What's The Difference Between Alternator And Generator
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
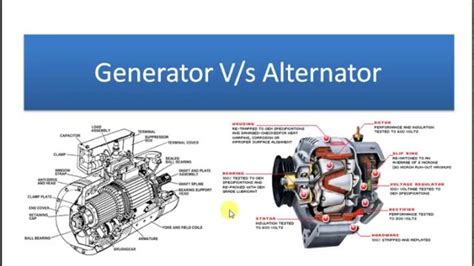
Table of Contents
What's the Difference Between an Alternator and a Generator?
While both alternators and generators produce electricity, they differ significantly in their design, operating principles, and applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone working with electrical systems, from automotive mechanics to power engineers. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the nuances of alternators and generators, helping you grasp the core distinctions and appreciate their unique roles in various contexts.
Fundamental Differences: AC vs. DC Output
The most significant difference lies in their output: alternators produce alternating current (AC), while generators typically produce direct current (DC), although some generators can produce AC. This seemingly simple distinction has profound implications for their internal mechanisms and applications.
Alternators: The AC Powerhouses
Alternators use the principle of electromagnetic induction to generate AC electricity. A rotating magnet (rotor) interacts with stationary coils of wire (stator), inducing a constantly changing voltage in the coils. This changing voltage is, by definition, alternating current, characterized by its sinusoidal waveform and its continuous reversal of polarity.
-
Construction: Alternators boast a robust and compact design. The rotor, typically incorporating permanent magnets or electromagnets, spins within the stator windings. This design facilitates higher rotational speeds and greater efficiency in generating electricity. The AC output is then often rectified using diodes to produce a DC output for specific applications like vehicle charging systems.
-
Applications: Alternators are prevalent in vehicles, powering everything from headlights and the radio to the engine control unit (ECU) and charging the battery. They're also found in smaller power generation systems, such as portable generators and some emergency power supplies. The ability to efficiently generate AC at high rotational speeds makes them ideal for these applications.
-
Advantages: High efficiency at higher speeds, compact design, relatively low maintenance.
-
Disadvantages: The AC output often needs rectification for DC applications, and the output voltage can fluctuate slightly depending on the load and speed.
Generators: The DC Pioneers and AC Adaptability
Generators, while often associated with DC output, are more diverse in their design and output capabilities. The traditional DC generator relies on a commutator, a rotating switch that converts the AC generated by the rotating armature into DC. This conversion process is less efficient than the direct AC production of an alternator.
-
Construction: DC generators often have a more complex construction than alternators, incorporating a rotating armature (with coils) and a commutator, which consists of segmented copper bars that periodically reverse the current flow, resulting in a pulsating DC output. AC generators, on the other hand, have a simpler construction similar to alternators, but without the rectifier.
-
Applications: DC generators were historically prominent in various applications, from early power generation systems to certain industrial processes that require DC power. Although largely replaced by alternators and rectified AC in many scenarios, some niche applications still utilize DC generators. AC generators are found in larger power plants, supplying electricity to homes and industries.
-
Advantages: (For DC generators): Historically provided a readily available DC source, crucial before widespread availability of rectification technology. (For AC Generators): Can provide high power output, suitable for large-scale power generation.
-
Disadvantages: (For DC generators): Lower efficiency compared to alternators, higher maintenance due to the commutator, more complex construction. (For AC Generators): Often larger and more complex than alternators for the same power output.
A Deeper Dive into Key Differences
Let's explore several more facets distinguishing these crucial power-generating devices:
1. Voltage Regulation:
-
Alternators: Employ voltage regulators to maintain a consistent output voltage despite varying engine speeds or loads. This ensures stable power supply to the vehicle's electrical systems.
-
Generators: Voltage regulation in generators can be more complex and may involve various methods depending on the type of generator and application. Some may use simple rheostats, while others use more sophisticated electronic controllers.
2. Efficiency:
-
Alternators: Generally more efficient than DC generators, especially at higher speeds. Their direct AC output eliminates the efficiency losses associated with converting AC to DC.
-
Generators: DC generators, with their commutators, inherently experience greater energy loss through friction and sparking. However, AC generators can be very efficient, particularly in large-scale power generation applications.
3. Maintenance:
-
Alternators: Require relatively less maintenance, typically involving occasional belt adjustments or replacement.
-
Generators: DC generators often require more frequent maintenance, primarily due to the commutator's wear and tear. Brush replacement and commutator cleaning are common tasks.
4. Size and Weight:
-
Alternators: Typically smaller and lighter than DC generators for a comparable power output.
-
Generators: AC generators can be significantly larger and heavier, especially those used for large-scale power generation. DC generators, although they can be compact in smaller sizes, can be bulkier compared to alternators with similar power ratings.
5. Cost:
-
Alternators: Generally less expensive to manufacture than DC generators.
-
Generators: Can range in cost widely depending on the size, output, and features. Large-scale AC generators used in power plants are significantly more expensive.
The Role of Rectification: Bridging the Gap
While alternators generate AC and generators typically generate DC, the line is blurred by the widespread use of rectification. Many modern automotive alternators include a rectifier to convert their AC output into DC to charge the vehicle's battery. Similarly, AC generators in power plants can be coupled with rectifiers to supply DC to specialized industrial applications. This demonstrates that the initial AC/DC distinction is not always absolute in practical applications.
Choosing the Right Device: Context Matters
The choice between an alternator and a generator depends heavily on the application. For automotive and small-scale power generation where high efficiency at high speeds is paramount, alternators are the clear choice. For larger-scale power generation supplying homes and industries, AC generators are the dominant technology. DC generators have largely been relegated to niche applications where specialized DC power is required.
Conclusion: Understanding the Nuances
The differences between alternators and generators extend beyond their output type. Factors like efficiency, maintenance requirements, size, cost, and voltage regulation all contribute to their distinct suitability for specific applications. By understanding these core differences and appreciating the role of rectification, you gain a deeper understanding of the fundamental principles underlying power generation and the technologies that power our world. This knowledge is invaluable whether you're working on your car's electrical system or pondering the complexities of the national power grid.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
10 Is A Multiple Of 5
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Edges Are There In A Rectangular Prism
Mar 14, 2025
-
Common Factors Of 32 And 40
Mar 14, 2025
-
Genes Had Been Absent On The Chromosomes
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is The Subunit For Lipids
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What's The Difference Between Alternator And Generator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
