Write The Chemical Formula For The Dichromate Ion
Juapaving
Mar 31, 2025 · 6 min read
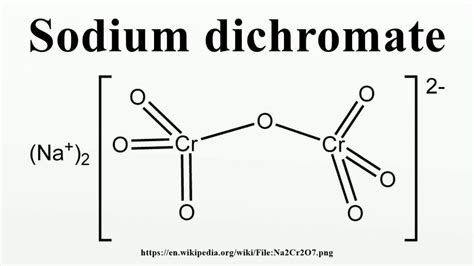
Table of Contents
The Dichromate Ion: Chemical Formula, Properties, and Applications
The dichromate ion, a vibrant orange-red species, plays a significant role in various chemical processes. Understanding its chemical formula, properties, and applications is crucial in numerous fields, from analytical chemistry to industrial manufacturing. This comprehensive article will delve deep into the fascinating world of the dichromate ion, exploring its structure, reactions, and uses.
Understanding the Chemical Formula: Cr₂O₇²⁻
The chemical formula for the dichromate ion is Cr₂O₇²⁻. This formula tells us that the ion consists of two chromium (Cr) atoms and seven oxygen (O) atoms, carrying a net charge of 2-. The arrangement of these atoms is crucial to understanding the ion's properties. The chromium atoms are in a +6 oxidation state, a characteristic feature that contributes to its strong oxidizing power. The seven oxygen atoms are bonded to the chromium atoms in a complex structure described below.
The Structure of the Dichromate Ion
The dichromate ion exhibits a linear bridge structure. This means that the two chromium atoms are connected by an oxygen atom bridging between them. Each chromium atom is further bonded to three other oxygen atoms, resulting in a somewhat distorted tetrahedral geometry around each chromium center. This structure can be visually represented through various molecular modeling techniques, illustrating the spatial arrangement of the atoms and their bonds. The bridging oxygen atom plays a crucial role in the stability and reactivity of the ion.
Properties of the Dichromate Ion
The dichromate ion's properties are largely determined by its chemical structure and the high oxidation state of chromium. These properties dictate its behaviour in chemical reactions and its applications in various contexts.
Strong Oxidizing Agent
The most prominent property of the dichromate ion is its strong oxidizing power. This stems from the chromium(VI) being readily reduced to chromium(III), a much more stable oxidation state. In acidic solutions, the dichromate ion is a particularly potent oxidizing agent. This characteristic is exploited in various redox reactions, which we will explore later.
Color and Spectra
The intense orange-red color of the dichromate ion is a result of its electronic structure and the absorption of light in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The specific wavelength of light absorbed and transmitted determines the observed color. Spectroscopic techniques can be used to precisely determine the concentration of dichromate ions in a solution based on its absorbance at characteristic wavelengths.
Solubility and Reactivity
Dichromate salts, like potassium dichromate (K₂Cr₂O₇) and sodium dichromate (Na₂Cr₂O₇), are generally highly soluble in water. However, their solubility can vary depending on the counterion. The solubility behaviour is critical when considering their applications in different chemical processes. The reactivity of the dichromate ion is significantly affected by pH. In acidic conditions, its oxidizing power is significantly enhanced, while in basic conditions, it may undergo different reactions, potentially forming chromate ions (CrO₄²⁻).
Preparation of Dichromate Salts
Dichromate salts are commonly prepared through the oxidation of chromium(III) compounds. This process often involves the use of strong oxidizing agents, such as potassium permanganate or sodium hypochlorite. The reaction conditions, including temperature, pH, and concentration, need to be carefully controlled to maximize the yield of the dichromate product.
Industrial Production
On an industrial scale, dichromate salts are primarily produced from chromite ore (FeCr₂O₄). This process involves a series of complex steps, including roasting, leaching, and crystallization, to extract and purify the dichromate salts. The specific techniques employed may vary depending on the available resources and desired purity of the product.
Applications of the Dichromate Ion
The diverse properties of the dichromate ion make it a versatile reagent in a wide range of applications, including:
Analytical Chemistry
Titrations: Dichromate's strong oxidizing ability makes it a suitable titrant in redox titrations. This is particularly useful for determining the concentration of reducing agents in various samples. The characteristic color change during the titration allows for precise endpoint determination.
Qualitative Analysis: Dichromate's distinctive color is used in various qualitative tests. Its reaction with specific ions or compounds can produce characteristic color changes, allowing for the identification of certain substances.
Industrial Applications
Leather Tanning: Dichromate salts are used in the tanning of leather, a process that involves converting animal hides into durable and flexible materials. The dichromate ions cross-link the collagen fibers in the hides, improving their stability and resistance to degradation.
Metal Finishing: Dichromate is used in the passivation of metals such as steel and aluminum, forming a protective layer that enhances corrosion resistance. This process is crucial in various industrial applications requiring durable and corrosion-resistant metallic components.
Organic Synthesis: Dichromate is employed as an oxidizing agent in organic synthesis. It can be used to convert alcohols to ketones or aldehydes, depending on the reaction conditions and structure of the alcohol. This oxidation reaction is a powerful tool in the synthesis of various organic molecules.
Other Applications
Beyond the mentioned applications, dichromate finds use in:
- Photography: Dichromate salts are utilized in specific photographic processes.
- Wood preservation: Dichromate compounds have been historically used in wood preservation treatments. However, due to environmental concerns, their use in this area is declining.
- Cement production: Dichromate plays a small role as a minor additive in some cement formulations.
Safety Precautions and Environmental Concerns
It's crucial to emphasize the toxicity of chromium(VI) compounds, including dichromate salts. Direct contact with these substances can cause skin irritation, allergic reactions, and more severe health problems. Inhalation of dichromate dust can lead to respiratory issues. Appropriate safety precautions, such as wearing protective gloves, eye protection, and respirators, are essential when handling dichromate. Moreover, proper disposal procedures are necessary to prevent environmental contamination.
Environmental Impact
Dichromate is a known environmental pollutant. Its release into the environment can cause harm to aquatic life and ecosystems. The hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) is particularly toxic, readily accumulating in the food chain. Therefore, minimizing the release of dichromate compounds into the environment through responsible industrial practices and waste management is of paramount importance. Regulations and stringent control measures are in place in many countries to limit the discharge of dichromate into water bodies and the atmosphere.
Conclusion
The dichromate ion (Cr₂O₇²⁻), with its distinctive orange-red color and strong oxidizing properties, is a fascinating and important chemical species. Its chemical formula reflects its structure and oxidation state, determining its behavior and applications. From its use in analytical chemistry to its role in industrial processes, the dichromate ion continues to find significant applications. However, awareness of its toxicity and potential environmental impact is paramount. Responsible handling, safe disposal, and environmentally conscious practices are crucial to minimizing the risks associated with this versatile yet potentially hazardous chemical. Further research into sustainable alternatives and safer handling practices will contribute to the responsible and effective utilization of dichromate while mitigating its associated risks.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Highest Common Factor Of 6 And 9
Apr 02, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Base Area
Apr 02, 2025
-
Are There Centrioles In Plant Cells
Apr 02, 2025
-
Common Factors Of 35 And 50
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Ac And Dc Motors
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Write The Chemical Formula For The Dichromate Ion . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
