Lowest Common Multiple Of 28 And 42
Juapaving
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
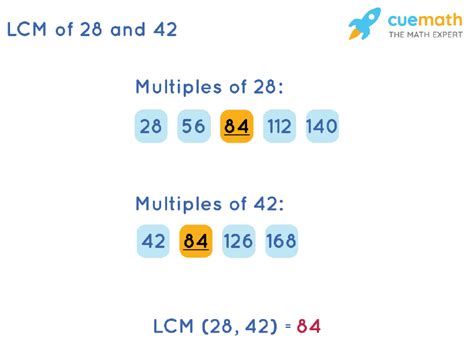
Table of Contents
Finding the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) of 28 and 42: A Comprehensive Guide
The lowest common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics with wide-ranging applications in various fields, from scheduling problems to music theory. Understanding how to calculate the LCM is crucial for anyone studying mathematics or related disciplines. This article delves into the intricacies of finding the LCM of 28 and 42, exploring multiple methods and providing a comprehensive understanding of the underlying principles.
Understanding the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM)
Before we dive into calculating the LCM of 28 and 42, let's establish a clear understanding of what the LCM represents. The LCM of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of all the given integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that can be divided evenly by all the numbers in question without leaving a remainder.
For instance, let's consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and so on. The multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, and so on. The smallest number that appears in both lists is 6, therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Methods for Finding the LCM of 28 and 42
Several methods exist for calculating the LCM of two numbers. We'll explore three common approaches: the listing method, the prime factorization method, and the greatest common divisor (GCD) method.
1. The Listing Method
This method involves listing the multiples of each number until a common multiple is found. While straightforward for smaller numbers, it becomes cumbersome for larger numbers.
Multiples of 28: 28, 56, 84, 112, 140, 168, 196, 224, 252, 280...
Multiples of 42: 42, 84, 126, 168, 210, 252, 294, 336, 378, 420...
By comparing the two lists, we can see that the smallest common multiple is 84. Therefore, the LCM of 28 and 42 using the listing method is 84.
However, this method can be time-consuming and inefficient for larger numbers. Let's explore more efficient methods.
2. The Prime Factorization Method
This method leverages the prime factorization of each number to determine the LCM. Prime factorization involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors.
- Prime factorization of 28: 28 = 2 x 2 x 7 = 2² x 7
- Prime factorization of 42: 42 = 2 x 3 x 7
To find the LCM using prime factorization:
- Identify the prime factors: The prime factors involved are 2, 3, and 7.
- Find the highest power of each prime factor: The highest power of 2 is 2², the highest power of 3 is 3¹, and the highest power of 7 is 7¹.
- Multiply the highest powers: LCM(28, 42) = 2² x 3 x 7 = 4 x 3 x 7 = 84
This method is more efficient than the listing method, especially for larger numbers. It provides a systematic approach to finding the LCM.
3. The Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method utilizes the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. The relationship between the LCM and GCD is given by the formula:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
where 'a' and 'b' are the two numbers.
First, let's find the GCD of 28 and 42 using the Euclidean algorithm:
- Divide 42 by 28: 42 = 28 x 1 + 14
- Divide 28 by the remainder 14: 28 = 14 x 2 + 0
The last non-zero remainder is 14, so the GCD(28, 42) = 14.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(28, 42) = (28 x 42) / GCD(28, 42) = (28 x 42) / 14 = 84
This method is also efficient and relies on a well-established algorithm for finding the GCD.
Applications of LCM
The LCM has a wide range of applications in various fields:
1. Scheduling Problems
Imagine two buses depart from the same station at different intervals. One bus departs every 28 minutes, and the other departs every 42 minutes. To find out when both buses will depart simultaneously again, we need to calculate the LCM(28, 42). The LCM, which is 84 minutes, indicates that both buses will depart together again after 84 minutes.
2. Fraction Operations
LCM is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. To add fractions, we need to find a common denominator, and the LCM provides the least common denominator.
For example, adding 1/28 and 1/42 requires finding the LCM of 28 and 42, which is 84. We then rewrite the fractions with the common denominator 84 and perform the addition.
3. Music Theory
In music theory, the LCM helps determine the least common period of two or more rhythmic patterns. This is useful in understanding how musical phrases interact and harmonize.
4. Gear Ratios
In mechanical engineering, understanding LCM is crucial when dealing with gear ratios and calculating rotational speeds of interconnected gears.
5. Number Theory
LCM plays a significant role in various number theory concepts, including modular arithmetic and solving Diophantine equations.
Advanced Concepts Related to LCM
While we've focused on finding the LCM of two numbers, the concept extends to finding the LCM of multiple numbers. The methods discussed, particularly the prime factorization method, can be easily adapted to handle more than two numbers. For instance, to find the LCM of 28, 42, and another number, say 21, we would follow similar steps as the prime factorization method, considering all the prime factors involved.
Conclusion
Finding the lowest common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental mathematical skill with diverse applications. While the listing method offers a simple visual approach, the prime factorization and GCD methods offer greater efficiency, particularly when dealing with larger numbers. Understanding these different methods provides a robust foundation for tackling LCM problems and applying this concept to solve real-world problems in various fields. By mastering these techniques, you'll enhance your mathematical proficiency and expand your problem-solving capabilities. Remember to choose the method best suited to the problem at hand; for smaller numbers, the listing method might suffice, whereas for larger numbers, the prime factorization or GCD method offers a more efficient and reliable approach.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Whats The Square Root Of 40
Mar 29, 2025
-
Common Factors Of 56 And 120
Mar 29, 2025
-
Is 23 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number
Mar 29, 2025
-
Which Organelle Is The Location Of Protein Synthesis
Mar 29, 2025
-
Difference Between Cell Wall And Cell Membrane
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lowest Common Multiple Of 28 And 42 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
