that every integer greater than 1 can be uniquely represented as a product of prime numbers, disregarding the order of the factors. This uniqueness is a cornerstone of number theory.
-
Infinite Number of Primes: Euclid's proof of the infinitude of prime numbers demonstrates that there is no largest prime number, highlighting the endless nature of prime numbers and their importance in mathematical structures.
-
Prime Number Distribution: The study of the distribution of prime numbers is a fascinating area of research, with mathematicians exploring patterns and irregularities in their occurrence. The Prime Number Theorem provides an approximation of the number of primes less than a given number.
-
Goldbach's Conjecture: This unsolved conjecture proposes that every even integer greater than 2 can be expressed as the sum of two prime numbers. It remains one of the most famous unsolved problems in mathematics, highlighting the ongoing mysteries surrounding prime numbers.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of 25, while a seemingly simple calculation (5²), serves as a gateway to a rich and complex field of mathematics. Understanding prime numbers and factorization is crucial for various applications, from simplifying fractions to securing online transactions. The fundamental concepts explored here—prime numbers, factorization, and the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic—provide a solid foundation for further exploration into the fascinating world of number theory and its wide-ranging applications. The seemingly simple question about the prime factorization of 25 opens doors to a universe of mathematical exploration, highlighting the profound and enduring importance of this fundamental concept.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Lcm Of 6 8 And 9
Mar 28, 2025
-
If The Diagonals Of A Quadrilateral Bisect Each Other
Mar 28, 2025
-
Write The Electron Configuration For A Neutral Atom Of Magnesium
Mar 28, 2025
-
Differentiate Between Chemical Reaction And Nuclear Reaction
Mar 28, 2025
-
Is 35 A Multiple Of 5
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Prime Factorization Of 25 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
