Common Factors Of 24 And 32
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
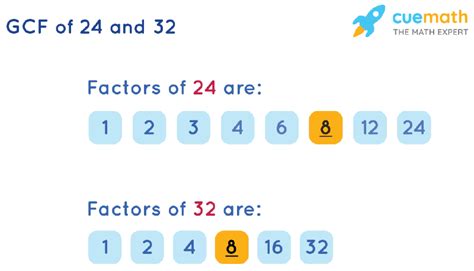
Table of Contents
Unlocking the Secrets of Common Factors: A Deep Dive into 24 and 32
Finding the common factors of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but it opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, laying the groundwork for understanding more complex mathematical concepts. This article delves deep into the common factors of 24 and 32, exploring various methods for finding them, their significance in mathematics, and practical applications in everyday life. We'll go beyond a simple answer, providing a comprehensive understanding of the underlying principles.
Understanding Factors and Common Factors
Before we dive into the specifics of 24 and 32, let's establish a solid foundation. A factor of a number is any integer that divides the number evenly, leaving no remainder. For instance, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. Each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder.
A common factor, as the name suggests, is a factor shared by two or more numbers. These are the numbers that divide both numbers without leaving a remainder. Identifying these common factors is crucial in many mathematical operations, particularly in simplifying fractions and solving algebraic equations.
Finding the Common Factors of 24 and 32: Method 1 - Listing Factors
The most straightforward method to find common factors is by listing all factors of each number and then identifying the ones they share.
Factors of 24: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24
Factors of 32: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32
By comparing the two lists, we can easily identify the common factors of 24 and 32: 1, 2, 4, and 8.
Finding the Common Factors of 24 and 32: Method 2 - Prime Factorization
Prime factorization is a more powerful and efficient method, especially when dealing with larger numbers. It involves expressing each number as a product of its prime factors. Prime factors are numbers that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, etc.).
Prime factorization of 24: 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 = 2³ x 3
Prime factorization of 32: 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 2⁵
To find the common factors using prime factorization, we look for the prime factors that appear in both factorizations. In this case, the only common prime factor is 2. The lowest power of 2 that appears in both factorizations is 2³.
Now, we find all possible combinations of these common prime factors:
- 2⁰ = 1
- 2¹ = 2
- 2² = 4
- 2³ = 8
Therefore, the common factors of 24 and 32 are 1, 2, 4, and 8. This method confirms the results obtained by listing factors.
Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Understanding common factors leads us to two important concepts: the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and the Least Common Multiple (LCM).
-
Greatest Common Factor (GCF): The largest common factor of two or more numbers. In the case of 24 and 32, the GCF is 8.
-
Least Common Multiple (LCM): The smallest positive number that is a multiple of two or more numbers. Finding the LCM is often done in conjunction with finding the GCF. We can use the following formula to relate the GCF and LCM:
LCM(a, b) x GCF(a, b) = a x b
Therefore, the LCM of 24 and 32 is (24 x 32) / 8 = 96.
Applications of Common Factors and GCF
The concepts of common factors and GCF are not just abstract mathematical ideas; they have practical applications across various fields:
-
Simplifying Fractions: Finding the GCF is essential for simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. For example, the fraction 24/32 can be simplified by dividing both the numerator and denominator by their GCF (8), resulting in the simplified fraction 3/4.
-
Measurement and Division: When dealing with measurements, finding common factors helps in efficiently dividing objects or quantities into equal parts. For instance, if you have 24 apples and 32 oranges, you can divide them equally into 8 groups, each containing 3 apples and 4 oranges.
-
Geometry and Problem Solving: Common factors often arise in geometric problems, like finding the dimensions of squares or rectangles that can be tiled using smaller squares.
-
Data Analysis: In statistical analysis, common factors can help to simplify and understand data relationships.
Beyond the Basics: Euclidean Algorithm
For larger numbers, finding common factors by listing factors or even prime factorization can become tedious. The Euclidean algorithm provides a more efficient method for determining the GCF of two numbers. It's a systematic approach based on repeated division.
Let's apply the Euclidean algorithm to find the GCF of 24 and 32:
-
Divide the larger number (32) by the smaller number (24): 32 ÷ 24 = 1 with a remainder of 8.
-
Replace the larger number with the smaller number (24) and the smaller number with the remainder (8): 24 ÷ 8 = 3 with a remainder of 0.
Since the remainder is 0, the GCF is the last non-zero remainder, which is 8. This confirms our earlier findings. The Euclidean algorithm is particularly useful for finding the GCF of very large numbers where other methods become impractical.
Exploring Deeper Number Theory Concepts
Understanding common factors provides a solid base for exploring more advanced concepts within number theory:
-
Modular Arithmetic: Modular arithmetic uses the concept of remainders, which is closely related to factors. Understanding common factors is crucial in modular arithmetic operations.
-
Diophantine Equations: These equations involve finding integer solutions, and often require finding GCFs to determine solvability.
-
Cryptography: Prime factorization and the concept of GCFs are fundamental in many cryptographic algorithms used to secure online transactions and communications.
Conclusion: The Significance of Common Factors
The seemingly simple task of finding the common factors of 24 and 32 opens doors to a rich understanding of fundamental mathematical concepts. From simplifying fractions to solving complex equations and securing online transactions, the applications are wide-ranging and impactful. Mastering the methods for finding common factors, including the Euclidean algorithm, equips you with valuable skills applicable across many disciplines. The journey into number theory begins with these fundamental building blocks. Remember that understanding the underlying principles is as important as obtaining the answer itself – it's this understanding that allows you to apply these concepts effectively in various contexts and further explore the fascinating world of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is 53 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 24 And 15
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Percent Is 2 3 Of A Circle
Mar 28, 2025
-
Ray Diagrams Of A Concave Mirror
Mar 28, 2025
-
Are The Diagonals Of An Isosceles Trapezoid Congruent
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Common Factors Of 24 And 32 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
