X 3 2x 2 X 2
Juapaving
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
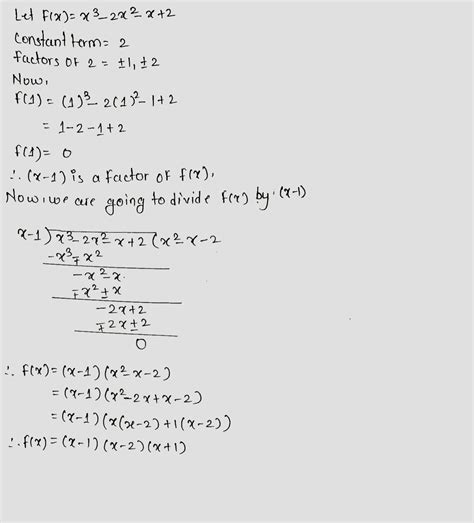
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mathematical Enigma: x³ + 2x² + 2x + 2
The expression x³ + 2x² + 2x + 2, seemingly simple at first glance, presents a fascinating challenge in the world of mathematics. While it lacks the immediate elegance of a quadratic equation or the straightforward nature of a linear equation, its cubic form opens doors to a rich exploration of algebraic manipulation, polynomial analysis, and even numerical approximation techniques. This article delves deep into the intricacies of this expression, examining its properties, exploring potential solutions, and outlining the various approaches one might take to understand it better.
Understanding the Structure: A Polynomial Perspective
At its core, x³ + 2x² + 2x + 2 is a polynomial of degree three, also known as a cubic polynomial. This means the highest power of the variable 'x' is 3. Understanding this fundamental characteristic is crucial to approaching its analysis. The polynomial consists of four terms:
- x³: The cubic term, representing x multiplied by itself three times.
- 2x²: The quadratic term, representing 2 multiplied by x squared.
- 2x: The linear term, representing 2 multiplied by x.
- 2: The constant term, an independent numerical value.
The coefficients of each term (1, 2, 2, and 2) dictate the polynomial's behavior and its graphical representation.
Exploring the Coefficients: Insights and Implications
The coefficients hold significant information about the polynomial. The fact that all coefficients are positive suggests a certain behavior of the function represented by this polynomial. Let's explore the implications:
- Positive Coefficients: Positive coefficients generally indicate that the polynomial will increase in value as x increases. We can expect the function to be predominantly positive for positive values of x. However, it's crucial to remember that this is a generalization, and the specific behavior depends on the interplay between the different terms.
- Relationship between Coefficients: The relative magnitudes of the coefficients influence the polynomial's shape. For instance, the dominance of the cubic term (x³) at larger values of x will determine the overall trend of the function. The presence of a significant quadratic term (2x²) implies a certain curvature, modifying the growth rate of the function.
- No Obvious Factorization: At first sight, there's no obvious way to factorize this polynomial into simpler expressions using common techniques. This makes finding its roots (the values of x that make the polynomial equal to zero) more challenging.
Finding Roots: Methods and Approaches
Determining the roots of a cubic polynomial is a more complex undertaking than solving quadratic equations. While there's a cubic formula analogous to the quadratic formula, it's significantly more unwieldy and less practical for hand calculations. Let's explore some viable approaches:
1. Numerical Methods: Approximating the Solution
For cubic polynomials lacking easily discernible factors, numerical methods offer a powerful way to approximate the roots. These methods involve iterative processes, refining an initial guess until a sufficiently accurate solution is reached. Some common numerical methods include:
- Newton-Raphson Method: This method uses the derivative of the polynomial to iteratively refine the approximation of the root. It converges relatively quickly for well-behaved functions, but its effectiveness depends on choosing a suitable initial guess.
- Bisection Method: This method repeatedly divides an interval known to contain a root, systematically narrowing down the search until the desired level of accuracy is achieved. It’s robust but converges more slowly than the Newton-Raphson method.
2. Graphical Analysis: Visualizing the Roots
Plotting the graph of the function y = x³ + 2x² + 2x + 2 allows for a visual assessment of its roots. The points where the graph intersects the x-axis (where y = 0) represent the roots of the polynomial. This graphical approach provides a qualitative understanding of the number and approximate locations of the roots. Modern graphing software and calculators make this a readily accessible method.
3. Advanced Algebraic Techniques: Exploring Potential Factorizations
While simple factorization might not be immediately apparent, more advanced algebraic techniques could potentially reveal hidden factors. Methods like polynomial long division or the rational root theorem (if rational roots exist) could be explored, though the lack of obvious factors suggests these methods might not lead to straightforward solutions.
Exploring the Function's Behavior: Beyond the Roots
Beyond the quest for roots, understanding the overall behavior of the function defined by x³ + 2x² + 2x + 2 is equally important.
1. Derivatives and Turning Points
Calculating the first and second derivatives of the polynomial provides information about its increasing/decreasing intervals and concavity. The first derivative helps identify critical points (local maxima and minima), while the second derivative determines the function's concavity (whether it curves upwards or downwards). This analysis provides a detailed picture of the function's shape.
2. Limits and Asymptotic Behavior
As x approaches positive or negative infinity, the cubic term (x³) dominates the polynomial's behavior. This means the function will tend towards positive infinity as x becomes very large and negative infinity as x becomes very large and negative.
3. Applications and Context
The expression x³ + 2x² + 2x + 2 might appear abstract, but it could represent various real-world phenomena depending on the context. It could model a cubic relationship between variables in physics, engineering, or economics. For example, it might represent the volume of a certain shape as a function of one of its dimensions or a rate of change in a dynamic system. Understanding the specific context in which this polynomial appears is crucial to interpreting its meaning and significance.
Conclusion: A Journey of Mathematical Exploration
The seemingly simple expression x³ + 2x² + 2x + 2 opens a doorway to a rich exploration of mathematical concepts. From numerical approximation methods to graphical analysis and considerations of derivatives and limits, this polynomial serves as a microcosm of the broader landscape of algebraic manipulation and function analysis. While finding exact roots might require sophisticated techniques, the journey of understanding its properties and behavior provides valuable insights into the beauty and complexity of mathematical relationships. The exploration continues beyond the confines of this article, inviting further investigation and deepening our appreciation for the power of mathematical tools.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
In The Modern Periodic Table Elements Are Arranged By
Mar 07, 2025
-
The Product Of Two Irrational Numbers Is
Mar 07, 2025
-
What Are The Factors For 31
Mar 07, 2025
-
What Is The Prime Factorization Of 22
Mar 07, 2025
-
Is Ba A Metal Or Nonmetal
Mar 07, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 3 2x 2 X 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
