Least Common Multiple Of 8 And 7
Juapaving
Mar 04, 2025 · 5 min read
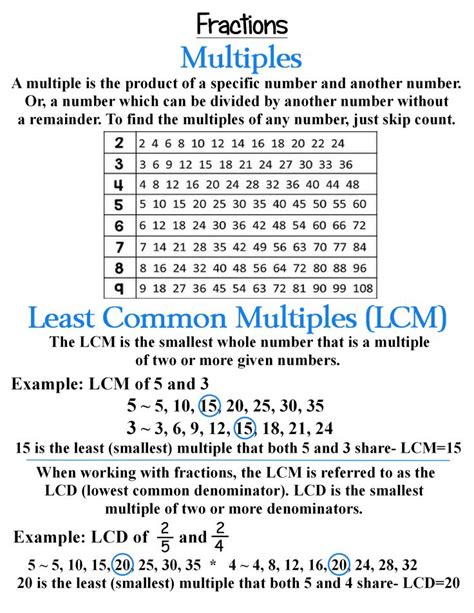
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 8 and 7: A Comprehensive Guide
The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in number theory and algebra. Understanding how to find the LCM is crucial for various applications, from simplifying fractions to solving problems involving rhythmic patterns or scheduling. This article delves deep into the process of determining the LCM of 8 and 7, exploring various methods and providing a comprehensive understanding of the underlying principles. We'll also touch upon the broader implications of LCM and its relevance in more advanced mathematical contexts.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Before we dive into calculating the LCM of 8 and 7, let's solidify our understanding of the concept. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that can be divided evenly by all the given numbers without leaving a remainder.
Key characteristics of LCM:
- Positive Integer: The LCM is always a positive integer.
- Smallest Multiple: It's the smallest number that satisfies the divisibility condition for all the given integers.
- Multiple of all Inputs: It's divisible by each of the input integers.
Methods for Finding the LCM of 8 and 7
There are several effective methods to calculate the LCM. Let's explore the most common approaches, applying them to find the LCM of 8 and 7:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is a straightforward method, particularly useful for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80...
Multiples of 7: 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, 56, 63, 70...
By comparing the lists, we can see that the smallest common multiple is 56. Therefore, the LCM(8, 7) = 56.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers. We find the prime factorization of each number and then construct the LCM using the highest powers of all prime factors present.
- Prime factorization of 8: 2³ (8 = 2 x 2 x 2)
- Prime factorization of 7: 7¹ (7 is a prime number)
Since 2 and 7 are the only prime factors, and their highest powers are 2³ and 7¹, respectively, the LCM is calculated as:
LCM(8, 7) = 2³ x 7¹ = 8 x 7 = 56
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method utilizes the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is equal to the product of the two numbers. The formula is:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
First, let's find the GCD of 8 and 7 using the Euclidean algorithm:
- Divide 8 by 7: 8 = 7 x 1 + 1
- Divide 7 by the remainder 1: 7 = 1 x 7 + 0
The last non-zero remainder is 1, so GCD(8, 7) = 1.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(8, 7) = (8 x 7) / GCD(8, 7) = 56 / 1 = 56
Why is understanding LCM important?
The concept of LCM extends far beyond simple arithmetic exercises. Its applications are widespread across various fields:
1. Fraction Simplification
Finding the LCM is crucial for adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. By finding the LCM of the denominators, we can convert the fractions into equivalent fractions with a common denominator, allowing for easy addition or subtraction.
2. Scheduling and Synchronization
LCM plays a vital role in scheduling problems. Imagine two buses that depart from the same station at different intervals. The LCM of their departure intervals will determine when they will depart simultaneously again. This principle applies to various scheduling scenarios, including production cycles, traffic light synchronization, and more.
3. Rhythmic Patterns and Music
In music, the LCM is used to determine the least common period of repeating musical phrases or rhythmic patterns. Understanding this helps in harmonizing different musical parts and creating complex yet cohesive rhythmic structures.
4. Modular Arithmetic and Cryptography
LCM is a fundamental concept in modular arithmetic, which has significant applications in cryptography, particularly in public-key cryptosystems like RSA. The properties of LCM are used in designing secure encryption and decryption algorithms.
5. Advanced Mathematical Applications
LCM finds its place in more complex mathematical fields such as abstract algebra, particularly in the study of rings and ideals. Its properties are used in proving theorems and solving problems related to algebraic structures.
Comparing the Methods: Efficiency and Applicability
While all three methods effectively calculate the LCM of 8 and 7, their efficiency varies depending on the numbers involved.
- Listing Multiples: This method is simple and intuitive for smaller numbers but becomes inefficient for larger numbers.
- Prime Factorization: This method is generally more efficient for larger numbers as it directly addresses the fundamental components of the numbers.
- GCD Method: This method leverages the relationship between LCM and GCD, making it efficient, especially when the GCD can be easily calculated using the Euclidean algorithm. This is often the most efficient method for larger numbers where finding prime factorizations might be more computationally intensive.
Conclusion: The LCM of 8 and 7 and Beyond
In conclusion, the least common multiple of 8 and 7 is 56. This seemingly simple calculation underscores a fundamental mathematical concept with wide-ranging applications. Understanding different methods for calculating LCM allows for selecting the most efficient approach depending on the context and the size of the numbers involved. The importance of LCM extends beyond basic arithmetic; it plays a crucial role in various fields, from fraction simplification to advanced mathematical concepts and real-world applications involving scheduling, music, and cryptography. Mastering the concept of LCM is a valuable asset for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of mathematics and its practical applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Feet In 100 Yards
Mar 04, 2025
-
How Many Hours In 7 Days
Mar 04, 2025
-
Example Of Electrical Energy Converted Into Chemical Energy
Mar 04, 2025
-
How Many Centimeters Is 6 Ft
Mar 04, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements Is Not True
Mar 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 8 And 7 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
