What Is The Lcm Of 4 6 8
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 4 min read
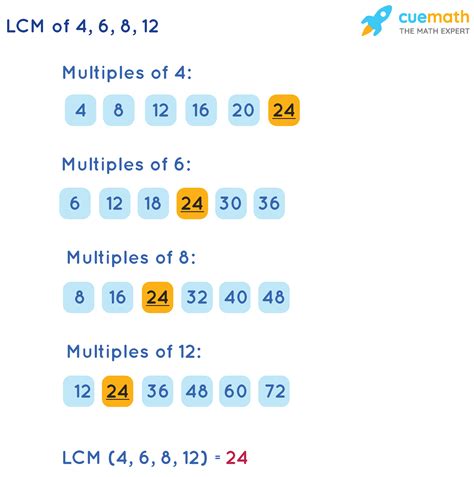
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 4, 6, and 8? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of a set of numbers is a fundamental concept in mathematics with wide-ranging applications in various fields, from scheduling problems to music theory. This article will explore the LCM of 4, 6, and 8, providing a comprehensive explanation of the process, different methods to solve it, and demonstrating its practical relevance.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before we delve into the specific calculation, let's solidify our understanding of LCM. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into evenly.
For example, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6 because 6 is the smallest positive integer divisible by both 2 and 3.
Methods for Finding the LCM of 4, 6, and 8
Several methods can be employed to calculate the LCM of 4, 6, and 8. We'll examine the most common and effective approaches:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This method involves listing the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40...
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48...
- Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48...
By comparing the lists, we can see that the smallest number appearing in all three lists is 24. Therefore, the LCM of 4, 6, and 8 is 24.
This method is straightforward for smaller numbers but can become cumbersome and time-consuming for larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This is a more efficient method, especially for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor.
- Prime factorization of 4: 2²
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
- Prime factorization of 8: 2³
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- The highest power of 2 is 2³ = 8
- The highest power of 3 is 3¹ = 3
Multiplying these highest powers together gives us the LCM: 8 x 3 = 24.
This method is generally preferred for its efficiency and systematic approach.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) of a set of numbers are related through the following formula:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
While this formula is generally applied to two numbers, it can be extended to multiple numbers by applying it iteratively. First, find the GCD of two numbers, then use the result to find the GCD with the next number, and so on. However, this method is less efficient than prime factorization for finding the LCM of three or more numbers.
Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM has numerous practical applications across various disciplines:
-
Scheduling: Imagine you have three events that repeat at intervals of 4, 6, and 8 days. The LCM (24) represents the number of days until all three events occur on the same day again. This is crucial for scheduling appointments, meetings, or even production cycles.
-
Fraction Operations: When adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators, finding the LCM of the denominators is essential for finding a common denominator, simplifying the calculation.
-
Music Theory: LCMs are used in music theory to determine the least common period for repeating musical patterns or rhythms.
-
Gear Ratios: In mechanical engineering, understanding LCMs is useful when designing gear systems to ensure smooth and efficient operation. The LCM helps to determine when gears will be in a synchronized position.
-
Project Management: In project scheduling, LCM can help in determining the next time multiple tasks will be completed simultaneously, which is important for project synchronization.
Further Exploration: LCM of Larger Numbers
The methods described above, particularly prime factorization, are easily scalable to larger numbers. Consider finding the LCM of 12, 18, and 24:
- Prime factorization of 12: 2² x 3
- Prime factorization of 18: 2 x 3²
- Prime factorization of 24: 2³ x 3
The highest power of 2 is 2³ = 8 The highest power of 3 is 3² = 9
Therefore, the LCM(12, 18, 24) = 8 x 9 = 72
Conclusion: The Power of Understanding LCM
Understanding the concept of LCM and mastering the various methods to calculate it is vital for anyone working with numbers. From solving simple mathematical problems to tackling complex real-world scenarios, the application of LCM is extensive. By mastering this concept, you enhance your problem-solving skills and open doors to a deeper appreciation of mathematical principles and their practical implications. The seemingly simple question of "What is the LCM of 4, 6, and 8?" opens up a pathway to a more profound understanding of mathematics and its utility in everyday life. Remember that consistent practice and employing the most efficient methods will help you become proficient in calculating LCMs of any size.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Joules Make One Kwh
Mar 25, 2025
-
The Only Movable Bone In The Skull
Mar 25, 2025
-
Specific Heat Of Aluminum J Kg K
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is The Reciprocal Of 1 3
Mar 25, 2025
-
Is Air A Mixture Or Pure Substance
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm Of 4 6 8 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
