What Are The Prime Factors Of 15
Juapaving
Mar 27, 2025 · 6 min read
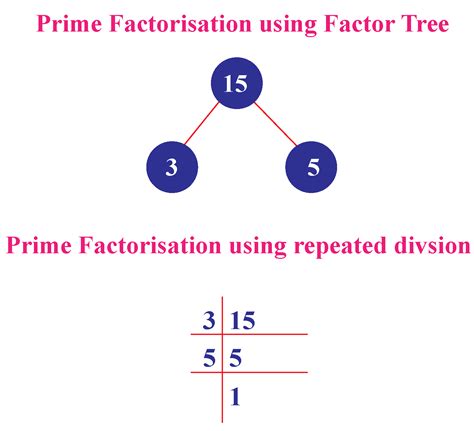
Table of Contents
What Are the Prime Factors of 15? A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What are the prime factors of 15?" opens a door to a fundamental concept in number theory: prime factorization. While the answer itself is straightforward, exploring the process and its implications reveals a fascinating world of mathematical principles and their practical applications. This article delves deep into the prime factors of 15, explaining the method, its significance, and its broader context within mathematics and computer science.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before we tackle the prime factors of 15, let's solidify our understanding of prime numbers themselves. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. This means it cannot be expressed as a product of two smaller natural numbers. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The number 1 is not considered prime, and neither are numbers that are divisible by numbers other than 1 and themselves (e.g., 4 is divisible by 2, 6 is divisible by 2 and 3).
The Importance of Prime Numbers
Prime numbers are the building blocks of all other whole numbers. This foundational role makes them incredibly important in various fields:
-
Cryptography: Many modern encryption methods rely heavily on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components. The security of online transactions and sensitive data often hinges on this principle.
-
Computer Science: Prime numbers are used in algorithms and data structures, contributing to the efficiency and performance of various software applications. Hashing techniques, for instance, often leverage prime numbers for optimal distribution.
-
Number Theory: Prime numbers are central to many theorems and conjectures in number theory, driving significant mathematical research and exploration. The Riemann Hypothesis, one of the most important unsolved problems in mathematics, directly relates to the distribution of prime numbers.
Finding the Prime Factors of 15: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's find the prime factors of 15. The process of finding the prime factors of a number is called prime factorization. There are several methods, but a straightforward approach involves repeatedly dividing the number by the smallest prime number that divides it evenly until you're left with 1.
-
Start with the smallest prime number, 2: 15 is not divisible by 2 (it's an odd number).
-
Try the next prime number, 3: 15 divided by 3 is 5. This means 3 is a prime factor of 15.
-
Continue with the quotient: Now we have 5. 5 is itself a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 15 is 3 x 5. The prime factors of 15 are 3 and 5.
Visualizing Prime Factorization: Factor Tree
A helpful visual aid for prime factorization is a factor tree. For 15:
15
/ \
3 5
This tree clearly shows that 15 breaks down into its prime factors, 3 and 5. Larger numbers may require longer factor trees, but the principle remains the same.
Beyond 15: Exploring Prime Factorization of Other Numbers
Let's extend our understanding by exploring the prime factorization of a few more numbers:
-
12: 12 = 2 x 2 x 3 = 2² x 3. The prime factors are 2 and 3.
-
24: 24 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 = 2³ x 3. The prime factors are 2 and 3.
-
35: 35 = 5 x 7. The prime factors are 5 and 7.
-
100: 100 = 2 x 2 x 5 x 5 = 2² x 5². The prime factors are 2 and 5.
Notice that some numbers have repeated prime factors, indicated by exponents. This is perfectly acceptable and a key aspect of prime factorization.
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
The fact that every integer greater than 1 can be uniquely represented as a product of prime numbers (ignoring the order of the factors) is known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic. This theorem is a cornerstone of number theory, ensuring that prime factorization is a well-defined and consistent process. The uniqueness of this representation is crucial for many mathematical operations and proofs.
Applications of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple act of finding prime factors has profound implications across various fields:
Cryptography: RSA Algorithm
The RSA algorithm, a widely used public-key cryptosystem, relies heavily on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components. The algorithm uses two large prime numbers to generate a public and a private key. Encrypting data requires the public key, but decrypting it requires the private key, which is mathematically linked to the prime factors. Since factoring very large numbers is computationally expensive, this asymmetry forms the basis of the RSA's security.
Simplifying Fractions
In arithmetic, prime factorization is crucial for simplifying fractions. By factoring both the numerator and denominator into their prime components, you can easily identify common factors and cancel them out, resulting in a simplified fraction. For example:
12/18 = (2 x 2 x 3) / (2 x 3 x 3) = 2/3
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) and Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
Prime factorization provides an efficient way to calculate the LCM and GCD of two or more numbers. The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all the given numbers, while the GCD is the largest number that divides all the given numbers without leaving a remainder.
Advanced Concepts and Related Topics
The exploration of prime numbers and their factorization extends far beyond the simple example of 15. Here are a few related advanced topics:
-
Distribution of Prime Numbers: The study of how prime numbers are distributed among the natural numbers is a fascinating area of research, leading to questions about prime gaps, prime-counting functions, and the Riemann Hypothesis.
-
Mersenne Primes: These are prime numbers that are one less than a power of 2 (e.g., 3, 7, 31, 127). Finding large Mersenne primes is a significant undertaking, often involving distributed computing projects.
-
Twin Primes: These are pairs of prime numbers that differ by 2 (e.g., 3 and 5, 11 and 13). The twin prime conjecture, which posits that there are infinitely many twin primes, remains unproven.
-
Algorithms for Prime Factorization: Efficient algorithms for factoring large numbers are crucial for cryptography and number theory. The difficulty of these algorithms underlies the security of many cryptographic systems.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Prime Factors
While the prime factors of 15 might seem insignificant at first glance, exploring this seemingly simple problem provides a gateway to a rich and complex world of mathematics and computer science. The concept of prime factorization is fundamental to numerous applications, from secure online transactions to the development of efficient algorithms. The unique properties of prime numbers continue to fascinate mathematicians and drive ongoing research into the deepest mysteries of number theory. Understanding prime factorization, even in its simplest form, provides a solid foundation for exploring these deeper concepts and appreciating the elegance and power of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Solving Systems Of Equations By Elimination Solver
Mar 30, 2025
-
What Is The Valence Value Of Carbon
Mar 30, 2025
-
These Neurons Transmit Impulses From Cns To Effectors
Mar 30, 2025
-
Place The Following Parts Of A Reflex Arc In Order
Mar 30, 2025
-
Least Common Denominator Of Rational Expressions Calculator
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Prime Factors Of 15 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
