What Is The Formula For Magnesium Carbonate
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
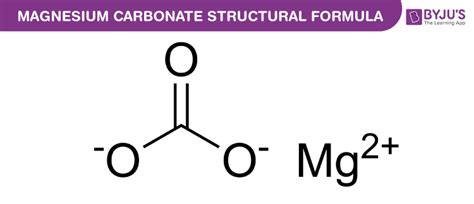
Table of Contents
What is the Formula for Magnesium Carbonate? Exploring its Properties, Uses, and Production
Magnesium carbonate, a naturally occurring mineral compound, finds widespread applications across various industries. Understanding its chemical formula, properties, and production methods is crucial for appreciating its versatility and significance. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of magnesium carbonate, providing a detailed explanation of its formula, properties, uses, and production process.
Understanding the Chemical Formula: MgCO₃
The chemical formula for magnesium carbonate is MgCO₃. This simple yet powerful formula tells us that one molecule of magnesium carbonate consists of:
- One magnesium ion (Mg²⁺): Magnesium, an alkaline earth metal, readily loses two electrons to form a positively charged ion.
- One carbonate ion (CO₃²⁻): The carbonate ion is a polyatomic anion composed of one carbon atom and three oxygen atoms, carrying a negative charge of 2.
The neutral overall charge of the molecule (0) is achieved through the electrostatic attraction between the 2+ charge of the magnesium ion and the 2- charge of the carbonate ion. This ionic bonding is fundamental to the structure and properties of magnesium carbonate.
Different Forms of Magnesium Carbonate: Hydrates and Polymorphs
While MgCO₃ represents the basic chemical formula, magnesium carbonate exists in several different forms due to variations in hydration and crystal structure:
1. Hydrates:
Magnesium carbonate can exist as hydrates, meaning water molecules are incorporated into its crystal structure. The most common hydrate is magnesium carbonate trihydrate (MgCO₃·3H₂O), also known as lansfordite. Other hydrates exist, but trihydrate is the most prevalent naturally and commercially. The presence of water molecules can significantly influence the properties of the compound, such as solubility and reactivity.
2. Polymorphs:
Polymorphs are different crystalline forms of the same chemical compound. Magnesium carbonate exhibits polymorphism, with the most common polymorphs being:
- Magnesite: This is the naturally occurring crystalline form of magnesium carbonate, possessing a trigonal crystal system. It's typically found in sedimentary rocks and is a significant source of magnesium.
- Hydromagnesite: A naturally occurring hydrated magnesium carbonate with the formula Mg₅(CO₃)₄(OH)₂·4H₂O. It exhibits a different crystal structure compared to magnesite.
Understanding the different forms of magnesium carbonate is important because their properties, such as solubility and reactivity, can vary. This necessitates careful consideration when selecting the appropriate form for specific applications.
Key Physical and Chemical Properties of Magnesium Carbonate
Magnesium carbonate possesses several key properties that determine its suitability for various applications:
- Appearance: Typically white, although impurities can lead to variations in color. It can exist as a powder, crystals, or dense masses.
- Solubility: Relatively insoluble in water, although its solubility increases slightly in acidic solutions. This low solubility contributes to its use as a filler and anticaking agent.
- Density: Around 2.16 g/cm³, depending on the form and level of hydration.
- Melting Point: Decomposes before melting, typically around 350°C (662°F), releasing carbon dioxide. This thermal decomposition is a significant aspect of its use in various processes.
- Reactivity: Reacts with acids to produce magnesium salts, water, and carbon dioxide. This reaction is utilized in applications involving acid neutralization.
- Stability: Relatively stable under normal conditions, although prolonged exposure to high humidity can affect its hydration state.
Diverse Applications of Magnesium Carbonate
The unique properties of magnesium carbonate lead to a wide range of applications across various sectors:
1. Pharmaceutical Industry:
- Antacid: Its ability to neutralize stomach acid makes it a common component in antacid medications, providing relief from heartburn and indigestion. The low solubility ensures minimal systemic absorption.
- Tablet Binder and Disintegrant: Magnesium carbonate serves as a binder in tablet manufacturing, helping to hold the ingredients together. It can also function as a disintegrant, aiding in the breakdown and absorption of the tablet.
- Filler and Diluent: Used to increase the bulk of tablets and capsules, allowing for easier handling and administration.
2. Food Industry:
- Food Additive: Used as an anticaking agent in powdered foods, preventing clumping and improving flowability. It also acts as a drying agent in some food products.
- Nutrient Supplementation: Magnesium is an essential mineral, and magnesium carbonate can serve as a source of magnesium in dietary supplements.
- Color Retention: In some food applications, it can help to maintain the color of the product.
3. Industrial Applications:
- Fire Retardant: Its thermal decomposition releases carbon dioxide, a fire-extinguishing agent. This property makes it valuable in fire-retardant materials and compositions.
- Rubber and Plastics Industry: Acts as a filler and reinforcing agent in rubber and plastic products, improving their properties.
- Cosmetics and Personal Care: Used in various cosmetic products, including talc and powders, acting as a filler and providing a smooth texture.
- Agriculture: Can be used as a soil amendment to improve soil pH and provide magnesium to plants.
- Environmental Remediation: Used in certain environmental remediation processes to neutralize acidic soils or wastewater.
Production Methods for Magnesium Carbonate
Magnesium carbonate is produced through various methods, primarily focusing on either extraction from natural sources or chemical synthesis:
1. Extraction from Magnesite Ore:
This is the most common method of obtaining magnesium carbonate. The process involves:
- Mining: Magnesite ore is mined from deposits.
- Crushing and Grinding: The ore is crushed and ground to a suitable size.
- Purification: Impurities are removed through various processes like washing and flotation.
- Calcination (optional): Heating the magnesite ore to high temperatures to remove carbon dioxide and produce magnesium oxide (MgO). The magnesium oxide can then be reacted with carbon dioxide to produce magnesium carbonate.
- Processing: The purified magnesium carbonate is then processed to meet specific quality requirements.
2. Chemical Synthesis:
Magnesium carbonate can also be synthesized chemically through the reaction of magnesium salts with sodium carbonate:
MgCl₂ + Na₂CO₃ → MgCO₃ + 2NaCl
This method provides a high degree of purity and control over the properties of the final product.
Safety Considerations and Handling
While generally considered safe, certain precautions should be taken when handling magnesium carbonate:
- Inhalation: Inhaling fine magnesium carbonate dust can cause respiratory irritation. Appropriate respiratory protection should be used in dusty environments.
- Skin and Eye Contact: Avoid direct contact with skin and eyes. Wash thoroughly with water if contact occurs.
- Ingestion: Ingesting large quantities can cause digestive upset. Follow proper handling and storage procedures to avoid accidental ingestion.
Conclusion: A Versatile Compound with Wide-Ranging Uses
Magnesium carbonate, with its simple chemical formula MgCO₃, is a versatile compound with significant applications across numerous industries. Its properties, including its low solubility, thermal decomposition, and reactivity with acids, make it a valuable material in pharmaceuticals, food processing, industrial manufacturing, and environmental applications. Understanding its various forms, production methods, and safety aspects is crucial for its effective and safe utilization. Further research and development continue to explore new and innovative applications of this important mineral compound.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Function Of The Motor End Plate
Mar 17, 2025
-
A Push Or A Pull Is Called
Mar 17, 2025
-
The Tendency Of An Atom To Attract Electrons
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Are The Most Reactive Elements On The Periodic Table
Mar 17, 2025
-
Colorless Gas With A Pungent Odor
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Formula For Magnesium Carbonate . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
