What Is The Prime Factorization Of 22
Juapaving
Mar 07, 2025 · 6 min read
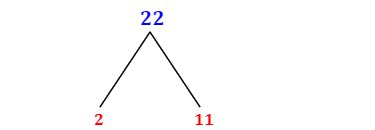
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization of 22? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization of 22?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, exploring fundamental concepts that underpin much of mathematics. While the answer itself is straightforward, understanding the process and the underlying principles provides valuable insight into the structure of numbers. This article will delve deeply into the prime factorization of 22, exploring the concepts of prime numbers, factorization, and their broader applications.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before we tackle the prime factorization of 22, let's establish a solid understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. In other words, it's only divisible by 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. Prime numbers are the building blocks of all other whole numbers, a concept that's crucial to understanding factorization.
Why are Prime Numbers Important?
Prime numbers are fundamental in mathematics for several reasons:
- Unique Factorization Theorem (Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic): This theorem states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers, disregarding the order of the factors. This uniqueness is what makes prime factorization so powerful.
- Cryptography: Prime numbers are the cornerstone of modern cryptography, playing a critical role in securing online transactions and communications. The difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime components is the basis for many encryption algorithms.
- Number Theory: Prime numbers are central to numerous areas of number theory, including the distribution of primes, prime gaps, and various unsolved problems like the Riemann Hypothesis.
- Abstract Algebra: Prime numbers and their properties extend into abstract algebra, impacting concepts like rings, fields, and modular arithmetic.
Factorization: Breaking Down Numbers
Factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its factors. Factors are numbers that divide evenly into a given number without leaving a remainder. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12.
Prime Factorization: The Prime Building Blocks
Prime factorization, also known as prime decomposition, is a specific type of factorization where a number is expressed as a product of its prime factors. This representation is unique for each number (excluding the order of the factors), as stated by the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic. This uniqueness is powerful because it provides a standard way to represent any integer greater than 1.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 22
Now, let's finally tackle the prime factorization of 22. We can use a method called the factor tree.
-
Start with the number 22.
-
Find the smallest prime number that divides 22. This is 2. However, 22 is not divisible by 2. The next prime number is 3; 22 is not divisible by 3. The next prime number is 5; 22 is not divisible by 5. The next prime number is 7; 22 is not divisible by 7. The next prime number is 11. 22 is divisible by 11 (22 ÷ 11 = 2).
-
Express 22 as a product of 11 and 2. 22 = 11 x 2.
-
Check if the factors are prime. Both 11 and 2 are prime numbers.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 22 is 2 x 11. We've broken down 22 into its fundamental prime components. This representation is unique; no other combination of prime numbers will multiply to give 22.
Applications of Prime Factorization
The concept of prime factorization extends far beyond simple mathematical exercises. Its applications are widespread and crucial in various fields:
1. Simplifying Fractions
Prime factorization is essential for simplifying fractions. By finding the prime factorization of both the numerator and the denominator, we can identify common factors that can be canceled out, leading to a simplified fraction in its lowest terms. For example, simplifying 22/44 involves finding the prime factorization of both 22 (2 x 11) and 44 (2 x 2 x 11). This reveals a common factor of 2 x 11, leading to a simplified fraction of 1/2.
2. Finding the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Prime factorization provides a systematic method for finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) and the least common multiple (LCM) of two or more numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides all the given numbers without leaving a remainder, while the LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all the given numbers.
For example, to find the GCD of 22 and 44, we use their prime factorizations:
- 22 = 2 x 11
- 44 = 2 x 2 x 11
The common prime factors are 2 and 11. Therefore, the GCD(22, 44) = 2 x 11 = 22.
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
LCM(22, 44) = 2² x 11 = 44.
3. Cryptography: Securing Online Transactions
As mentioned earlier, the difficulty of factoring extremely large numbers into their prime components is fundamental to many modern encryption algorithms. RSA encryption, a widely used public-key cryptosystem, relies on the computational infeasibility of factoring the product of two large prime numbers. This ensures the security of sensitive data transmitted over the internet, protecting online transactions and communications.
4. Modular Arithmetic and Number Theory
Prime factorization plays a crucial role in various aspects of number theory, including modular arithmetic, which involves performing arithmetic operations within a fixed range (a modulus). Prime numbers exhibit unique properties within modular arithmetic, contributing to the development of sophisticated mathematical concepts and algorithms.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Further
The prime factorization of 22, while seemingly simple, serves as a gateway to a vast and intricate world of mathematical concepts. Further exploration could involve:
- Investigating algorithms for prime factorization: Efficient algorithms for finding the prime factors of large numbers are actively researched due to their importance in cryptography. Methods like the trial division, Pollard's rho algorithm, and the general number field sieve are examples of such algorithms.
- Exploring the distribution of prime numbers: The way prime numbers are distributed among integers is a fascinating and complex area of study. The prime number theorem provides an estimate of the density of primes, but many open questions remain.
- Delving into the Riemann Hypothesis: This unsolved problem in number theory relates to the distribution of prime numbers and has profound implications for various branches of mathematics.
Conclusion: The Significance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of 22, being 2 x 11, is a seemingly simple result. However, the process and the underlying concepts reveal the fundamental importance of prime numbers and factorization in mathematics and its applications. From simplifying fractions to securing online transactions, prime factorization is a cornerstone of numerous mathematical disciplines and real-world technologies. Understanding this seemingly simple concept opens the door to a deeper appreciation of the elegant structure and power of numbers.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is An Advantage Of Sole Proprietorship
Mar 09, 2025
-
Magnesium And Hydrochloric Acid Balanced Equation
Mar 09, 2025
-
3 Out Of 9 As A Percentage
Mar 09, 2025
-
How Are Hypotheses And Theories Related
Mar 09, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Characteristic Of Cancer Cells
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Prime Factorization Of 22 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
