What Is The Name Of Mg No3 2
Juapaving
Mar 28, 2025 · 5 min read
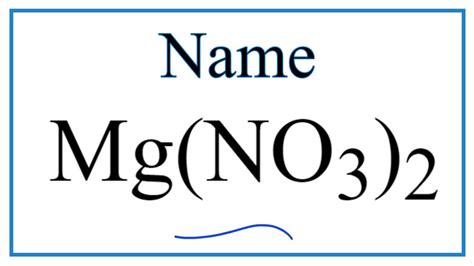
Table of Contents
What is the Name of Mg(NO₃)₂? A Deep Dive into Magnesium Nitrate
Magnesium nitrate, with the chemical formula Mg(NO₃)₂, is a fascinating inorganic compound with a wide array of applications. This article will delve into the details of this compound, exploring its properties, uses, safety considerations, and its importance in various fields. We’ll go beyond simply stating its name to provide a comprehensive understanding of magnesium nitrate.
Understanding the Chemical Formula: Mg(NO₃)₂
The chemical formula Mg(NO₃)₂ tells us the composition of the compound. Let's break it down:
-
Mg: This represents the magnesium ion (Mg²⁺), a divalent cation, meaning it carries a +2 charge. Magnesium is an alkaline earth metal, known for its reactivity and presence in numerous biological processes.
-
(NO₃): This represents the nitrate ion (NO₃⁻), a polyatomic anion with a -1 charge. Nitrate is a crucial component of fertilizers and plays a role in various chemical reactions.
-
₂: The subscript '2' indicates that there are two nitrate ions for every one magnesium ion to balance the charges, resulting in a neutral compound.
Therefore, magnesium nitrate is an ionic compound formed by the electrostatic attraction between the positively charged magnesium ion and the negatively charged nitrate ions.
Properties of Magnesium Nitrate
Magnesium nitrate exhibits several key physical and chemical properties:
Physical Properties:
- Appearance: It typically exists as a colorless crystalline solid or white powder.
- Solubility: It's highly soluble in water, readily dissolving to form a clear solution. This high solubility is crucial for many of its applications.
- Melting Point: It melts at a relatively high temperature, demonstrating strong ionic bonding.
- Density: It possesses a specific density, contributing to its unique behavior in various solutions and mixtures.
- Hygroscopic Nature: Magnesium nitrate is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the air. This property makes it important to store it in airtight containers to prevent clumping and degradation.
Chemical Properties:
- Thermal Decomposition: Upon heating, magnesium nitrate undergoes thermal decomposition, releasing nitrogen dioxide (NO₂), oxygen (O₂), and leaving behind magnesium oxide (MgO). This decomposition reaction is exothermic, releasing heat.
- Reactivity with Acids and Bases: Magnesium nitrate reacts with acids and bases, undergoing typical salt reactions. The nitrate ion is relatively inert in many reactions, but the magnesium ion can participate in various chemical processes.
- Oxidation States: Magnesium exists in a +2 oxidation state, and nitrogen in the nitrate ion has a +5 oxidation state. These oxidation states are stable and contribute to the overall stability of the compound.
Common Names and Synonyms
While the systematic name is magnesium nitrate, it might also be referred to by other names or synonyms, although these are less frequently used in scientific contexts. These might include:
- Magnesium dinitrate: This name emphasizes the presence of two nitrate ions.
- Magnesia nitrate: A slightly older or less formal variation of the name.
However, magnesium nitrate remains the most commonly accepted and preferred name due to its clarity and accordance with IUPAC nomenclature.
Applications of Magnesium Nitrate
Magnesium nitrate’s versatility leads to its use in a wide variety of applications across multiple industries:
1. Fertilizers:
Magnesium is an essential plant nutrient, playing a vital role in photosynthesis and enzyme activation. Magnesium nitrate serves as a valuable source of both magnesium and nitrogen, two key macronutrients for plant growth. Its high solubility makes it easily absorbed by plants through the soil. This is particularly useful in hydroponic systems where nutrient delivery is critical.
2. Pyrotechnics:
Magnesium nitrate is used as an oxidizer in pyrotechnic compositions. Its ability to release oxygen during thermal decomposition contributes to the burning process, enhancing the brilliance and intensity of firework displays. The choice of magnesium nitrate over other oxidizers often depends on specific color effects and desired combustion characteristics.
3. Chemical Synthesis:
In various chemical syntheses, magnesium nitrate acts as a source of magnesium ions or as a catalyst in specific reactions. Its solubility and reactivity profile make it suitable for a range of applications within industrial chemistry.
4. Concrete Admixtures:
In the construction industry, magnesium nitrate can be used as an admixture in concrete. It can influence the setting time and other properties of concrete, potentially enhancing its strength and durability under certain conditions. However, the use in this application needs careful consideration and specific formulations.
5. Food Processing:
Magnesium nitrate has some limited applications in food processing as a nutrient supplement or processing aid. However, its use needs stringent adherence to food safety regulations and guidelines. Its role is typically minor and focused on specific types of food products.
Safety Precautions and Handling
While magnesium nitrate is generally considered relatively safe, certain precautions should be taken during its handling and storage:
- Eye and Skin Protection: Direct contact with magnesium nitrate can cause irritation to the eyes and skin. Appropriate safety glasses and gloves should be worn when handling the compound.
- Inhalation Hazards: Inhalation of magnesium nitrate dust or fumes can be irritating to the respiratory system. Well-ventilated areas are necessary when working with this compound.
- Storage: As mentioned earlier, magnesium nitrate is hygroscopic, so it should be stored in airtight containers in a cool, dry place to prevent moisture absorption and clumping.
- Disposal: Proper disposal methods must be followed, adhering to local environmental regulations. Avoid dumping magnesium nitrate into drains or waterways.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of magnesium nitrate is relatively low compared to some other chemical compounds. However, excessive use of magnesium nitrate fertilizers can contribute to nutrient runoff into water bodies, potentially causing eutrophication and harming aquatic ecosystems. Sustainable agricultural practices and responsible use are crucial to minimize any potential negative environmental effects.
Conclusion: More than Just a Name
Mg(NO₃)₂, or magnesium nitrate, is much more than just a chemical formula. It is a versatile inorganic compound with diverse and valuable applications across various sectors, from agriculture and pyrotechnics to chemical synthesis and concrete production. While its properties and applications are extensive, careful handling and responsible usage are essential to mitigate any potential safety or environmental concerns. Understanding the nature of this compound, its properties, and its uses is key to leveraging its benefits responsibly and sustainably. The seemingly simple name, magnesium nitrate, belies a complex and multifaceted chemical with significant contributions to various aspects of modern society. Future research will likely continue to uncover additional applications and explore the compound's potential further.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Prime Factors Of 24
Mar 31, 2025
-
Notes On Newtons Laws Of Motion
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Many Bonds Does Sulfur Have
Mar 31, 2025
-
Prime Numbers Between 80 And 90
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Is The Prime Factorization Of 420
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Name Of Mg No3 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
