How Does Amoeba Get Its Food
Juapaving
Mar 29, 2025 · 5 min read
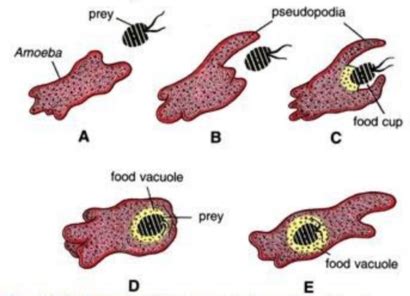
Table of Contents
- How Does Amoeba Get Its Food
- Table of Contents
- How Does an Amoeba Get Its Food? A Deep Dive into Amoeba Nutrition
- Understanding Amoeba: A Single-Celled Wonder
- The Amazing Process of Phagocytosis: Amoeba's Feeding Mechanism
- 1. Detection and Recognition:
- 2. Pseudopodia Extension and Engulfment:
- 3. Formation of the Food Vacuole:
- 4. Digestion and Nutrient Absorption:
- 5. Waste Expulsion:
- Variations in Amoeba Diet and Feeding Strategies
- The Importance of Amoeba Nutrition in the Ecosystem
- Amoeba Nutrition: A Microscopic Marvel
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
How Does an Amoeba Get Its Food? A Deep Dive into Amoeba Nutrition
Amoebas, those fascinating single-celled organisms, represent a captivating example of how life can thrive at the most fundamental level. Their existence hinges on their ability to acquire nutrients from their environment, a process that's both remarkably efficient and surprisingly complex for such a simple creature. This article delves into the intricate world of amoeba nutrition, exploring the mechanisms behind their food acquisition, digestion, and waste expulsion. We'll uncover the fascinating adaptations that allow these microscopic organisms to flourish in diverse environments.
Understanding Amoeba: A Single-Celled Wonder
Before we delve into the specifics of amoeba feeding, let's establish a foundational understanding of these remarkable organisms. Amoebas are classified as protists, belonging to a vast group of eukaryotic microorganisms. They lack the complex organ systems found in multicellular organisms, yet they perform all essential life functions within the confines of a single cell. This single cell is incredibly dynamic, constantly changing shape and extending pseudopodia – temporary projections of cytoplasm – to move and interact with their surroundings. It’s these very pseudopodia that play a crucial role in their unique feeding mechanism.
Key Characteristics of Amoebas:
- Eukaryotic: Possessing a membrane-bound nucleus and other organelles.
- Heterotrophic: Unable to produce their own food, requiring external sources of organic matter.
- Phagotrophic: Feeding by engulfing solid food particles through a process called phagocytosis.
- Unicellular: Existing as a single cell, performing all life functions within that cell.
- Amoeboid Movement: Utilizing pseudopodia for locomotion and food capture.
The Amazing Process of Phagocytosis: Amoeba's Feeding Mechanism
The primary method by which amoebas obtain food is phagocytosis, a type of endocytosis where the cell membrane actively surrounds and engulfs a solid particle. This is a visually stunning process, easily observable under a microscope. The steps involved are as follows:
1. Detection and Recognition:
The amoeba's journey to a meal begins with chemotaxis, the movement towards a chemical attractant. When an amoeba senses a food particle – be it a bacterium, algae, or other organic debris – nearby, it responds to the chemical signals released by the food source. This directional movement ensures that the amoeba efficiently locates potential nourishment.
2. Pseudopodia Extension and Engulfment:
Upon encountering a suitable food particle, the amoeba extends its pseudopodia, forming temporary arm-like extensions of its cytoplasm. These pseudopodia flow around the food particle, gradually enveloping it within a membrane-bound vesicle. This process is remarkably dynamic, showcasing the fluid nature of the amoeba's cytoplasm. The pseudopodia fuse at their tips, completely enclosing the food particle within a vacuole called a food vacuole or phagosome.
3. Formation of the Food Vacuole:
The food vacuole, now containing the captured food particle, pinches off from the cell membrane, moving into the amoeba's cytoplasm. This newly formed vacuole is essentially an intracellular compartment where digestion will take place.
4. Digestion and Nutrient Absorption:
The food vacuole fuses with lysosomes, organelles containing digestive enzymes. These enzymes break down the complex organic molecules within the food particle into simpler, usable components like amino acids, sugars, and fatty acids. The digested nutrients then diffuse across the vacuole membrane into the amoeba's cytoplasm, fueling its metabolic processes.
5. Waste Expulsion:
Once the nutrients have been absorbed, the food vacuole now contains indigestible waste products. This residual material is expelled from the cell through a process called exocytosis. The waste-filled vacuole fuses with the cell membrane, releasing its contents into the surrounding environment.
Variations in Amoeba Diet and Feeding Strategies
While phagocytosis is the central theme of amoeba nutrition, there is some diversity in their dietary preferences and feeding strategies. Different amoeba species may specialize in consuming specific types of food sources. Some prefer bacteria, others algae, while some are opportunistic feeders, consuming a variety of organic matter available in their environment.
Variations based on food source:
- Bacteriovorous Amoebas: These species primarily feed on bacteria, playing a crucial role in regulating bacterial populations in their ecosystems.
- Algivorous Amoebas: These amoebas specialize in consuming algae, contributing to the balance of aquatic ecosystems.
- Detritivorous Amoebas: These amoebas feed on decaying organic matter, acting as decomposers and playing a vital role in nutrient cycling.
Variations based on feeding strategy:
- Active Hunting: Some amoebas actively hunt their prey, pursuing and engulfing their food sources.
- Passive Feeding: Others passively collect food particles that drift into their vicinity.
The Importance of Amoeba Nutrition in the Ecosystem
Amoebas, despite their microscopic size, play a vital role in the functioning of various ecosystems. Their feeding habits contribute significantly to nutrient cycling and the overall balance of their respective habitats. They serve as a crucial link in the food chain, acting as both consumers and prey. By consuming bacteria and other microorganisms, they help control their populations, preventing unchecked growth. They also serve as a food source for larger organisms, passing on the energy they have acquired from their food sources.
Ecological roles of amoebas:
- Nutrient cycling: Decomposition of organic matter releases vital nutrients back into the environment.
- Food source: Amoebas serve as a food source for other protists, invertebrates, and even some vertebrates.
- Regulation of microbial populations: Controlling bacterial populations prevents potential overgrowth.
Amoeba Nutrition: A Microscopic Marvel
In conclusion, the process by which an amoeba obtains its food is a testament to the elegant simplicity and remarkable efficiency of life at its most basic level. Phagocytosis, with its dynamic interplay of chemotaxis, pseudopodia extension, food vacuole formation, digestion, and waste expulsion, represents a captivating example of how a single cell can effectively acquire and utilize nutrients to sustain itself. The diversity in their feeding strategies and dietary preferences further underscores the adaptability of these fascinating organisms and their significant contribution to the ecological balance of various ecosystems. Their microscopic world reveals a complexity and beauty that continues to captivate scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. Understanding amoeba nutrition offers a crucial window into the fundamental processes that drive life on Earth. Further research into these organisms will undoubtedly continue to unveil new insights into the intricacies of cellular biology and their vital roles in our planet's ecosystems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Largest Gland In The Body
Apr 02, 2025
-
Identity Property Of Addition And Multiplication
Apr 02, 2025
-
How To Find A Gcf Using Prime Factorization
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Does Line Mean In Math
Apr 02, 2025
-
Difference Between Electron Pair Geometry And Molecular Geometry
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Does Amoeba Get Its Food . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
