Why Is Capillary Action Important To Plants
Juapaving
Mar 31, 2025 · 6 min read
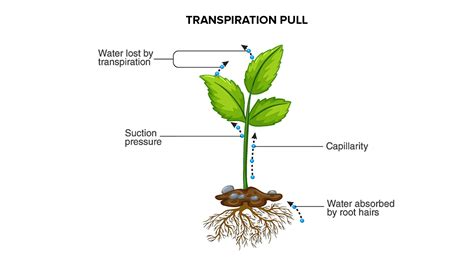
Table of Contents
Why is Capillary Action Important to Plants?
Capillary action is a vital process for plant survival, playing a critical role in their ability to absorb and transport water and nutrients. This phenomenon, governed by the interplay of adhesion, cohesion, and surface tension, is the unsung hero behind the remarkable ability of plants to thrive in diverse environments. Understanding the importance of capillary action in plants is key to appreciating the intricate mechanisms that support plant life.
What is Capillary Action?
Capillary action, also known as capillarity, is the ability of a liquid to flow in narrow spaces without the assistance of, or even in opposition to, external forces like gravity. This phenomenon is observable in thin tubes, porous materials, and even within the complex network of plant tissues. It's driven by two primary forces:
Adhesion and Cohesion: The Driving Forces
-
Adhesion: This refers to the attractive force between water molecules and the solid surfaces of the xylem vessels within a plant. Water molecules are attracted to the hydrophilic (water-loving) cell walls of the xylem, essentially "clinging" to them.
-
Cohesion: This is the attractive force between water molecules themselves. These molecules are linked together through hydrogen bonds, forming a cohesive column of water that extends from the roots to the leaves.
These two forces work in tandem. Adhesion pulls the water molecules upwards along the xylem walls, while cohesion pulls the remaining water molecules along, maintaining the continuous water column. The resulting upward movement of the water column against gravity is capillary action.
Surface Tension: A Supporting Player
Surface tension, the tendency of a liquid's surface to minimize its area, also contributes to capillary action. The surface tension of water creates a meniscus – a curved surface – in the xylem vessels. This curved surface creates an upward pull that further assists in water movement.
The Importance of Capillary Action in Plants
Capillary action is not merely a passive process; it's an essential mechanism underpinning several crucial aspects of plant life:
1. Water Uptake from the Soil: The Foundation of Life
Plants absorb water primarily through their roots. The root hairs, with their vast surface area, maximize contact with the soil water. Capillary action is crucial here, as it facilitates the movement of water from the soil, across the root cortex, and into the xylem vessels. Without capillary action, the uptake of water from soil would be severely hampered, particularly in drier conditions where the soil water potential is low. This initial step is the cornerstone of the entire water transport system within the plant.
2. Water Transport Through the Xylem: Reaching the Heights
The xylem, a complex network of specialized cells within the plant, forms a continuous pathway for water transport from the roots to the leaves. The xylem vessels are incredibly narrow, providing the ideal environment for capillary action to operate effectively. The cohesive forces between water molecules and the adhesive forces between water and the xylem walls work together to lift the water column, defying gravity. This allows taller plants to access water from the soil and transport it to their leaves, even at considerable heights. This continuous column of water, held together by cohesion and capillary action, is sometimes referred to as the transpiration stream.
3. Nutrient Transport: Essential Nutrients Delivered
Capillary action isn't solely responsible for water transport. It also plays a significant role in the transport of essential nutrients dissolved in the water. These nutrients, absorbed by the roots, are carried upwards along with the water through the xylem, reaching all parts of the plant. This delivery system ensures that the leaves, stems, and other plant tissues receive the vital nutrients needed for growth, development, and metabolic processes. This nutrient transport, facilitated by the movement of water via capillary action, underpins the health and productivity of the plant.
4. Maintaining Turgor Pressure: Standing Tall
Turgor pressure, the pressure exerted by water within the plant cells against their cell walls, is essential for maintaining plant structure and rigidity. Capillary action contributes to maintaining turgor pressure by facilitating the continuous supply of water to the plant cells. This pressure keeps plant tissues firm and prevents wilting. The adequate water supply, facilitated by capillary action, is instrumental in enabling the plant to stand tall and maintain its structure. Without sufficient turgor pressure, the plant would become limp and vulnerable.
5. Transpiration: Cooling and Gas Exchange
Transpiration, the process of water loss from the plant through stomata (pores) in the leaves, is crucial for several reasons. It helps to cool the plant, especially in hot environments, preventing overheating damage. It also facilitates gas exchange, allowing carbon dioxide (necessary for photosynthesis) to enter the plant and oxygen to escape. Capillary action plays a vital role in maintaining the transpiration stream, ensuring a continuous supply of water to the leaves, enabling efficient transpiration. The efficient transpiration process, in turn, is directly linked to the plant's overall health and productivity.
Factors Affecting Capillary Action in Plants
Several factors can influence the effectiveness of capillary action in plants:
-
Diameter of Xylem Vessels: Narrower xylem vessels lead to stronger capillary action. This is because the ratio of surface area to volume is higher, increasing the adhesive forces relative to the weight of the water column.
-
Temperature: Temperature affects the viscosity of water. Higher temperatures result in lower viscosity, making it easier for water to move through the xylem vessels. Conversely, lower temperatures increase viscosity and decrease capillary action.
-
Soil Water Potential: The availability of water in the soil directly impacts water uptake. Dry soil has a lower water potential, reducing the driving force for capillary action.
-
Plant Species: Different plant species have varying xylem vessel diameters and structures, leading to variations in capillary action efficiency. This is one factor explaining why certain plants thrive in specific environments.
-
Presence of Solutes: The presence of dissolved minerals and salts in the soil water can alter the water potential and thus the rate of capillary action. Osmosis plays a crucial role here, as the water moves to areas with higher solute concentration.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Plant Life
Capillary action is a fundamentally important process in plants, underpinning their ability to survive and thrive. From water uptake from the soil to nutrient transport and maintaining turgor pressure, this phenomenon is integral to every aspect of plant life. Understanding the principles of capillary action, its driving forces, and the factors influencing its efficiency allows for a deeper appreciation of the complex and fascinating world of plant biology. Its significance extends beyond the individual plant level; it's fundamental to the health of ecosystems and the balance of the planet. The efficient operation of capillary action is crucial for the continued survival and success of the plant kingdom, highlighting its importance in maintaining the biodiversity and health of our planet. Further research into the nuances of capillary action in plants could lead to innovations in agriculture and our understanding of plant adaptation to various environments.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Chemical Bonds In Order From Strongest To Weakest
Apr 03, 2025
-
Calculate The Molar Mass Of Ca No3 2
Apr 03, 2025
-
Do The Diagonals Of A Kite Bisect Bisect The Angles
Apr 03, 2025
-
Peasants And Workers Party Of India
Apr 03, 2025
-
Compressions And Rarefactions Are Characteristics Of
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Why Is Capillary Action Important To Plants . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
