How Many Protons Are In Phosphorus
Juapaving
Mar 04, 2025 · 6 min read
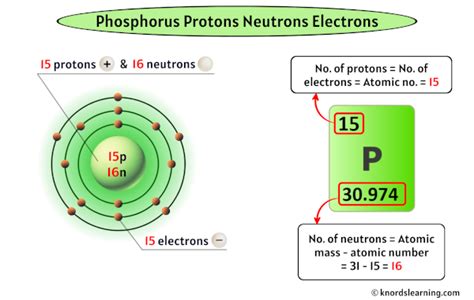
Table of Contents
How Many Protons Are in Phosphorus? Understanding Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
Determining the number of protons in an atom of any element is fundamental to understanding chemistry. This article delves into the specifics of phosphorus, exploring not only its proton count but also its place within the periodic table and its significance in various fields. We’ll unpack the concept of atomic number, explore the relationship between protons, neutrons, and electrons, and discover why the proton count is so crucial.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
At the heart of every atom lies the nucleus, a dense core containing two types of subatomic particles: protons and neutrons. Orbiting this nucleus are electrons, which are significantly lighter than protons and neutrons.
- Protons: Positively charged particles that contribute to the atom's overall positive charge. The number of protons defines the element.
- Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles that contribute to the atom's mass but not its charge. The number of neutrons can vary within an element, leading to isotopes.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in shells or energy levels. The number of electrons typically equals the number of protons in a neutral atom, resulting in a net charge of zero.
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in its nucleus. This number uniquely identifies each element on the periodic table. It's a fundamental property that determines an element's chemical behavior and its place in the periodic system. It's crucial to understand that the atomic number never changes for a given element; it's a defining characteristic.
Phosphorus: Unveiling the Atomic Number and Proton Count
Phosphorus (symbol: P), a vital element for life, resides in Group 15 (also known as the pnictogens) and Period 3 of the periodic table. Its atomic number is 15. This means that every atom of phosphorus invariably contains 15 protons in its nucleus. This consistent proton count is what makes it phosphorus and distinguishes it from all other elements.
Isotopes of Phosphorus: The Role of Neutrons
While the number of protons remains constant for phosphorus (always 15), the number of neutrons can vary. These variations lead to different isotopes of phosphorus. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. They have the same atomic number but different mass numbers (the sum of protons and neutrons).
The most common isotope of phosphorus is phosphorus-31 (³¹P), which contains 15 protons and 16 neutrons. Other isotopes exist, but they are less abundant and often radioactive. These radioactive isotopes have applications in various fields, including medical imaging and research. The differing neutron numbers affect the isotope's stability and half-life.
Understanding isotopes is crucial because the properties of an element are primarily determined by its number of protons, but the presence of different isotopes can affect its overall mass and behavior in certain applications.
The Significance of Phosphorus in Biology and Beyond
Phosphorus plays an indispensable role in numerous biological processes:
- DNA and RNA: Phosphorus is a crucial component of the backbone of DNA and RNA molecules, the genetic material of all living organisms. The phosphate groups linking the sugar molecules form the structural framework of these vital molecules.
- ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate): ATP is the primary energy currency of cells. It contains phosphate groups, and the energy released during the hydrolysis of these groups powers cellular processes.
- Bones and Teeth: Phosphorus is a major component of bones and teeth, contributing to their strength and structure. It forms calcium phosphate, a crucial mineral in bone formation.
- Cellular Membranes: Phospholipids, which are crucial components of cell membranes, contain phosphate groups. These lipids form bilayers that regulate the passage of substances into and out of cells.
- Fertilizers: Phosphorus is a vital nutrient for plant growth and is a key component of many fertilizers. It's essential for root development, flowering, and fruit production.
Beyond its biological importance, phosphorus finds applications in various industrial processes:
- Matchsticks: Red phosphorus is used in the striking surface of matchboxes.
- Detergents: Phosphates were once commonly used in detergents, but their environmental impact has led to their restricted use in many areas.
- Metal Alloys: Phosphorus is used in the production of certain metal alloys to improve their properties.
- Semiconductors: Phosphorus is used as a dopant in semiconductors to alter their electrical properties.
The Periodic Table and the Organization of Elements
The periodic table is a structured arrangement of chemical elements, organized based on their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. Phosphorus’s position within this table, Group 15 and Period 3, reflects its electronic structure and chemical behavior. The table provides invaluable information about each element, including its atomic number (and thus, its proton count), atomic mass, and chemical properties. This systematization is critical for understanding the relationships between elements and predicting their behavior.
The organization by atomic number directly reveals the proton count for each element, making the periodic table an indispensable resource for any scientific study. Understanding the periodic trends, such as electronegativity and ionization energy, further elucidates the chemical reactivity of phosphorus.
Practical Applications and Further Exploration
The information discussed regarding the number of protons in phosphorus has far-reaching implications across various scientific disciplines:
- Analytical Chemistry: Determining the amount of phosphorus in a sample often involves techniques like atomic absorption spectroscopy or inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Understanding the atomic structure is fundamental to these analyses.
- Nuclear Chemistry: The study of phosphorus isotopes, particularly the radioactive ones, is crucial for applications such as radioactive tracing and medical imaging.
- Biochemistry: The role of phosphorus in biological systems is extensively researched, and understanding its atomic composition is essential for comprehending its function in DNA, RNA, ATP, and other biomolecules.
- Material Science: The properties of materials containing phosphorus are heavily influenced by its atomic structure and chemical behavior.
Conclusion: The Significance of a Simple Number
The seemingly simple answer—15 protons—to the question of how many protons are in phosphorus opens a vast landscape of scientific understanding. This number, the atomic number, is the key that unlocks phosphorus's unique properties, its biological importance, and its industrial applications. From its role in the genetic code to its presence in fertilizers and semiconductors, the 15 protons within each phosphorus atom are fundamental to its significance in the world around us. A deep understanding of atomic structure, the periodic table, and isotopes provides a solid foundation for appreciating the impact of this seemingly simple number. Further exploration into the world of chemistry and related fields will further reveal the complexities and fascinating intricacies of phosphorus and its essential contributions to life and technology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Boiling Water Endothermic Or Exothermic
Mar 04, 2025
-
What Is A Common Multiple Of 8 And 10
Mar 04, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 8 And 7
Mar 04, 2025
-
1 Universal Mass Unit Eual To
Mar 04, 2025
-
Name 3 Ways To Dissolve Something Faster
Mar 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Protons Are In Phosphorus . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
