How Many Lines Of Symmetry On A Hexagon
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
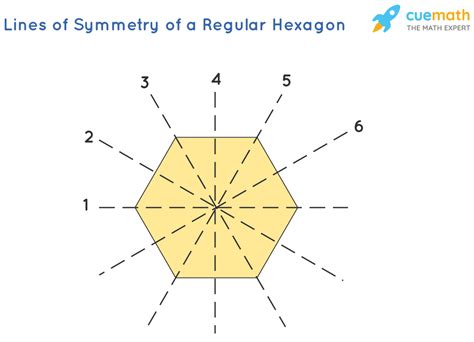
Table of Contents
How Many Lines of Symmetry Does a Hexagon Have? A Comprehensive Guide
Symmetry, a captivating concept in geometry, explores the inherent balance and harmony within shapes. Understanding lines of symmetry is crucial for grasping the properties of various geometric figures, including the fascinating hexagon. This article delves deep into the world of hexagonal symmetry, answering the central question: how many lines of symmetry does a hexagon have? We’ll explore different types of hexagons and their corresponding lines of symmetry, providing a comprehensive guide for students, enthusiasts, and anyone curious about the elegance of geometric forms.
Understanding Lines of Symmetry
Before we dive into hexagons, let's establish a clear understanding of what a line of symmetry is. A line of symmetry, also known as a line of reflection, is a line that divides a shape into two identical halves that are mirror images of each other. If you were to fold the shape along the line of symmetry, both halves would perfectly overlap.
Types of Hexagons
Not all hexagons are created equal. The number of lines of symmetry a hexagon possesses depends heavily on its type. The two main categories we'll consider are:
1. Regular Hexagons
A regular hexagon is a hexagon with all sides equal in length and all interior angles equal (120° each). This perfect symmetry leads to a predictable and relatively high number of lines of symmetry.
2. Irregular Hexagons
Irregular hexagons, on the other hand, have sides and angles of varying lengths and measures. This lack of uniformity significantly impacts the number of lines of symmetry they possess.
Lines of Symmetry in a Regular Hexagon
A regular hexagon exhibits a remarkable degree of symmetry. Let's explore how to find its lines of symmetry:
Identifying the Lines
Consider a regular hexagon. Imagine drawing lines through opposite vertices (corners). How many such lines can you draw? Three. These lines are lines of symmetry because they divide the hexagon into two identical mirrored halves.
Now, let's consider lines connecting the midpoints of opposite sides. Again, how many such lines can be drawn? Three. These lines also act as lines of symmetry, perfectly bisecting the hexagon.
Therefore, a regular hexagon has a total of six lines of symmetry: three lines connecting opposite vertices and three lines connecting midpoints of opposite sides.
Visualizing the Symmetry
To solidify your understanding, try visualizing a regular hexagon. Draw a hexagon on a piece of paper and experiment with folding it along different lines. You'll quickly discover the six lines of symmetry that perfectly bisect the shape into mirror images.
Lines of Symmetry in Irregular Hexagons
Unlike regular hexagons, irregular hexagons possess significantly less symmetry. The number of lines of symmetry can vary greatly depending on the specific dimensions and angles of the irregular hexagon. In most cases, an irregular hexagon will have:
-
Zero lines of symmetry: This is the most common scenario for irregular hexagons. The lack of uniform sides and angles typically prevents the existence of any lines that can divide the shape into identical mirrored halves.
-
One or Two Lines of Symmetry (Rare Cases): It is possible, although highly unlikely, for an irregular hexagon to possess one or two lines of symmetry. This would require a very specific configuration of sides and angles. However, such instances are rare exceptions rather than the norm.
Mathematical Proof for the Regular Hexagon's Symmetry
The six lines of symmetry in a regular hexagon can be mathematically proven using rotational symmetry and reflectional symmetry.
-
Rotational Symmetry: A regular hexagon possesses rotational symmetry of order 6. This means it can be rotated 60° (360°/6) about its center and still look identical. Each rotation reveals a different orientation, but the shape remains unchanged.
-
Reflectional Symmetry: The reflectional symmetry is directly linked to the lines of symmetry. As we've seen, there are six lines along which the hexagon can be reflected to produce a congruent image. These six lines of reflection are the six lines of symmetry.
The combination of rotational and reflectional symmetry elegantly proves the existence of the six lines of symmetry in a regular hexagon.
Applications of Hexagonal Symmetry
Understanding the symmetry of hexagons has numerous applications across various fields:
-
Honeycombs: The hexagonal structure of honeycombs is a prime example of hexagonal symmetry in nature. Bees instinctively build their honeycombs using hexagons because they are the most efficient shape for maximizing space and minimizing material usage. The symmetry of the honeycomb ensures structural integrity and optimal storage.
-
Architecture and Design: Hexagonal patterns appear frequently in architecture and design, often employed for their aesthetic appeal and structural efficiency. The symmetric nature of hexagons lends itself well to creating visually pleasing and stable structures.
-
Engineering and Manufacturing: Hexagonal shapes are utilized in engineering and manufacturing for their inherent strength and stability. The uniform distribution of load across a hexagon's sides contributes to its structural robustness.
-
Computer Graphics and Games: Hexagonal grids are often used in computer graphics and game design due to their ability to seamlessly tile a plane, enabling efficient representation of landscapes and maps.
-
Crystallography: The study of crystal structures frequently involves analyzing hexagonal symmetry. Many naturally occurring crystals exhibit hexagonal patterns, showcasing the prevalence of hexagonal symmetry in the natural world.
Distinguishing Between Regular and Irregular Hexagons
It’s crucial to accurately differentiate between regular and irregular hexagons to determine the number of lines of symmetry. Remember these key distinctions:
-
Regular Hexagon: All sides are equal in length, and all interior angles are equal (120°). It always has six lines of symmetry.
-
Irregular Hexagon: Sides and angles vary in length and measure. It typically has zero lines of symmetry, although exceptionally rare cases might show one or two.
Activities to Reinforce Understanding
To further solidify your understanding of hexagonal symmetry, try these activities:
-
Draw Hexagons: Draw various hexagons, both regular and irregular. Identify and draw the lines of symmetry where they exist.
-
Paper Folding: Cut out hexagons from paper. Experiment with folding them to discover the lines of symmetry.
-
Online Simulations: Explore online interactive geometry tools that allow you to manipulate hexagons and visualize their lines of symmetry.
Conclusion
The question of how many lines of symmetry a hexagon has depends entirely on whether it's a regular or irregular hexagon. A regular hexagon has six lines of symmetry, three connecting opposite vertices and three connecting midpoints of opposite sides. Irregular hexagons, on the other hand, typically have zero lines of symmetry, although exceedingly rare exceptions may exist. Understanding this distinction is fundamental to grasping the concept of symmetry in geometry and its numerous applications in various fields. By exploring the properties of regular and irregular hexagons, we gain a deeper appreciation for the beauty and mathematical elegance of geometric shapes.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Prime Factorization Of 192
Mar 27, 2025
-
Which Color Has The Shortest Wavelength
Mar 27, 2025
-
Explain What Determines A Substances State At A Given Temperature
Mar 27, 2025
-
What Is The Factors Of 89
Mar 27, 2025
-
Name The Structural And Functional Unit Of All Living Things
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Lines Of Symmetry On A Hexagon . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
