What Is The Factor Of 73
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
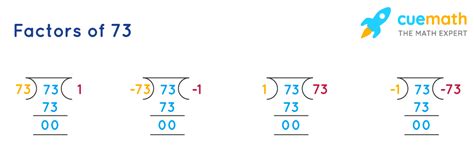
Table of Contents
What is the Factor of 73? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The question, "What is the factor of 73?" might seem simple at first glance. However, exploring this seemingly straightforward query opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, prime numbers, and the fundamentals of factorization. This comprehensive article will delve into the concept of factors, explore the unique properties of the number 73, and discuss its significance within the broader context of mathematics.
Understanding Factors: The Building Blocks of Numbers
Before we tackle the specific factors of 73, let's establish a solid understanding of what a factor actually is. In mathematics, a factor (or divisor) of a number is an integer that divides that number without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's a number that can be multiplied by another integer to produce the original number.
For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because:
- 1 x 12 = 12
- 2 x 6 = 12
- 3 x 4 = 12
Finding all the factors of a number is a crucial step in various mathematical operations, including simplifying fractions, solving equations, and understanding number properties.
The Distinctive Nature of Prime Numbers
Prime numbers play a pivotal role in factorization. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. This means it cannot be expressed as the product of two smaller natural numbers. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. Prime numbers are the fundamental building blocks of all other integers, forming the basis of many important mathematical concepts.
Determining the Factors of 73: A Prime Example
Now, let's return to our original question: What are the factors of 73? Through systematic checking, or by applying knowledge of prime numbers, we quickly discover a key characteristic of 73: it's a prime number.
This means that 73 is only divisible by 1 and itself. Therefore, the only factors of 73 are 1 and 73. This simple answer highlights the fundamental role of prime numbers in number theory.
Why is 73 a Prime Number?
To definitively establish 73 as a prime number, we could perform a primality test. However, a simpler approach involves checking for divisibility by prime numbers less than the square root of 73 (approximately 8.54). Since 73 is not divisible by 2, 3, 5, or 7, we can confidently conclude that it's a prime number.
This process of checking for divisibility by smaller primes is an efficient way to determine the primality of relatively small numbers. For larger numbers, more sophisticated algorithms are employed.
The Significance of Prime Numbers: Beyond Factorization
The significance of prime numbers extends far beyond simply finding factors. They are crucial in various areas of mathematics and computer science, including:
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers form the backbone of many modern encryption algorithms, securing online transactions and sensitive data. The difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components is the foundation of RSA encryption, a widely used cryptographic system.
-
Number Theory: Prime numbers are central to many fundamental theorems and conjectures in number theory, such as the Prime Number Theorem, which describes the distribution of primes.
-
Abstract Algebra: Prime numbers have profound implications in abstract algebra, particularly in the study of rings and fields.
-
Computer Science: Prime numbers are used in hash table algorithms, which efficiently store and retrieve data. They also play a role in generating pseudo-random numbers.
Exploring Factorization Techniques
While the factorization of 73 is straightforward, understanding different factorization techniques is essential for tackling larger numbers. Several methods are used:
-
Trial Division: This involves systematically testing divisibility by each integer, starting from 2. It's simple for smaller numbers but becomes computationally expensive for larger ones.
-
Sieve of Eratosthenes: This algorithm efficiently identifies all prime numbers up to a specified limit. It's useful for generating a list of primes to check for divisibility when factoring larger numbers.
-
Pollard's Rho Algorithm: This probabilistic algorithm is more efficient than trial division for factoring larger composite numbers. It's used in cryptography to break encryption systems (although very large prime numbers are used to make this practically impossible).
-
General Number Field Sieve (GNFS): Currently, the most efficient algorithm known for factoring extremely large numbers, GNFS is used to factor numbers with hundreds of digits. Its complexity relies on sophisticated mathematical concepts and requires significant computational resources.
Applications of Factorization in Real-World Scenarios
The seemingly abstract concept of factorization has practical applications in numerous real-world scenarios:
-
Cryptography: As previously mentioned, the difficulty of factoring large numbers underpins the security of many cryptographic systems.
-
Coding Theory: Factorization is involved in designing error-correcting codes, crucial for reliable data transmission and storage.
-
Computer Graphics: Factorization plays a role in algorithms used for texture mapping and rendering in computer graphics.
-
Data Compression: Some data compression techniques utilize factorization to efficiently represent data.
-
Scheduling and Optimization: Factorization can be applied to various optimization problems, including task scheduling and resource allocation.
Conclusion: The Simplicity and Significance of 73's Factors
The seemingly simple question of finding the factors of 73 leads us to a deep appreciation for prime numbers and their importance in various fields. The fact that 73 is a prime number, with only 1 and itself as factors, highlights its fundamental role in mathematical structures and algorithms. Understanding factorization and prime numbers is not just an academic exercise; it's a key to unlocking insights into many fundamental aspects of mathematics and its widespread applications in the real world. From the security of online transactions to the design of error-correcting codes, the influence of prime numbers and their factorization is undeniable and pervasive. The seemingly straightforward "What is the factor of 73?" therefore opens a vast and fascinating landscape of mathematical exploration.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Highest Common Factor Of 24 And 36
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Goes Up And Down But Doesnt Move
Mar 17, 2025
-
Where Does Most Metabolic Activity In The Cell Occur
Mar 17, 2025
-
The Most Reactive Group Of The Nonmetals Is The
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Time Zones Is Earth Divided Into
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Factor Of 73 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
