What Is Xx11 In Roman Numerals
Juapaving
Apr 05, 2025 · 5 min read
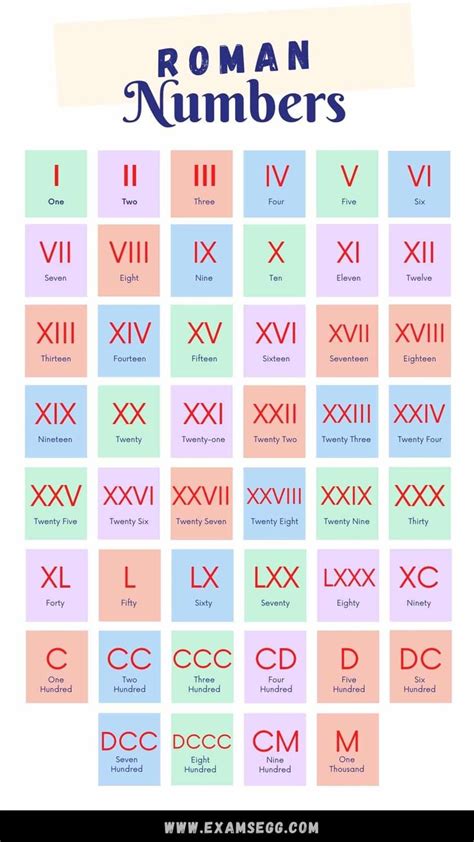
Table of Contents
What is XX11 in Roman Numerals? Decoding the Mystery and Exploring Roman Numeral Systems
The seemingly simple question, "What is XX11 in Roman numerals?" unveils a fascinating dive into the intricacies of ancient Roman numerical notation. While the combination of "XX11" might appear unusual at first glance, understanding the underlying principles of the Roman numeral system allows us to decipher it and appreciate its historical significance. This comprehensive guide will explore the meaning of XX11, delve into the rules governing Roman numerals, and examine their evolution and enduring relevance.
Understanding the Roman Numeral System
The Roman numeral system, developed in ancient Rome, utilizes a combination of seven Latin letters to represent numerical values. These letters are I (1), V (5), X (10), L (50), C (100), D (500), and M (1000). The system relies on both additive and subtractive principles to express numbers.
Additive Principle:
The additive principle is straightforward. When a smaller numeral is placed before a larger one, it's added to the larger numeral's value. For example:
- VI = 5 + 1 = 6
- XI = 10 + 1 = 11
- LXV = 50 + 10 + 5 = 65
Subtractive Principle:
The subtractive principle introduces a layer of complexity. When a smaller numeral precedes a larger one of a specific magnitude, it's subtracted from the larger numeral. This principle only applies in certain cases:
- IV = 5 - 1 = 4 (I before V)
- IX = 10 - 1 = 9 (I before X)
- XL = 50 - 10 = 40 (X before L)
- XC = 100 - 10 = 90 (X before C)
- CD = 500 - 100 = 400 (C before D)
- CM = 1000 - 100 = 900 (C before M)
It's crucial to note that the subtractive principle is only applied for one smaller numeral preceding a larger one. You wouldn't write IIX for 8; it would be VIII. This is a key rule to remember.
Deciphering XX11: The Anomaly
Now, let's address the core question: what is XX11 in Roman numerals? The combination "XX11" is not a standard representation within the traditional Roman numeral system. The system generally avoids repeating the same numeral more than three times consecutively. The expression "XX11" attempts to represent 211 using this unorthodox approach, but it is not formally correct Roman notation.
The standard and correct way to write 211 in Roman numerals is CCXI. Let's break it down:
- CC = 100 + 100 = 200
- XI = 10 + 1 = 11
- CCXI = 200 + 11 = 211
Why XX11 is Incorrect and the Importance of Standard Notation
The use of "XX11" is problematic because it deviates from established conventions. The Roman numeral system, despite its apparent simplicity, has specific rules to ensure clarity and avoid ambiguity. Using non-standard forms like "XX11" can lead to confusion and misinterpretations. Sticking to the established rules—the additive and subtractive principles, and the limitation on repetition—is essential for accurate representation.
Historical Context and Evolution of Roman Numerals
The Roman numeral system, while seemingly archaic, played a significant role in the development of mathematics and record-keeping in the Roman Empire and beyond. Its influence can still be observed today in various contexts, such as clock faces, chapter numbering in books, and even some architectural markings.
The system's evolution was gradual. Early forms were less systematic, and the rules evolved over time. The consistent use of the subtractive principle, for instance, wasn't always present in the earliest Roman writings. The standardization we know today came about through years of practice and refinement. Understanding the historical context helps appreciate the system's nuances.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Roman Numeral Concepts
While the fundamental principles of Roman numerals are relatively simple, there are some advanced concepts worth exploring:
-
Large Numbers: For extremely large numbers, the Roman system employed bar notation, placing a line above a numeral to multiply its value by 1000. For example, $\overline{V}$ represents 5000, and $\overline{X}$ represents 10,000.
-
Fractions: Roman numerals weren't well-suited to represent fractions in the same way that our decimal system is. They relied on more complex systems involving fractional units.
-
Variations and Regional Differences: Throughout Roman history and across different regions, minor variations in Roman numeral representation existed. While these regional variations were not substantial, they highlight the evolving nature of the system.
Practical Applications of Roman Numerals Today
Although the Hindu-Arabic decimal system has largely superseded Roman numerals in daily calculations, Roman numerals retain some practical applications:
-
Clock faces: Many clocks still use Roman numerals to represent the hours.
-
Chapter numbering: Books often use Roman numerals to number chapters or sections, often for aesthetic or stylistic reasons.
-
Outlines: Roman numerals are sometimes used in creating outlines to organize points hierarchically.
-
Copyright dates: You can sometimes see Roman numerals in copyright dates, giving a stylized look.
-
Architectural markings: Roman numerals can be found in architectural inscriptions on buildings and monuments.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Roman Numerals
To avoid common errors when working with Roman numerals, remember these points:
-
Avoid repetition beyond three times: Never repeat a numeral more than three times in succession.
-
Subtractive Principle Limitations: Apply the subtractive principle correctly and only when dealing with the specifically allowed combinations (IV, IX, XL, XC, CD, CM).
-
Consistency: Maintain consistency in your use of the additive and subtractive principles throughout the expression.
-
Verification: Always verify your representation using a reliable source or converter to double-check your work.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Roman Numerals
In conclusion, while the combination "XX11" isn't standard Roman numeral notation, understanding the principles of the Roman numeral system allows us to translate its intended meaning: 211. The standard representation is CCXI. The Roman numeral system, despite its limitations in handling large numbers and fractions compared to modern systems, stands as a testament to the ingenuity of ancient Roman mathematicians and continues to have its place in modern notation. Its enduring legacy reminds us of the fascinating journey of mathematical expression across history. Understanding the rules and avoiding common mistakes are key to correctly interpreting and using Roman numerals effectively. From clock faces to architectural inscriptions, the elegance and history inherent in Roman numerals continue to resonate today.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Test For Hydrogen Gas Called
Apr 05, 2025
-
Common Factors Of 15 And 25
Apr 05, 2025
-
Are Polar Covalent Bonds Stronger Than Nonpolar
Apr 05, 2025
-
What Is A Quarter Of A Half
Apr 05, 2025
-
Difference Between Molecular Geometry And Electron Geometry
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Xx11 In Roman Numerals . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
