What Is The Factor Of 96
Juapaving
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
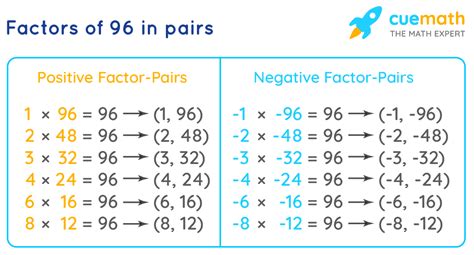
Table of Contents
What are the Factors of 96? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the factors of a number might seem like a simple arithmetic exercise, but it opens the door to a fascinating world of number theory and its applications in various fields. This article explores the factors of 96 in detail, explaining the process of finding them, different methods to approach the problem, and the broader mathematical concepts involved. We'll also touch upon the practical uses of factorization in areas like cryptography and computer science.
Understanding Factors
Before diving into the specifics of 96, let's define what a factor is. A factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides the number exactly without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's a number that can be multiplied by another whole number to get the original number.
For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because:
- 1 x 12 = 12
- 2 x 6 = 12
- 3 x 4 = 12
Finding the Factors of 96: A Systematic Approach
There are several ways to find the factors of 96. Let's explore a few, starting with the most straightforward method:
Method 1: The Pairwise Approach
This method involves systematically checking each whole number to see if it divides 96 without a remainder. We start with 1 and continue until we reach the number itself (96).
- 1: 96 ÷ 1 = 96 (1 and 96 are factors)
- 2: 96 ÷ 2 = 48 (2 and 48 are factors)
- 3: 96 ÷ 3 = 32 (3 and 32 are factors)
- 4: 96 ÷ 4 = 24 (4 and 24 are factors)
- 6: 96 ÷ 6 = 16 (6 and 16 are factors)
- 8: 96 ÷ 8 = 12 (8 and 12 are factors)
- 12: 96 ÷ 12 = 8 (We've already found 8 and 12)
Notice that after we reach 12, we start repeating factor pairs. This is because factors often come in pairs. Once we reach a factor whose pair is a factor we've already identified, we can stop.
Therefore, the factors of 96 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 24, 32, 48, and 96.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
Prime factorization is a more efficient method, especially for larger numbers. It involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...).
To find the prime factorization of 96:
- Start with the smallest prime number, 2: 96 ÷ 2 = 48
- Continue dividing by 2: 48 ÷ 2 = 24; 24 ÷ 2 = 12; 12 ÷ 2 = 6; 6 ÷ 2 = 3
- Now we have a prime number (3): The prime factorization of 96 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 3, or 2<sup>5</sup> x 3.
Once you have the prime factorization, you can find all the factors by systematically combining the prime factors. For example:
- 2<sup>1</sup> = 2
- 2<sup>2</sup> = 4
- 2<sup>3</sup> = 8
- 2<sup>4</sup> = 16
- 2<sup>5</sup> = 32
- 3<sup>1</sup> = 3
- 2<sup>1</sup> x 3 = 6
- 2<sup>2</sup> x 3 = 12
- 2<sup>3</sup> x 3 = 24
- 2<sup>4</sup> x 3 = 48
- 2<sup>5</sup> x 3 = 96
- And, of course, 1 is always a factor.
This method systematically generates all the factors of 96.
Types of Factors: Exploring Further
Understanding the factors of 96 leads us to explore different categories of factors:
Prime Factors
As we saw in the prime factorization, the prime factors of 96 are 2 and 3. These are the fundamental building blocks of the number.
Composite Factors
Composite factors are factors that are not prime numbers. All the factors of 96, except 2 and 3, are composite factors (e.g., 4, 6, 8, 12, etc.).
Proper Factors
Proper factors are all factors of a number excluding the number itself. Therefore, the proper factors of 96 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 24, 32, and 48.
Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
These concepts become relevant when working with multiple numbers. The greatest common factor (GCF) is the largest number that divides both numbers without a remainder. The least common multiple (LCM) is the smallest number that is a multiple of both numbers.
Let's say we want to find the GCF and LCM of 96 and another number, for instance, 72. We can use the prime factorization method:
- Prime factorization of 96: 2<sup>5</sup> x 3
- Prime factorization of 72: 2<sup>3</sup> x 3<sup>2</sup>
GCF: To find the GCF, we take the lowest power of each common prime factor: 2<sup>3</sup> x 3 = 24. The GCF of 96 and 72 is 24.
LCM: To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization: 2<sup>5</sup> x 3<sup>2</sup> = 288. The LCM of 96 and 72 is 288.
Applications of Factorization
The seemingly simple act of finding factors has significant applications in various fields:
Cryptography
Factorization plays a crucial role in modern cryptography. Many encryption algorithms rely on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime factors. The security of these systems depends on the computational infeasibility of factoring these enormous numbers, even with powerful computers.
Computer Science
In computer science, factorization is used in algorithms for tasks such as optimizing code and data structures. Understanding the factors of numbers can improve efficiency and reduce processing time.
Number Theory and Mathematics
Factorization is a fundamental concept in number theory, forming the basis for many other advanced mathematical ideas and theorems. It helps us understand the structure and properties of numbers.
Conclusion: Beyond the Basics of Factoring 96
Finding the factors of 96, while seemingly elementary, provides a gateway to understanding core concepts in number theory and their practical applications in diverse fields. From the simple pairwise approach to the more sophisticated prime factorization method, understanding the various ways to find factors helps build a strong foundation in mathematics and its relevance in the modern world. The concept extends beyond simply identifying divisors; it unlocks doors to more complex mathematical explorations and technological advancements. The seemingly simple task of factoring a number like 96 highlights the profound interconnectedness of mathematical principles and their widespread influence.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Do Plants Store Glucose As
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Equation Of A Horizontal Line
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 6 10 And 15
Mar 28, 2025
-
1500 Minutes Is How Many Hours
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Side Does A Hexagon Have
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Factor Of 96 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
