Which Of The Following Are Homologous Structures
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
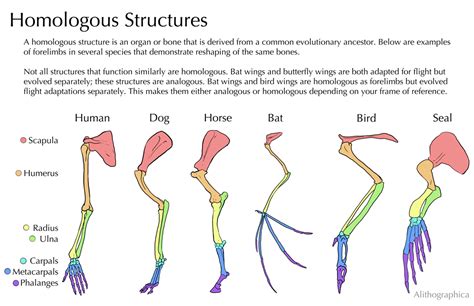
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Are Homologous Structures? A Deep Dive into Evolutionary Biology
Homologous structures are a cornerstone of evolutionary biology, providing compelling evidence for common ancestry. Understanding what constitutes a homologous structure, and how to differentiate it from analogous structures, is crucial for grasping the principles of evolution and phylogenetic relationships. This article will delve deep into the concept of homologous structures, exploring various examples and clarifying common misconceptions. We'll also touch upon the importance of homologous structures in reconstructing evolutionary history and addressing challenges in their identification.
Defining Homologous Structures: Shared Ancestry, Divergent Functions
Homologous structures are similar physical features in organisms that share a common ancestor, even if those features serve different functions in the modern organisms. The key here is the shared ancestry, not the functional similarity. This similarity stems from the inheritance of the same genetic blueprint from a common ancestor, which has been modified over time through evolutionary processes like natural selection and adaptation.
Think of it like this: imagine a family recipe for bread. Each generation might tweak the recipe slightly – adding more herbs, changing the type of flour, adjusting the baking time. While the final products (loaves of bread) might look different, they all share a common ancestor – the original recipe. Similarly, homologous structures have a common ancestral origin, even if their functions have diverged significantly over evolutionary time.
Key Characteristics of Homologous Structures:
- Shared structural elements: Despite functional differences, homologous structures share fundamental structural similarities. These similarities might be evident in the arrangement of bones, tissues, or even the developmental pathways that give rise to the structures.
- Common embryonic origin: Homologous structures often develop from similar embryonic tissues. This shared developmental pathway further strengthens the evidence for shared ancestry.
- Genetic basis: The underlying genetic mechanisms responsible for the development of homologous structures often share similarities, reflecting their shared evolutionary origin.
Examples of Homologous Structures: Across the Animal Kingdom
Let's explore some striking examples of homologous structures across diverse groups of animals:
1. Mammalian Forelimbs: This is arguably the most classic example. The forelimbs of mammals – including humans, bats, whales, and cats – show remarkable similarities in their bone structure, despite serving vastly different functions:
- Humans: Used for manipulating objects and locomotion.
- Bats: Adapted for flight.
- Whales: Modified for swimming and propulsion.
- Cats: Specialized for running, jumping, and catching prey.
While the functions differ greatly, the underlying structure – a humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges – remains strikingly consistent, providing strong evidence of a shared mammalian ancestor.
2. Vertebrate Vertebrae: The vertebral column, the backbone of vertebrates, is another excellent example. From the long, flexible spine of a snake to the relatively rigid spine of a human, the basic structure of vertebrae – individual bony units forming a column – persists across diverse vertebrate groups. This shared structure reflects their common ancestry, even though the specific adaptations of the vertebral column vary drastically depending on the animal's lifestyle and environment.
3. Plant Leaves and Thorns: The diversity of plant structures offers further illustration. Consider the modification of leaves into thorns in cacti. While a cactus thorn and a broad leaf serve entirely different functions (protection vs. photosynthesis), their underlying structure reveals a shared origin. Both are modified leaves, demonstrating the adaptation of a basic structure to diverse ecological needs.
4. Bird Wings and Insect Wings: It's crucial to note that not all similar structures are homologous. This leads us to the concept of analogous structures. Bird wings and insect wings are analogous structures. Although both structures enable flight, they have evolved independently and have fundamentally different structures. Bird wings are modifications of forelimbs, containing bones, muscles, and feathers, while insect wings are chitinous extensions of the exoskeleton. This example highlights the importance of understanding the underlying structure and developmental origins when determining homology.
Analogous Structures: Convergent Evolution
To further clarify the concept of homology, let's consider analogous structures. These are structures that have similar functions but different evolutionary origins. They arise through convergent evolution, where unrelated species independently evolve similar traits because they face similar environmental pressures or selective challenges.
The bird wing and insect wing example perfectly illustrates convergent evolution. Both structures facilitate flight, but their underlying structure and developmental origins are completely different. This reflects the independent evolution of flight in birds and insects, driven by similar environmental pressures. Other examples include the streamlined bodies of dolphins (mammals) and sharks (fish), or the similar shapes of cacti and euphorbias, both of which are adapted to arid environments but belong to completely different plant families.
Homoplasy: A Complication in Homology Assessment
Another important concept to understand is homoplasy. This term refers to similarities in structure that are not due to common ancestry but have evolved independently. Homoplasy can complicate the identification of homologous structures, as it can lead to misleading resemblances between organisms. Convergent evolution is a major source of homoplasy.
Identifying Homologous Structures: Challenges and Considerations
Identifying homologous structures is not always straightforward. Several factors can complicate the process:
- Significant evolutionary divergence: Over vast evolutionary timescales, homologous structures can become highly modified, making their shared ancestry less obvious. Detailed comparative anatomical studies, developmental biology data, and genetic analyses are essential to clarify homology in such cases.
- Incomplete fossil record: The lack of a complete fossil record can hinder the reconstruction of evolutionary relationships and make it challenging to definitively establish homology.
- Developmental plasticity: The development of a structure can be influenced by environmental factors, creating variations that might obscure underlying homology.
The Importance of Homologous Structures in Evolutionary Biology
Homologous structures are invaluable tools for reconstructing phylogenetic relationships. They provide crucial evidence for common ancestry, allowing scientists to build evolutionary trees (phylogenies) that reflect the evolutionary history of different organisms. By comparing homologous structures across species, scientists can infer evolutionary relationships, identify common ancestors, and understand the evolutionary pathways that have led to the diversity of life on Earth. The study of homologous structures continues to be a driving force in the field of evolutionary biology, providing insights into the processes that shape the diversity of life and the relationships between organisms.
Conclusion
The concept of homologous structures is fundamental to understanding the principles of evolution and the evolutionary relationships between organisms. By carefully analyzing structural similarities, embryonic development, and genetic evidence, scientists can uncover the shared ancestry of seemingly disparate species. While the identification of homology can present challenges, the insights gained from studying homologous structures remain crucial to our understanding of the history and diversity of life on Earth. The continued study of homologous structures promises further advancements in our comprehension of evolutionary processes and the intricate tapestry of life's evolutionary history. Distinguishing homology from analogy remains an active field of research, continually refined through new technological and analytical approaches.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Difference Between Nerve And Neuron
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is The Sum Of The Angles Of A Hexagon
Mar 25, 2025
-
Rectangular Oyramid Labeling Of The Length Width And Hiegh Base
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Type Of Cell Has Large Vacuoles
Mar 25, 2025
-
Light Microscope And Electron Microscope Differences
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Are Homologous Structures . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
