What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 24 And 12
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
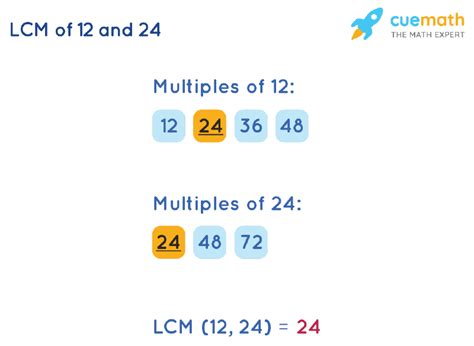
Table of Contents
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 24 and 12? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying principles reveals a fascinating connection to number theory and its applications in various fields. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question – what is the least common multiple of 24 and 12 – but will also explore the concept of LCM in depth, examining different methods for calculating it and demonstrating its relevance beyond basic mathematics.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the given integers. It's a fundamental concept in mathematics with far-reaching implications. Think of it as the smallest number that contains all the factors of the given numbers within its own factorization.
For example, consider the numbers 6 and 9. The multiples of 6 are 6, 12, 18, 24, 30… and the multiples of 9 are 9, 18, 27, 36… The smallest number that appears in both lists is 18. Therefore, the LCM of 6 and 9 is 18.
Calculating the LCM of 24 and 12
Now, let's address the core question: What is the least common multiple of 24 and 12? We'll explore several methods to determine this, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This is the most straightforward approach, especially for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of both 24 and 12 until we find the smallest common multiple.
Multiples of 24: 24, 48, 72, 96, 120, 144...
Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84, 96, 108, 120...
By observing the lists, we see that the smallest number appearing in both sequences is 24. Therefore, the LCM(24, 12) = 24.
This method is simple to understand but becomes less efficient as the numbers get larger. Imagine trying to find the LCM of 144 and 252 using this method!
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of the underlying mathematical principles. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM from these prime factors.
- Prime Factorization of 24: 24 = 2³ x 3¹
- Prime Factorization of 12: 12 = 2² x 3¹
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
- Highest power of 2: 2³ = 8
- Highest power of 3: 3¹ = 3
Multiply these highest powers together: 8 x 3 = 24. Therefore, LCM(24, 12) = 24.
This method is significantly more efficient for larger numbers and provides a more structured approach.
Method 3: Using the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The LCM and GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) are closely related. There's a formula connecting them:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
First, we find the GCD of 24 and 12. Using the Euclidean algorithm or prime factorization, we find that GCD(24, 12) = 12.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(24, 12) = (24 x 12) / GCD(24, 12) = (24 x 12) / 12 = 24
This method is also efficient, especially when dealing with larger numbers where finding the GCD is relatively easier than directly finding the LCM.
The Significance of LCM in Real-World Applications
While the calculation of LCM might seem purely academic, its applications extend to numerous practical scenarios:
1. Scheduling and Timing
Imagine you have two machines that perform a specific task. Machine A completes the task every 24 hours, while machine B completes it every 12 hours. To determine when both machines will complete the task simultaneously again, you need to find the LCM of 24 and 12, which is 24. Both machines will finish the task together after 24 hours.
This concept is crucial in scheduling events, coordinating transportation, and managing production lines where processes need to be synchronized.
2. Fraction Arithmetic
When adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators, you need to find a common denominator – and the least common denominator is usually the LCM of the original denominators. This ensures the simplest possible calculation.
For example, to add 1/12 and 1/24, you would find the LCM of 12 and 24 (which is 24) and then rewrite the fractions with this common denominator before adding them.
3. Music Theory
LCM plays a significant role in music theory, particularly in understanding rhythmic patterns and harmonic relationships. The LCM helps determine when different rhythmic patterns will align, creating specific musical effects.
4. Engineering and Design
In engineering and construction, the LCM is crucial in calculating the optimal timing of various processes or the synchronization of different systems within a larger project.
5. Computer Science
LCM is utilized in algorithms and data structures, particularly those dealing with cyclic processes or synchronization problems.
Beyond Two Numbers: LCM for Multiple Integers
The concept of LCM can be extended to more than two numbers. The process remains similar, whether using prime factorization or other methods. For example, to find the LCM of 12, 18, and 24:
-
Prime Factorization:
- 12 = 2² x 3¹
- 18 = 2¹ x 3²
- 24 = 2³ x 3¹
-
Identify Highest Powers:
- Highest power of 2: 2³ = 8
- Highest power of 3: 3² = 9
-
Calculate LCM: 8 x 9 = 72. Therefore, LCM(12, 18, 24) = 72
Conclusion: The LCM's Enduring Relevance
The seemingly simple question of finding the least common multiple of 24 and 12 opens a window into the world of number theory and its broad applicability. From scheduling tasks to simplifying fraction arithmetic, the LCM is a fundamental concept with far-reaching implications in diverse fields. Mastering the different methods for calculating the LCM, including prime factorization and the relationship with the GCD, provides valuable mathematical tools applicable beyond the classroom. The understanding of LCM provides a solid foundation for tackling more complex mathematical problems and enhances problem-solving skills in various practical scenarios. Understanding the significance of LCM goes beyond mere calculation; it unveils a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts and their real-world relevance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Factor Of 73
Mar 17, 2025
-
Protein Polymers Are Made Up Of
Mar 17, 2025
-
Difference Between A Mixture And A Solution
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Type Of Rock Can Contain Fossils
Mar 17, 2025
-
Write The Chemical Formula For Chloric Acid
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 24 And 12 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
