What Is The Square Root Of 42
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
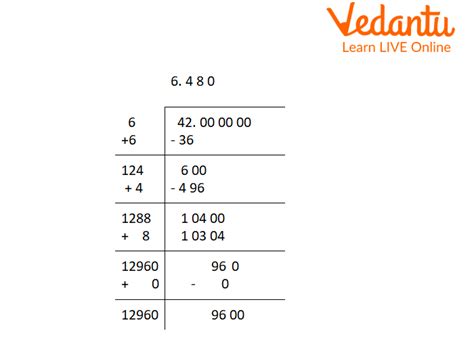
Table of Contents
What is the Square Root of 42? A Deep Dive into Irrational Numbers
The seemingly simple question, "What is the square root of 42?" opens a fascinating window into the world of mathematics, specifically the realm of irrational numbers. While the square roots of some numbers are neat and tidy integers (like √9 = 3), others, including √42, are not so easily expressed. This article will explore the nature of √42, delving into its properties, approximations, and applications, offering a comprehensive understanding of this intriguing mathematical concept.
Understanding Square Roots
Before diving into the specifics of √42, let's establish a foundational understanding of square roots. The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself (squared), equals the original number. For example, the square root of 9 (√9) is 3 because 3 x 3 = 9. This can be represented mathematically as:
x² = n => x = √n
where 'n' is the number and 'x' is its square root.
The Nature of √42: An Irrational Number
Unlike the square root of perfect squares (1, 4, 9, 16, etc.), which yield whole numbers, √42 is an irrational number. This means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction (a ratio of two integers). Its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating, meaning it goes on forever without any discernible pattern. This is a fundamental characteristic of irrational numbers, setting them apart from rational numbers like 1/2 or 0.75.
Approximating √42
Since we cannot express √42 exactly as a fraction or a terminating decimal, we rely on approximations. Several methods exist for calculating an approximate value:
1. Using a Calculator
The simplest approach is using a calculator. Most calculators will provide a close approximation, often accurate to several decimal places. For example, a calculator might show:
√42 ≈ 6.4807406984
2. Numerical Methods
More sophisticated methods, such as the Babylonian method (also known as Heron's method), provide increasingly accurate approximations through iterative calculations. This method involves making an initial guess, then refining that guess through repeated calculations based on a specific formula. The closer the initial guess is to the actual square root, the faster the convergence.
3. Linear Approximation
A simpler, yet less precise, method is linear approximation. This involves finding two perfect squares that bracket 42 (36 and 49) and using their square roots (6 and 7) to estimate. Since 42 is closer to 49 than 36, a reasonable estimation would be slightly above 6.5. While less accurate than other methods, it provides a quick, rough estimate.
The Significance of Irrational Numbers
The existence of irrational numbers like √42 might seem abstract, but they are crucial to numerous areas of mathematics and science:
1. Geometry
Irrational numbers frequently appear in geometric calculations. For instance, the diagonal of a square with sides of length 1 is √2, an irrational number. Similarly, the relationship between the diameter and circumference of a circle involves π (pi), another famous irrational number. The diagonal of a rectangle or the lengths of sides in many other geometric shapes often involve irrational numbers.
2. Trigonometry
Trigonometric functions, which describe angles and their relationships in triangles, often result in irrational values. This is particularly true when dealing with angles that are not multiples of 30 or 45 degrees.
3. Calculus
Irrational numbers are essential in calculus, the study of continuous change. Many important mathematical constants and limits involve irrational numbers, influencing calculations of areas, volumes, and rates of change. Derivatives and integrals frequently lead to irrational results.
4. Physics
Irrational numbers frequently emerge in physics, especially when dealing with natural phenomena exhibiting continuous change or relationships defined by curves and circles. These numbers play a role in describing everything from wave functions in quantum mechanics to the trajectory of projectiles.
Practical Applications of √42 (and other Irrational Numbers)
While it might seem less practical than working with integers or rational numbers, irrational numbers play a significant role in various real-world applications. Although we may approximate them in real-world problem solving, their underlying precision and properties remain critical:
1. Engineering and Construction
Engineers utilize irrational numbers in calculations for building design, such as determining the exact dimensions of components or calculating the lengths of diagonals in structures. Precise measurements, especially in large-scale projects, often require dealing with irrational values for optimal accuracy.
2. Computer Graphics and Game Development
In computer graphics and game development, irrational numbers are crucial for creating realistic simulations and rendering 3D models. Generating smooth curves and accurately representing natural shapes often requires calculations involving irrational values.
3. Financial Modeling
Financial models frequently employ irrational numbers in complex calculations involving interest rates, compound growth, and probabilities. These models require precise calculations to assess risk and predict future outcomes.
4. Scientific Research
Scientific research across various disciplines relies on irrational numbers for accurate data analysis and modeling. From understanding complex systems in biology and chemistry to analyzing astronomical data, precise calculations are crucial, and those often involve irrational numbers.
Conclusion: The Beauty of √42
The square root of 42, while not a whole number or a simple fraction, is a fascinating example of an irrational number. Its inherent complexity showcases the rich and nuanced nature of mathematics, demonstrating how seemingly simple questions can lead to deeper explorations of abstract concepts. Understanding irrational numbers, such as √42, not only enhances our mathematical knowledge but also provides a crucial foundation for comprehending and applying mathematics in various scientific, engineering, and technological fields. Its existence, though inexpressible as a simple fraction, points to a beauty and elegance within the mathematical universe. The endless decimal expansion of √42, while impossible to write in full, represents an infinite potential for mathematical investigation and practical application. Its approximation, despite its limitations, serves as a practical tool in a multitude of fields, demonstrating the power and relevance of this fascinating irrational number.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 4 9 As A Percent
Mar 26, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 28 And 42
Mar 26, 2025
-
Moment Of Inertia Of A Wheel
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is 120 Cm In Inches
Mar 26, 2025
-
At What Temperature Does Your Blood Boil
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Square Root Of 42 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
