What Is The Reciprocal Of 1 3
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
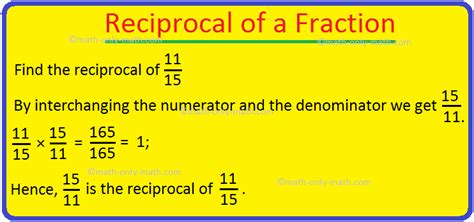
Table of Contents
What is the Reciprocal of 1/3? A Deep Dive into Reciprocals and Their Applications
The seemingly simple question, "What is the reciprocal of 1/3?" opens the door to a fascinating exploration of mathematical concepts with wide-ranging applications. Understanding reciprocals is fundamental to various areas, from basic arithmetic to advanced calculus and beyond. This article delves into the concept of reciprocals, explains how to find the reciprocal of a fraction, particularly 1/3, and explores its significance in different mathematical contexts.
Understanding Reciprocals: The Multiplicative Inverse
A reciprocal, also known as a multiplicative inverse, is a number that, when multiplied by the original number, results in a product of 1. In simpler terms, it's the number you need to multiply a given number by to get 1. This concept applies to various number types, including integers, fractions, and even more complex mathematical entities.
For example:
- The reciprocal of 5 is 1/5 (because 5 x 1/5 = 1)
- The reciprocal of 2/7 is 7/2 (because 2/7 x 7/2 = 1)
- The reciprocal of -3 is -1/3 (because -3 x -1/3 = 1)
Finding the Reciprocal of a Fraction: A Step-by-Step Guide
Finding the reciprocal of a fraction is straightforward. You simply switch the numerator and the denominator. The numerator becomes the denominator, and the denominator becomes the numerator.
Let's illustrate this with the example of 1/3:
-
Identify the numerator and denominator: In the fraction 1/3, the numerator is 1, and the denominator is 3.
-
Swap the numerator and denominator: Switching the positions gives us 3/1.
-
Simplify (if necessary): 3/1 simplifies to 3.
Therefore, the reciprocal of 1/3 is 3.
The Reciprocal of 1/3 in Different Contexts
The reciprocal of 1/3, being 3, appears in diverse mathematical and real-world scenarios. Let's explore some of these:
1. Solving Equations
Reciprocals are crucial for solving equations involving fractions. Consider the equation:
(1/3)x = 5
To solve for 'x', we multiply both sides of the equation by the reciprocal of 1/3, which is 3:
3 * (1/3)x = 5 * 3
This simplifies to:
x = 15
2. Division of Fractions
Division by a fraction is equivalent to multiplication by its reciprocal. This is a fundamental property of fractions and simplifies calculations significantly. For instance:
5 ÷ (1/3) = 5 * 3 = 15
This shows how knowing the reciprocal of 1/3 is essential for handling division problems involving fractions.
3. Unit Conversions
Reciprocals often play a critical role in unit conversions. Imagine you have a recipe that calls for 1/3 of a cup of sugar, and you want to convert this to tablespoons. Knowing that there are 16 tablespoons in a cup, you would use the reciprocal of 1/3 (which is 3) to calculate the number of tablespoons:
(1/3 cup) * (16 tablespoons/cup) * 3 = 16 tablespoons
This example demonstrates how the reciprocal simplifies calculations within unit conversions.
4. Geometry and Trigonometry
Reciprocals appear in various trigonometric functions. For instance, the cosecant (csc) function is the reciprocal of the sine (sin) function, and the secant (sec) function is the reciprocal of the cosine (cos) function. Understanding reciprocals is therefore fundamental for grasping trigonometric relationships. In geometry, reciprocals can simplify calculations involving areas and volumes of shapes with fractional dimensions.
5. Advanced Mathematics
The concept of reciprocals extends far beyond basic arithmetic. In linear algebra, the inverse of a matrix (a rectangular array of numbers) is its reciprocal. Finding the inverse of a matrix is essential for solving systems of linear equations and other advanced mathematical applications. In calculus, reciprocals are frequently encountered when dealing with derivatives and integrals.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Related Concepts
Understanding the reciprocal of 1/3 leads us to explore related mathematical concepts, such as:
1. Inverse Functions
Reciprocals are closely related to the concept of inverse functions. An inverse function "undoes" the action of a given function. For example, if a function f(x) multiplies a number by 3, its inverse function would divide the number by 3 (which involves using the reciprocal of 3).
2. Negative Reciprocals
The reciprocal of a negative number is also negative. For example, the reciprocal of -1/3 is -3. This concept is important in understanding the properties of negative numbers and their interaction within algebraic expressions.
3. Reciprocals of Complex Numbers
Even complex numbers (numbers containing both a real and an imaginary part) have reciprocals. Finding the reciprocal of a complex number involves a slightly more complex calculation, but the fundamental concept remains the same.
Real-World Applications: Where Reciprocals Matter
The seemingly abstract concept of reciprocals has practical implications in a wide array of real-world scenarios:
-
Engineering: Calculations in structural engineering, electrical engineering, and mechanical engineering frequently involve reciprocals. These calculations are essential for designing safe and efficient structures and systems.
-
Physics: Many physical phenomena involve relationships that can be expressed using reciprocals. For example, the relationship between resistance and conductance in electrical circuits involves reciprocals.
-
Finance: Calculating interest rates, amortization schedules, and other financial metrics often involve the use of reciprocals.
-
Computer Science: Reciprocals are fundamental in computer graphics, algorithms, and data structures. Many computer algorithms rely on efficient calculations involving reciprocals.
-
Chemistry: In chemistry, the concept of molarity (moles per liter) often requires using reciprocals for calculations.
Conclusion: The Significance of Understanding Reciprocals
This in-depth exploration demonstrates that the simple question of "What is the reciprocal of 1/3?" leads to a much broader and deeper understanding of mathematical concepts with significant real-world applications. Mastering the concept of reciprocals is fundamental for success in various mathematical fields and essential for solving problems across numerous disciplines. The ability to confidently find and utilize reciprocals strengthens mathematical skills and paves the way for tackling more complex mathematical challenges. From solving basic equations to comprehending advanced mathematical concepts, the reciprocal of 1/3, and reciprocals in general, are building blocks of a solid mathematical foundation. Understanding them unlocks a deeper appreciation of the interconnectedness of mathematical ideas and their practical relevance in our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Least Common Factor Of 4 And 9
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Multiples Of 30
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is 40 Percent Of 32
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Are In Potassium
Mar 26, 2025
-
When Gas Turns Into A Liquid
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Reciprocal Of 1 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
