What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 6 And 5
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 4 min read
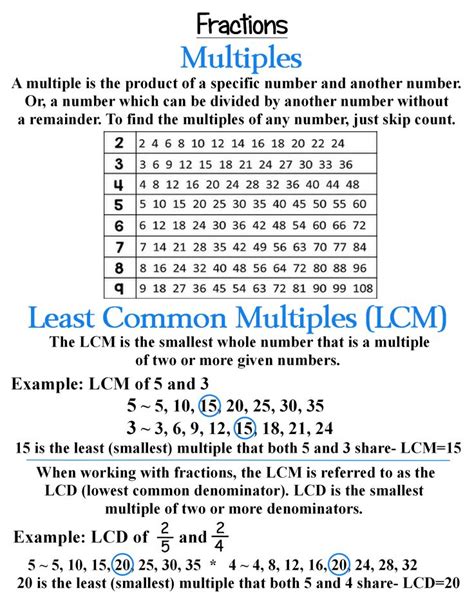
Table of Contents
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 6 and 5? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying principles reveals a fascinating glimpse into number theory and its applications. This article delves deep into the concept of LCM, focusing specifically on the LCM of 6 and 5, and exploring various methods to calculate it, along with real-world examples where this seemingly basic concept finds practical use.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the integers as its factors. Think of it as the smallest common "measuring stick" that can precisely measure lengths representing both numbers.
For example, let's consider the numbers 2 and 3. Multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12... Multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15... The smallest number that appears in both lists is 6. Therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Calculating the LCM of 6 and 5: Methods and Approaches
Now, let's focus on the LCM of 6 and 5. We can use several methods to determine this:
1. Listing Multiples Method
The simplest method, particularly for smaller numbers, is to list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36...
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35...
The smallest number that appears in both lists is 30. Therefore, the LCM of 6 and 5 is 30.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor present.
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 × 3
- Prime factorization of 5: 5 (5 is a prime number)
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization: 2, 3, and 5. Multiplying these together gives us 2 × 3 × 5 = 30.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) of two numbers are related through the following formula:
LCM(a, b) × GCD(a, b) = a × b
First, we find the GCD of 6 and 5. The GCD is the largest number that divides both 6 and 5 without leaving a remainder. In this case, the GCD of 6 and 5 is 1 (as they are coprime, meaning they share no common factors other than 1).
Now, using the formula:
LCM(6, 5) × GCD(6, 5) = 6 × 5
LCM(6, 5) × 1 = 30
LCM(6, 5) = **30**
This method is particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers where finding the prime factorization might be more time-consuming.
Why Understanding LCM is Important
The LCM isn't just an abstract mathematical concept; it has significant practical applications across various fields:
1. Scheduling and Synchronization
Imagine you have two machines that perform cycles at different intervals. One completes a cycle every 6 minutes, and the other every 5 minutes. To determine when both machines will simultaneously complete a cycle, you need to find the LCM of 6 and 5. The answer, 30 minutes, indicates the time it takes for both machines to be synchronized.
2. Fraction Operations
When adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators, finding the LCM of the denominators is crucial. The LCM becomes the least common denominator (LCD), allowing for the fractions to be expressed with a common denominator, simplifying the calculation.
For example, adding 1/6 + 1/5 requires finding the LCM of 6 and 5 (which is 30). Then we rewrite the fractions as 5/30 and 6/30, allowing for easy addition.
3. Real-World Scenarios
- Construction: Calculating material quantities or aligning structural elements.
- Music: Determining the rhythmic patterns and synchronization of multiple instruments.
- Manufacturing: Coordinating production cycles of different machines on an assembly line.
- Project Management: Scheduling tasks with interdependent timelines.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Further
The concept of LCM extends beyond just two numbers. You can find the LCM of three or more integers using similar methods; the prime factorization method becomes increasingly efficient as the number of integers increases.
Furthermore, the concept is closely linked to other number theoretical concepts like GCD, prime numbers, and modular arithmetic, enriching the mathematical landscape.
Conclusion: The Significance of 30
We've explored several methods to determine the LCM of 6 and 5, consistently arriving at the answer: 30. This seemingly simple calculation unveils the power of number theory and its practical relevance. Understanding LCM is not just about solving arithmetic problems; it’s about understanding fundamental mathematical principles that underpin many aspects of our world, from scheduling complex tasks to simplifying seemingly intractable calculations. Mastering the LCM opens doors to a deeper appreciation of the elegance and power of mathematics. Remember that the LCM of 6 and 5, 30, is not just a number; it's a foundational concept with widespread implications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Terminal Electron Acceptor In Aerobic Respiration Is
Mar 14, 2025
-
Whats The Difference Between Alternator And Generator
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Does Xlv Mean In Roman Numbers
Mar 14, 2025
-
Is Melting Ice Chemical Or Physical Change
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Are In Strontium
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 6 And 5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
