How Many Neutrons Does Ca Have
Juapaving
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
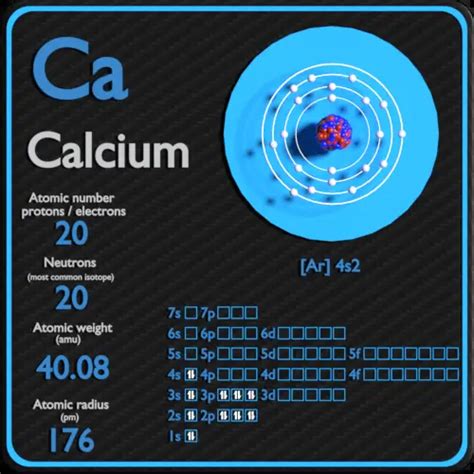
Table of Contents
How Many Neutrons Does Calcium (Ca) Have? A Deep Dive into Isotopes and Atomic Structure
Calcium (Ca), a vital element for life, presents a fascinating study in atomic structure, particularly concerning its neutrons. Understanding the number of neutrons in calcium isn't simply about memorizing a number; it's about grasping the concept of isotopes, their implications for chemical behavior, and their application in various scientific fields. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of calcium's neutron count, exploring its different isotopes and their significance.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Before we delve into the specifics of calcium's neutron count, let's refresh our understanding of fundamental atomic structure. An atom consists of three primary subatomic particles:
-
Protons: Positively charged particles residing in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element's atomic number and its identity. Calcium's atomic number is 20, meaning every calcium atom possesses 20 protons.
-
Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles also found within the nucleus. Unlike protons, the number of neutrons in an atom can vary, leading to the existence of isotopes. The mass number of an atom is the sum of its protons and neutrons.
-
Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells. The number of electrons generally equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
Isotopes: The Key to Variable Neutron Count
The crux of the question "How many neutrons does calcium have?" lies in the concept of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element (same number of protons) but with varying numbers of neutrons. This variation in neutron number affects the atom's mass but not its chemical properties significantly.
Calcium has several naturally occurring isotopes, each with a different number of neutrons. The most common isotopes are:
-
⁴⁰Ca: This is the most abundant isotope of calcium, comprising approximately 96.94% of naturally occurring calcium. It contains 20 protons and 20 neutrons (40 - 20 = 20).
-
⁴²Ca: A less abundant isotope, it makes up about 0.65% of natural calcium. This isotope has 20 protons and 22 neutrons (42 - 20 = 22).
-
⁴³Ca: A trace isotope, present in approximately 0.14% of natural calcium, with 20 protons and 23 neutrons (43 - 20 = 23).
-
⁴⁴Ca: Another relatively abundant isotope (2.09% of natural calcium) containing 20 protons and 24 neutrons (44 - 20 = 24).
-
⁴⁶Ca: A less common isotope (0.004% of natural calcium) possessing 20 protons and 26 neutrons (46 - 20 = 26).
-
⁴⁸Ca: The least abundant naturally occurring calcium isotope (0.18% of natural calcium) with 20 protons and 28 neutrons (48 - 20 = 28).
Beyond these naturally occurring isotopes, several radioactive isotopes of calcium have been synthesized. These isotopes have even higher neutron counts and are unstable, undergoing radioactive decay.
The Significance of Calcium Isotopes
The varying neutron counts in calcium isotopes don't drastically alter their chemical behavior. This is because chemical reactions primarily involve the electrons, which are not directly affected by the neutron number. However, the differences in mass do have implications in various contexts:
-
Geochronology: The isotopic ratios of calcium, specifically the abundance of different isotopes like ⁴⁰Ca and ⁴⁴Ca, are used in geochronological studies to determine the age of rocks and minerals. Slight variations in these ratios can provide valuable insights into geological processes and the Earth's history.
-
Biological Processes: While the chemical reactivity remains largely unchanged, the subtle mass differences between calcium isotopes can influence biological processes at a cellular level. Studies are ongoing to understand the precise nature and extent of these effects.
-
Nuclear Medicine: Certain radioactive calcium isotopes are employed in nuclear medicine for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Their radioactivity allows them to be tracked within the body, providing insights into calcium metabolism and bone health.
-
Environmental Science: The isotopic composition of calcium can be used to trace the movement and sources of water in hydrological systems.
Calculating Neutron Count: A Simple Formula
Calculating the number of neutrons in any atom, including calcium isotopes, is straightforward. You simply subtract the atomic number (number of protons) from the mass number (total number of protons and neutrons):
Number of neutrons = Mass number - Atomic number
For example, for ⁴⁰Ca:
Number of neutrons = 40 - 20 = 20 neutrons
This formula applies to all isotopes of calcium and indeed, to all elements.
Beyond the Basics: Nuclear Stability and Binding Energy
The number of neutrons significantly impacts an atom's nuclear stability. While the ideal neutron-to-proton ratio varies depending on the element, deviations from this ratio often result in unstable isotopes that undergo radioactive decay. For lighter elements, a roughly equal number of protons and neutrons is generally preferred for stability. However, for heavier elements, a higher neutron-to-proton ratio is needed to overcome the repulsive forces between protons. The strong nuclear force, responsible for binding protons and neutrons together in the nucleus, plays a critical role in determining an atom's stability. The energy required to break apart the nucleus is known as binding energy, and it's directly related to the number and arrangement of protons and neutrons.
Conclusion: A Multifaceted Element
The seemingly simple question, "How many neutrons does calcium have?" leads us on a journey through the fascinating world of atomic structure, isotopes, and their diverse applications. While there's no single answer due to the existence of multiple isotopes, understanding the concept of isotopes and how to calculate neutron numbers is crucial for grasping the behavior and significance of calcium in various scientific and technological fields. The varying isotopic abundances and their implications in fields ranging from geology to nuclear medicine highlight the complexities and richness of this seemingly simple element. The continuous research and development surrounding calcium isotopes underscore its continued relevance in advancing our understanding of the natural world and developing new technologies.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Whats The Prime Factorization Of 15
Mar 29, 2025
-
37 Inches Is How Many Feet
Mar 29, 2025
-
Find The Lcm Of 3 And 5
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Do You Do Average In Math
Mar 29, 2025
-
Liquids At Room Temperature Periodic Table
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Neutrons Does Ca Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
