Rectangular Oyramid Labeling Of The Length Width And Hiegh Base
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
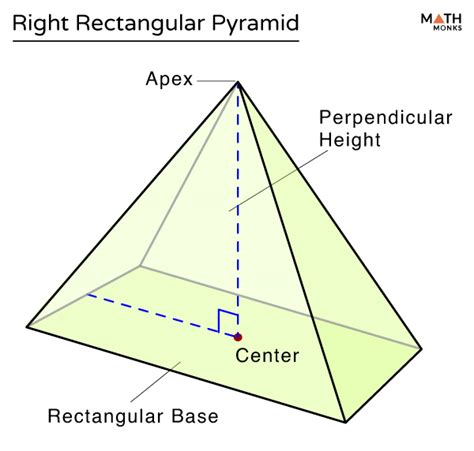
Table of Contents
Rectangular Pyramid Labeling: A Comprehensive Guide to Length, Width, and Base Height
Understanding the labeling conventions for a rectangular pyramid is crucial for accurate calculations and clear communication in geometry and related fields. This comprehensive guide will delve into the specifics of identifying and labeling the length, width, and base height of a rectangular pyramid, clarifying common points of confusion and providing practical examples.
Defining the Rectangular Pyramid
Before we jump into labeling, let's establish a firm understanding of what a rectangular pyramid is. A rectangular pyramid is a three-dimensional geometric shape with a rectangular base and four triangular faces that meet at a single point called the apex. It's important to distinguish it from other pyramid types, such as square pyramids (where the base is a square) or triangular pyramids (where the base is a triangle).
The key components of a rectangular pyramid include:
- Base: The rectangular surface forming the bottom of the pyramid.
- Apex: The single point where all four triangular faces meet at the top.
- Lateral Faces: The four triangular faces connecting the base to the apex.
- Edges: The line segments where two faces meet.
- Vertices: The points where edges intersect.
Labeling the Length and Width of the Rectangular Base
The rectangular base is the foundation of our labeling system. Imagine the base lying flat on a surface. We need to define two perpendicular dimensions for this rectangle:
- Length (l): This represents the longer dimension of the rectangular base. It's the distance between two opposite vertices along the longer side.
- Width (w): This represents the shorter dimension of the rectangular base. It's the distance between two opposite vertices along the shorter side.
Important Note: There's no universally accepted convention dictating which side should be labeled as length and which as width. Consistency is key. Once you define length and width in your diagram or problem, stick to that convention throughout your calculations. Clearly labeling your diagram is crucial to avoid ambiguity.
Understanding and Labeling the Base Height
The base height, often confused with the pyramid's slant height, is a critical dimension for calculating the volume and surface area of a rectangular pyramid. It's defined as follows:
- Base Height (h): This is the perpendicular distance from the apex to the plane of the rectangular base. It's crucial to understand that this is not the length of the edges connecting the apex to the base vertices (those are slant heights). The base height is always perpendicular to the base's surface.
Visualizing the Labeling: A Step-by-Step Approach
Let's walk through a practical example of labeling a rectangular pyramid:
-
Draw the Rectangular Base: Start by drawing a rectangle. This will represent the base of your pyramid.
-
Label Length and Width: Choose one side of the rectangle and label it 'l' for length. Label the other perpendicular side 'w' for width. Remember: your choice of which is length and which is width is arbitrary as long as you remain consistent.
-
Draw the Apex: Above the rectangle, draw a point representing the apex of the pyramid.
-
Connect the Apex to the Base Vertices: Draw four lines connecting the apex to each of the four vertices (corners) of the rectangular base. These lines create the four triangular lateral faces.
-
Draw and Label the Base Height: Draw a line segment from the apex straight down to the plane of the rectangular base, ensuring it meets the base at a 90-degree angle. Label this line segment 'h' for base height.
-
Label Slant Heights (Optional): The lines connecting the apex to each of the base vertices are called slant heights. You can label these differently (e.g., s1, s2, s3, s4) or use a single 's' if all slant heights are equal (this is only true for specific pyramid types).
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Several common mistakes can lead to inaccurate calculations and misunderstandings:
-
Confusing Base Height with Slant Height: The most frequent error is mistaking the slant height for the base height. Remember, the base height is always perpendicular to the base.
-
Inconsistent Labeling: Using 'l' for width and 'w' for length in one part of the calculation and switching them later is a recipe for disaster. Maintain a consistent labeling scheme throughout.
-
Neglecting to Draw a Clear Diagram: A well-labeled diagram is an invaluable tool for visualizing the problem and avoiding mistakes.
Applications and Real-World Examples
Understanding the labeling conventions for rectangular pyramids extends beyond abstract geometry problems. It's essential in various fields, including:
-
Architecture: Designing structures like pyramids and roofs often involves calculating volumes and surface areas, requiring accurate labeling of the pyramid's dimensions.
-
Engineering: Civil and structural engineers need precise measurements for designing stable and efficient structures.
-
Computer Graphics and 3D Modeling: Creating 3D models requires a solid understanding of geometric principles, including accurate labeling of shapes like rectangular pyramids.
-
Packaging and Design: Optimizing package shapes and sizes often utilizes geometric principles, where understanding the dimensions of rectangular pyramids becomes crucial for efficiency and cost savings.
Advanced Concepts and Calculations
Once you have correctly labeled your rectangular pyramid, you can move on to more advanced calculations, such as:
-
Surface Area: The total area of all five faces (the rectangular base and four triangular lateral faces). The formulas for calculating this depend on the lengths, widths, and slant heights.
-
Volume: The amount of space enclosed within the pyramid. The volume of a rectangular pyramid is given by the formula: (1/3) * l * w * h, where 'l' is length, 'w' is width, and 'h' is base height.
-
Slant Height Calculation: If you know the base height and the dimensions of the base, you can use the Pythagorean theorem to calculate the slant height of each triangular face.
Conclusion: Master the Art of Rectangular Pyramid Labeling
Mastering the art of labeling a rectangular pyramid is fundamental to success in various disciplines requiring spatial reasoning and geometric calculations. By carefully following the guidelines outlined in this guide, and by focusing on clarity, consistency, and careful diagram sketching, you can confidently tackle complex geometric problems and communicate your findings with precision and accuracy. Remember, a well-labeled diagram is your best ally in navigating the intricacies of rectangular pyramid geometry. Practice regularly, and you'll soon find that labeling these shapes becomes second nature.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is 9 A Multiple Of 3
Mar 28, 2025
-
Lcm Of 5 7 And 2
Mar 28, 2025
-
Barium Chloride Reacts With Sodium Sulfate
Mar 28, 2025
-
Tension Is Measured In What Units
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Decimal For 7
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Rectangular Oyramid Labeling Of The Length Width And Hiegh Base . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
