How Do I Find The Lateral Area Of A Cylinder
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
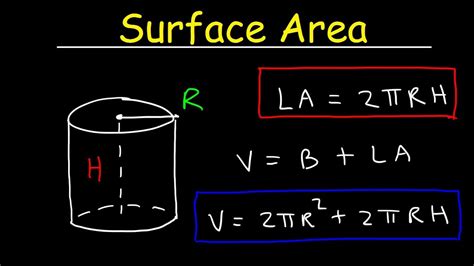
Table of Contents
How Do I Find the Lateral Area of a Cylinder? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding how to calculate the lateral surface area of a cylinder is a fundamental concept in geometry with practical applications in various fields, from engineering and architecture to packaging and design. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process, providing a clear understanding of the formula, its derivation, and practical examples. We'll also explore related concepts to solidify your grasp of this important geometrical calculation.
Understanding Cylinders and Their Components
Before diving into the calculation, let's clarify what constitutes a cylinder. A cylinder is a three-dimensional geometric shape with two parallel circular bases connected by a curved surface. Key components include:
- Radius (r): The distance from the center of a circular base to any point on its circumference. This is a crucial measurement for calculating the area.
- Height (h): The perpendicular distance between the two circular bases. This determines the length of the cylinder's curved surface.
- Lateral Surface Area (LSA): The area of the curved surface connecting the two bases. This is the focus of our discussion.
- Total Surface Area (TSA): The sum of the lateral surface area and the areas of the two circular bases.
Deriving the Formula for Lateral Surface Area
The lateral surface area of a cylinder can be visualized by imagining unrolling the curved surface into a rectangle. The length of this rectangle is the circumference of the circular base, and its width is the height of the cylinder.
The circumference of a circle is given by the formula: C = 2πr, where 'r' is the radius.
The area of a rectangle is given by the formula: Area = length × width.
Therefore, the lateral surface area (LSA) of a cylinder is:
LSA = 2πrh
where:
- 2πr represents the circumference of the circular base (the length of the rectangle)
- h represents the height of the cylinder (the width of the rectangle)
Step-by-Step Calculation of Lateral Surface Area
Let's break down the calculation into easy-to-follow steps:
-
Identify the radius (r) and height (h): Carefully examine the cylinder and determine the values for the radius and height. Make sure both measurements are in the same units (e.g., centimeters, meters, inches).
-
Substitute the values into the formula: Plug the values of 'r' and 'h' into the lateral surface area formula:
LSA = 2πrh. -
Calculate the circumference: If you prefer, you can calculate the circumference (2πr) separately before multiplying it by the height.
-
Perform the calculation: Use a calculator or perform the multiplication to obtain the numerical value of the lateral surface area. Remember to include the correct units (e.g., square centimeters, square meters, square inches).
Worked Examples: Finding the Lateral Surface Area
Let's solidify our understanding with some practical examples:
Example 1:
A cylindrical water tank has a radius of 5 meters and a height of 10 meters. Calculate its lateral surface area.
-
r = 5 meters, h = 10 meters
-
LSA = 2πrh = 2 * π * 5 meters * 10 meters = 100π square meters
-
Approximating π as 3.14159: LSA ≈ 314.16 square meters
Therefore, the lateral surface area of the water tank is approximately 314.16 square meters.
Example 2:
A cylindrical can of soup has a diameter of 8 centimeters and a height of 12 centimeters. Find its lateral surface area.
-
Diameter = 8 cm, so radius (r) = 4 cm. h = 12 cm
-
LSA = 2πrh = 2 * π * 4 cm * 12 cm = 96π square centimeters
-
Approximating π as 3.14159: LSA ≈ 301.59 square centimeters
Therefore, the lateral surface area of the soup can is approximately 301.59 square centimeters.
Example 3: A Real-World Application
Imagine you're designing a label for a cylindrical jar. You need to determine the size of the label to perfectly cover the jar's lateral surface. Measuring the jar's radius and height will allow you to calculate the required label area using the lateral surface area formula.
Beyond the Basics: Total Surface Area and Volume
While we've focused on lateral surface area, understanding the total surface area and volume of a cylinder is also crucial.
Total Surface Area (TSA): This includes the lateral surface area plus the areas of the two circular bases. The formula is:
TSA = 2πrh + 2πr²
Volume (V): The amount of space enclosed within the cylinder. The formula is:
V = πr²h
Understanding these additional formulas provides a more complete picture of cylindrical geometry.
Troubleshooting Common Mistakes
Here are some common errors to avoid when calculating the lateral surface area:
- Incorrect units: Ensure consistent units throughout the calculation.
- Confusing radius and diameter: Remember that the radius is half the diameter.
- Using the wrong formula: Double-check that you are using the correct formula for lateral surface area (LSA = 2πrh).
- Calculation errors: Carefully perform the multiplication and use a calculator to minimize mistakes.
Practical Applications and Further Exploration
The ability to calculate the lateral surface area of a cylinder has numerous practical applications:
- Packaging design: Determining the amount of material needed for labels or packaging.
- Civil engineering: Calculating the surface area of cylindrical structures like pipes or silos.
- Manufacturing: Estimating the material required for cylindrical components.
- Architectural design: Calculating the surface area of cylindrical columns or structures.
This guide provides a strong foundation for understanding and calculating the lateral surface area of a cylinder. By mastering this concept, you'll enhance your problem-solving skills in geometry and gain a valuable tool for various real-world applications. Further exploration might involve investigating more complex shapes incorporating cylindrical elements or delving into related concepts like surface integrals in calculus. Remember to practice regularly to solidify your understanding and build confidence in your calculations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is A Factor Of 180
Mar 28, 2025
-
Why Doesnt Hydrogen Have A Neutron
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Molecular And Electron Geometry
Mar 28, 2025
-
Whats The Molar Mass Of Nh3
Mar 28, 2025
-
Describing Words That Start With S
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do I Find The Lateral Area Of A Cylinder . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
