What Are The Factors For 31
Juapaving
Mar 07, 2025 · 6 min read
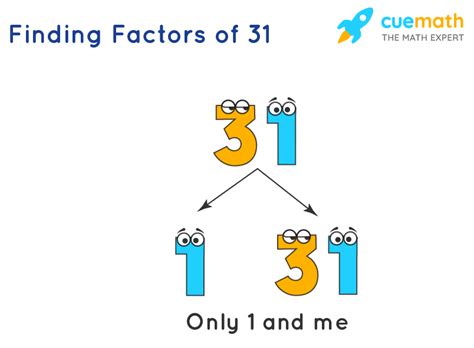
Table of Contents
Decoding the Factors of 31: A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Divisibility
The seemingly simple question, "What are the factors of 31?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, prime numbers, and divisibility rules. While the answer itself is straightforward, understanding why the answer is what it is provides a valuable insight into fundamental mathematical concepts. This article will not only answer the question directly but also explore the broader mathematical context, explaining the significance of prime numbers and providing a deeper understanding of factors and divisibility.
What are Factors?
Before we delve into the factors of 31, let's define what a factor is. A factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides the number exactly without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's a number you can multiply by another whole number to get your original number. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because:
- 1 x 12 = 12
- 2 x 6 = 12
- 3 x 4 = 12
Finding the Factors of 31
Now, let's tackle the main question: What are the factors of 31? The only whole numbers that divide 31 without leaving a remainder are 1 and 31 itself. Therefore, the factors of 31 are 1 and 31.
The Significance of Prime Numbers
The fact that 31 has only two factors—1 and itself—makes it a prime number. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. Prime numbers are fundamental building blocks in number theory, and their properties have captivated mathematicians for centuries. They are crucial in cryptography, ensuring the security of online transactions and data protection.
Distinguishing Prime Numbers from Composite Numbers
It's important to differentiate between prime numbers and composite numbers. A composite number is a positive integer that has at least one divisor other than 1 and itself. For example, 12 is a composite number because it has factors 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. The number 1 is neither prime nor composite; it's a unique case.
Identifying Prime Numbers: Methods and Techniques
Determining whether a number is prime can be challenging for larger numbers. While trial division (checking for divisibility by all numbers up to the square root of the number) works, it becomes computationally expensive for very large numbers. More sophisticated algorithms, like the Sieve of Eratosthenes, are used to efficiently identify prime numbers within a given range. These algorithms are essential for various applications, including cryptography and computer science.
The Infinitude of Prime Numbers
One of the most remarkable facts about prime numbers is that there are infinitely many of them. This was proven by Euclid over 2000 years ago, and it highlights the boundless nature of prime numbers and their importance in mathematics. The distribution of prime numbers, however, remains a topic of ongoing research and fascination, with mathematicians continuously exploring patterns and properties.
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
The concept of prime numbers is central to the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, which states that every integer greater than 1 can be uniquely expressed as a product of prime numbers (ignoring the order of the factors). This theorem demonstrates the fundamental role prime numbers play in the structure of integers. It is the cornerstone of many areas of number theory and has far-reaching implications in various fields.
Applications of Prime Numbers
The significance of prime numbers extends beyond theoretical mathematics. They have crucial applications in various fields:
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers form the backbone of many modern encryption algorithms, such as RSA. The difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime factors underpins the security of these systems, protecting sensitive information.
-
Hashing: Prime numbers are used in hashing algorithms, which are essential for data storage and retrieval. They help distribute data evenly across hash tables, minimizing collisions and improving efficiency.
-
Random Number Generation: Prime numbers are used in algorithms for generating pseudo-random numbers, essential for simulations, statistical analysis, and computer graphics.
-
Coding Theory: Prime numbers play a significant role in error-correcting codes, used to ensure reliable data transmission and storage. They are crucial in ensuring data integrity and recovery.
Divisibility Rules: Simplifying Factor Identification
While trial division can determine factors, divisibility rules offer a more efficient approach. Divisibility rules are shortcuts that help determine whether a number is divisible by another number without performing the actual division. Knowing these rules can significantly simplify the process of identifying factors, especially for larger numbers.
For example:
- Divisibility by 2: A number is divisible by 2 if its last digit is even (0, 2, 4, 6, 8).
- Divisibility by 3: A number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3.
- Divisibility by 5: A number is divisible by 5 if its last digit is 0 or 5.
- Divisibility by 10: A number is divisible by 10 if its last digit is 0.
Understanding and applying these rules can greatly speed up the process of factor identification and contribute to a deeper understanding of number relationships.
Exploring Further: Beyond the Factors of 31
The exploration of factors goes beyond individual numbers like 31. Analyzing the factors of different numbers reveals patterns and relationships that underpin various mathematical concepts. For instance, comparing the factors of different numbers helps understand the concepts of greatest common divisor (GCD) and least common multiple (LCM), which are crucial in simplifying fractions and solving various mathematical problems.
Furthermore, the study of prime factorization helps in understanding the distribution of prime numbers, a topic that continues to fascinate mathematicians and remains an active area of research. The Riemann Hypothesis, one of the most significant unsolved problems in mathematics, directly relates to the distribution of prime numbers.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Prime Numbers and Factors
The seemingly simple question of determining the factors of 31 leads us on a journey into the fascinating world of number theory and the significance of prime numbers. Understanding prime numbers and their properties is not only essential for mathematicians but also has far-reaching implications in various fields, from cryptography to computer science. The concepts discussed here—factors, prime numbers, divisibility rules, and their applications—form fundamental building blocks in understanding the structure of numbers and their relationships, making them crucial elements in various scientific and technological applications. The seemingly simple number 31, therefore, serves as a gateway to a rich and complex mathematical landscape, emphasizing the importance of exploring fundamental mathematical concepts to appreciate their broader significance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are The Building Blocks Of All Matter
Mar 09, 2025
-
Type Of Inflorescence Is Represented S Typical Of Sunflowers
Mar 09, 2025
-
Product Of Two Irrational Numbers Is Always
Mar 09, 2025
-
Ordering Numbers From Least To Greatest
Mar 09, 2025
-
Words With S At The End
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors For 31 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
