What Is The Multiples Of 30
Juapaving
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
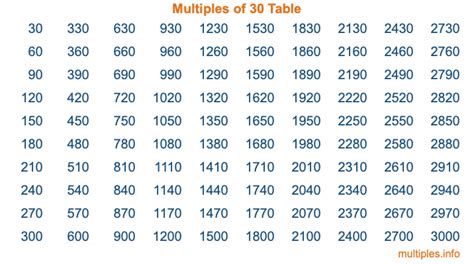
Table of Contents
What are the Multiples of 30? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Multiples, in the simplest terms, are the numbers you get when you multiply a specific number by other whole numbers. So, the multiples of 30 are the numbers you obtain when you multiply 30 by 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. Understanding multiples is fundamental to grasping various mathematical concepts, from basic arithmetic to more advanced areas like algebra and number theory. This comprehensive guide will explore the multiples of 30, delve into their properties, and showcase their applications in different contexts.
Understanding Multiples: A Foundational Concept
Before we dive into the specifics of the multiples of 30, let's solidify our understanding of the core concept of multiples. A multiple of a number is the product of that number and any whole number (0, 1, 2, 3, and so on). For instance:
- Multiples of 5: 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35… (5 multiplied by 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7…)
- Multiples of 12: 0, 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72… (12 multiplied by 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6…)
Notice that zero (0) is always a multiple of any number. This is because any number multiplied by zero equals zero.
Generating the Multiples of 30
Now, let's focus on the multiples of 30. To generate these, we simply multiply 30 by each whole number:
- 30 x 0 = 0
- 30 x 1 = 30
- 30 x 2 = 60
- 30 x 3 = 90
- 30 x 4 = 120
- 30 x 5 = 150
- 30 x 6 = 180
- 30 x 7 = 210
- 30 x 8 = 240
- 30 x 9 = 270
- 30 x 10 = 300
- and so on...
This sequence continues infinitely. There's no largest multiple of 30. We can continue this process indefinitely, generating an endless stream of multiples.
Properties of Multiples of 30
The multiples of 30 possess several interesting properties stemming from the fact that 30 itself is a composite number (a number with more than two factors). Let's explore some of these:
Divisibility Rules:
- Divisible by 2: All multiples of 30 are even numbers and therefore divisible by 2. This is because 30 itself is divisible by 2.
- Divisible by 3: All multiples of 30 are divisible by 3. This is because 30 is divisible by 3 (30 = 3 x 10).
- Divisible by 5: All multiples of 30 are divisible by 5. This is because 30 is divisible by 5 (30 = 5 x 6).
- Divisible by 6: All multiples of 30 are divisible by 6. This follows from the divisibility rules of 2 and 3 (30 = 6 x 5).
- Divisible by 10: All multiples of 30 are divisible by 10. This is due to 30 being a multiple of 10 (30 = 10 x 3).
- Divisible by 15: All multiples of 30 are divisible by 15 (30 = 15 x 2).
- Divisible by 30: Naturally, all multiples of 30 are divisible by 30.
This inherent divisibility by multiple numbers makes the multiples of 30 useful in various mathematical problems and real-world applications.
Patterns and Sequences:
The sequence of multiples of 30 forms an arithmetic progression with a common difference of 30. This means that the difference between any consecutive multiples is always 30. This predictable pattern makes it easy to identify and predict multiples within the sequence.
Applications of Multiples of 30
Understanding multiples, specifically those of 30, has practical applications in various fields:
Time Measurement:
- Minutes in Half an Hour: 30 minutes is a common unit of time measurement, and understanding multiples of 30 helps in calculating durations involving half-hour increments.
- Degrees in a Clock: The minute hand on a clock travels 30 degrees in every minute. Therefore, multiples of 30 are crucial in understanding the minute hand's position at different times.
Geometry and Measurement:
- Angles: Multiples of 30 degrees are frequently encountered in geometry when dealing with angles in various shapes (e.g., equilateral triangles, regular hexagons).
- Calculations involving measurements: In fields like construction or engineering where measurements are made in units of 30 (e.g., 30 centimeters, 30 inches), understanding multiples of 30 simplifies calculations.
Everyday Life:
- Counting Objects: When counting objects arranged in groups of 30, multiples of 30 help in quickly determining the total number of objects.
- Financial Calculations: In scenarios involving payments or transactions in multiples of 30 (e.g., monthly rent of $300, a product costing $30), the understanding of multiples of 30 facilitates calculations.
Beyond Basic Multiples: Exploring Factors and Prime Factorization
Understanding the factors of 30 helps further illuminate its multiples. Factors are the numbers that divide evenly into a given number without leaving a remainder. The factors of 30 are: 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15, and 30.
Prime factorization breaks down a number into its prime factors (numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves). The prime factorization of 30 is 2 x 3 x 5. This prime factorization reveals the fundamental building blocks of 30, which in turn influences the properties of its multiples.
Advanced Applications: Modular Arithmetic and Congruences
In modular arithmetic, multiples of 30 play a significant role. Modular arithmetic deals with remainders after division. For example, consider the modulo operation (mod). When we take a number modulo 30, we find the remainder when that number is divided by 30.
All multiples of 30 are congruent to 0 (mod 30). This property is crucial in various areas like cryptography and computer science where modular arithmetic is extensively used. Understanding congruence relations simplifies computations involving large numbers and helps in efficiently solving problems within specific modular systems.
Conclusion: The Significance of Multiples of 30
From simple counting to complex mathematical operations, understanding multiples of 30 proves invaluable. Its inherent divisibility, its predictable pattern in arithmetic progressions, and its applications in time measurement, geometry, and even modular arithmetic highlight its significance. This comprehensive exploration of the multiples of 30 not only clarifies the fundamental concept of multiples but also demonstrates its broader applications across diverse mathematical and real-world contexts. The seemingly simple concept of multiples holds a key position in unlocking a deeper appreciation for the intricacies and elegance of number theory.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
One Million Two Hundred Thousand In Numbers
Mar 27, 2025
-
Discuss The Effects Of Deforestation On The Following Wild Animals
Mar 27, 2025
-
Is A Parabola A One To One Function
Mar 27, 2025
-
Which Pair Of Triangles Is Congruent
Mar 27, 2025
-
Difference Between Distance And Displacement For Class 9
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Multiples Of 30 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
