Are There Mitochondria In Plant Cells
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
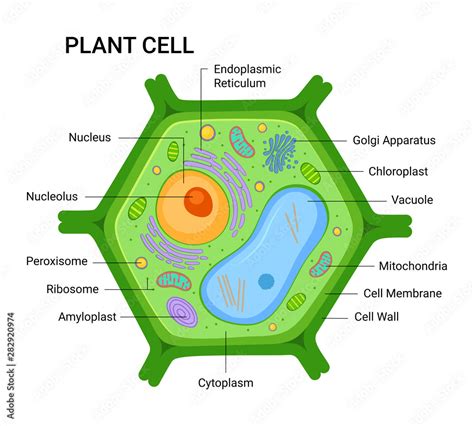
Table of Contents
Are There Mitochondria in Plant Cells? A Deep Dive into Plant Cell Organelles
The question, "Are there mitochondria in plant cells?" might seem simple at first glance. The answer, however, opens the door to a fascinating exploration of plant cell biology, revealing intricate details about energy production, cellular respiration, and the evolutionary journey of eukaryotic life. This comprehensive article will delve into the presence, function, and unique characteristics of mitochondria within plant cells, debunking myths and highlighting the critical role these organelles play in plant life.
Mitochondria: The Powerhouses of the Cell – Plants Included
Yes, plant cells do contain mitochondria. These vital organelles, often referred to as the "powerhouses of the cell," are responsible for generating the majority of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency used for cellular processes. While animals and plants share this fundamental cellular component, there are subtle but significant differences in their structure and function within the respective cellular contexts.
The Shared Ancestry and Fundamental Role
The presence of mitochondria in both plant and animal cells speaks to their shared evolutionary history. The endosymbiotic theory proposes that mitochondria originated from free-living bacteria that were engulfed by a host cell billions of years ago. This symbiotic relationship proved mutually beneficial, with the host cell providing protection and the engulfed bacterium providing energy through respiration. This evolutionary event is a cornerstone of eukaryotic cell biology and explains the presence of mitochondria in a wide range of organisms, including plants.
ATP Production: The Core Function
The primary function of mitochondria in both plant and animal cells remains consistent: ATP synthesis through cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is a complex process that breaks down glucose and other organic molecules in the presence of oxygen, releasing energy that is then harnessed to produce ATP. This process occurs in several stages, with key steps taking place within specific compartments of the mitochondrion:
- Glycolysis: This initial stage occurs in the cytoplasm, breaking down glucose into pyruvate.
- Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle): Pyruvate enters the mitochondrion and is further oxidized in the Krebs cycle, generating reducing equivalents (NADH and FADH2).
- Oxidative Phosphorylation: This crucial stage, occurring in the inner mitochondrial membrane, utilizes the reducing equivalents from the Krebs cycle to drive ATP synthesis through chemiosmosis. This process involves the electron transport chain and ATP synthase.
This fundamental process of ATP generation underscores the crucial role of mitochondria in maintaining cellular function in both plant and animal cells. Without functional mitochondria, cells would lack the energy needed for growth, metabolism, and survival.
Unique Aspects of Plant Cell Mitochondria
While the fundamental role of mitochondria is conserved across eukaryotes, plant mitochondria exhibit certain unique characteristics that reflect the specific metabolic demands and environmental adaptations of plant life.
Larger and More Diverse Genome
Plant mitochondrial genomes are typically larger and more complex than their animal counterparts. They often contain more genes and exhibit greater variation in size and gene content across different plant species. This larger genome reflects the greater metabolic diversity and specialized functions required to support plant life, such as photosynthesis and adaptation to various environmental stresses.
Interaction with Other Organelles
Plant mitochondria engage in intricate interactions with other organelles within the plant cell, most notably the chloroplasts (the sites of photosynthesis) and peroxisomes (involved in fatty acid metabolism). These interactions are essential for coordinating various metabolic processes and ensuring efficient energy transfer within the cell. For instance, some metabolic intermediates generated during photosynthesis in the chloroplast are utilized by the mitochondria for respiration. This interconnectedness highlights the integrated nature of plant cell metabolism.
Metabolic Flexibility and Environmental Adaptation
Plant mitochondria demonstrate a remarkable degree of metabolic flexibility, enabling plants to adapt to changing environmental conditions. For example, they can adjust their respiratory rate in response to fluctuations in light intensity, temperature, and oxygen availability. This plasticity is critical for plant survival in diverse and often challenging environments. They also play a crucial role in stress responses, such as drought, salinity, and pathogen attack.
Regulation and Control Mechanisms
The activity of plant mitochondria is subject to complex regulatory mechanisms that ensure efficient energy production and metabolic coordination. These mechanisms involve various signaling pathways, transcriptional regulation, and post-translational modifications of mitochondrial proteins. This sophisticated control system ensures that mitochondrial function is finely tuned to meet the ever-changing demands of the plant cell.
Mitochondria and Plant Growth and Development
The role of mitochondria extends far beyond simple energy production. They are deeply involved in various aspects of plant growth and development, including:
- Seed Germination: Mitochondria provide the initial energy burst needed for seed germination, powering the early stages of seedling development.
- Root Development: Mitochondria are critical for the growth and development of roots, which are essential for nutrient and water uptake.
- Flowering and Fruit Development: Mitochondrial function is crucial for the energy demands of flowering and fruit development, influencing yield and quality.
- Stress Response: Mitochondria play a vital role in mediating the plant's response to various environmental stresses, including drought, salinity, and pathogen attack.
Disruptions in mitochondrial function can lead to significant impairments in plant growth, development, and overall fitness. This highlights the fundamental importance of these organelles for plant life.
Distinguishing Plant and Animal Mitochondria: Key Differences Summarized
While sharing fundamental functions, plant and animal mitochondria possess key distinctions:
| Feature | Plant Mitochondria | Animal Mitochondria |
|---|---|---|
| Genome Size | Larger and more complex | Smaller and less complex |
| Gene Content | More genes, greater variation among species | Fewer genes, more conserved among species |
| Interaction with Other Organelles | Extensive interaction with chloroplasts & peroxisomes | Less extensive interaction with other organelles |
| Metabolic Flexibility | High degree of flexibility and adaptation to stress | Lower degree of metabolic flexibility |
| Sensitivity to Environmental Stress | Crucial role in stress response | Significant role in stress response, but less dominant |
Conclusion: Mitochondria are Essential for Plant Life
In conclusion, the answer to the question "Are there mitochondria in plant cells?" is a resounding yes. These organelles are not only present but play a pivotal and multifaceted role in plant life. From providing the energy for cellular processes to mediating stress responses and driving growth and development, plant mitochondria are essential components of plant cells. Their unique features, including their larger genomes and intricate interactions with other organelles, reflect the specific metabolic demands and adaptive strategies of plant life. Understanding the intricacies of plant mitochondrial biology is critical for advancing our knowledge of plant physiology, improving crop yields, and developing strategies for sustainable agriculture. Further research into plant mitochondria continues to unveil new insights into their complexity and importance in the fascinating world of plant biology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Common Factors Of 24 And 32
Mar 25, 2025
-
Find The Missing Number With Answer
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry On A Hexagon
Mar 25, 2025
-
Common Denominator Of 7 And 5
Mar 25, 2025
-
The Atomic Number Is Equal To The
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Are There Mitochondria In Plant Cells . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
