What Is The Latitude Of The North Pole
Juapaving
Mar 28, 2025 · 5 min read
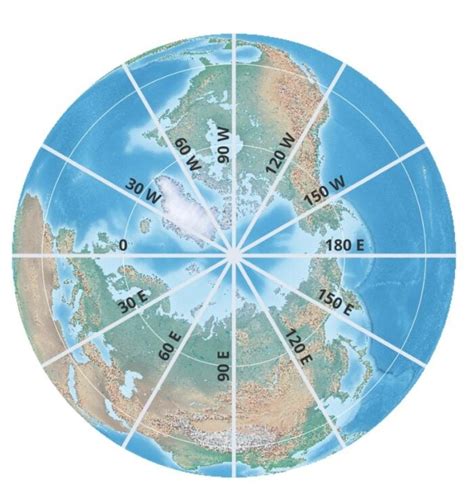
Table of Contents
What is the Latitude of the North Pole? A Comprehensive Exploration
The North Pole, a point of fascination and scientific inquiry for centuries, holds a unique geographical position. Its latitude, a key element defining its location on Earth, is a fundamental concept in geography and navigation. This article delves deep into the question: What is the latitude of the North Pole? and explores the broader implications of this seemingly simple answer.
Understanding Latitude and Longitude
Before we pinpoint the latitude of the North Pole, let's establish a foundational understanding of latitude and longitude. These are two coordinates used to specify the location of any point on the Earth's surface.
Latitude: Measuring North and South
Latitude measures a point's location north or south of the Equator. The Equator, an imaginary line circling the Earth midway between the North and South Poles, serves as the zero-degree line of latitude. Lines of latitude, also known as parallels, run parallel to the Equator. Latitude values range from 0° at the Equator to 90° North at the North Pole and 90° South at the South Pole.
Longitude: Measuring East and West
Longitude measures a point's location east or west of the Prime Meridian. The Prime Meridian, another imaginary line, runs from the North Pole to the South Pole through Greenwich, England. Lines of longitude, also called meridians, converge at the poles. Longitude values range from 0° at the Prime Meridian to 180° East and 180° West.
The Latitude of the North Pole: A Simple Answer
The latitude of the North Pole is 90° North. This is the highest possible latitude on Earth, representing the northernmost point on the globe. All lines of longitude converge at the North Pole, making it a singular point with no defined longitude.
The Significance of the North Pole's Latitude
The 90° North latitude of the North Pole is far more than just a number; it holds immense significance in several areas:
1. Navigation and Mapping:
The North Pole's precise latitude is crucial for navigation and mapping systems. Global Positioning Systems (GPS) rely on latitude and longitude to pinpoint locations worldwide. Knowing the North Pole's latitude is fundamental to understanding the global coordinate system.
2. Scientific Research:
The North Pole is a critical site for scientific research, particularly in fields like climatology, oceanography, and glaciology. Scientists study the Arctic ice cap, weather patterns, and the impact of climate change in this region. The 90° North latitude provides a precise location for conducting these studies and comparing data over time.
3. Geopolitics:
The North Pole's location and the surrounding Arctic region have significant geopolitical implications. Several countries border the Arctic Ocean, raising issues concerning territorial claims, resource extraction, and environmental protection. Understanding the exact location of the North Pole is vital in navigating these complex geopolitical issues.
4. Cultural and Historical Significance:
The North Pole holds a special place in human culture and imagination. It has been a legendary goal for explorers and adventurers for centuries, symbolizing extreme environments and challenges. The pursuit of reaching the North Pole has shaped human history and spurred technological advancements in navigation and exploration.
Exploring the Geographic Features at 90° North
While the latitude pinpoints the location, understanding the geographic reality of the North Pole is equally important. Unlike the South Pole, which sits atop a landmass (Antarctica), the North Pole is located in the middle of the Arctic Ocean, covered by a layer of constantly shifting sea ice.
The Shifting Ice Cap:
The sea ice at the North Pole is not a static feature. Its extent and thickness vary seasonally and annually, influenced by factors like temperature, wind patterns, and ocean currents. The ice floes constantly move, making the precise surface location of the North Pole constantly changing.
The Arctic Ocean:
Beneath the sea ice lies the Arctic Ocean, a relatively shallow ocean compared to other major oceans. The ocean floor at the North Pole has unique geological features and is a subject of ongoing scientific investigation.
Lack of Terrestrial Features:
Unlike many other locations on Earth identified by their latitude and longitude, the North Pole lacks distinct terrestrial features. There are no mountains, rivers, or prominent landforms. The lack of fixed points contributes to the challenges of studying and characterizing this region.
The North Pole in the Global Coordinate System
The North Pole's latitude (90°N) is the anchor point of the global coordinate system. All lines of latitude run parallel to the Equator, with the North Pole being the northernmost point on these parallels. The convergence of all lines of longitude at the North Pole further emphasizes its unique position in the global coordinate system.
Technological Advancements and the North Pole's Latitude
Modern technology, including GPS and satellite imagery, has significantly enhanced our ability to accurately determine and monitor the North Pole's latitude and the surrounding region. This allows for precise tracking of ice movement, weather patterns, and other environmental changes.
The North Pole and Climate Change
The North Pole is a region particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change. Rising global temperatures are leading to a significant decline in Arctic sea ice extent and thickness. This has far-reaching consequences for global weather patterns, marine ecosystems, and the stability of the Earth's climate system. Understanding the North Pole's latitude is crucial in tracking and predicting these climate change effects.
Challenges and Future Research
Despite advancements in technology and research, several challenges remain in fully understanding the North Pole. The dynamic nature of the sea ice, harsh environmental conditions, and logistical difficulties continue to pose obstacles to scientific studies. Future research will likely focus on enhancing our understanding of the Arctic Ocean's ecosystem, the impact of climate change, and the complex interplay between the North Pole and global climate systems.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of 90° North
The latitude of the North Pole, 90° North, is not merely a geographical coordinate; it represents a crucial point on Earth with immense scientific, geopolitical, cultural, and historical significance. From navigation and mapping to scientific research and climate change studies, the understanding of this latitude plays a vital role in our comprehension of the planet and its future. As technology continues to advance and research progresses, our knowledge of this unique point on Earth will undoubtedly deepen, further highlighting the enduring importance of 90° North.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Are In A Star
Mar 31, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Ecosystem
Mar 31, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 20 And 50
Mar 31, 2025
-
List The Factors Of 100 That Are Prime
Mar 31, 2025
-
Do The Diagonals Of A Kite Bisect Teachother
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Latitude Of The North Pole . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
