How Many Side Does A Hexagon Have
Juapaving
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
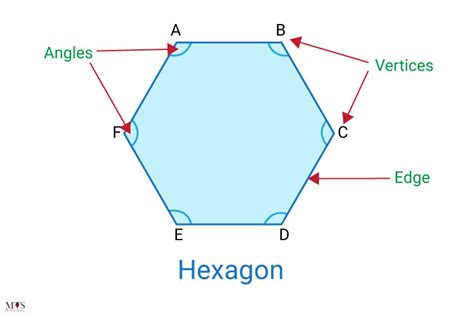
Table of Contents
- How Many Side Does A Hexagon Have
- Table of Contents
- How Many Sides Does a Hexagon Have? A Deep Dive into Hexagonal Geometry
- Understanding the Hexagon: A Six-Sided Polygon
- Types of Hexagons: Regular vs. Irregular
- The Prevalence of Hexagons in Nature and Design
- Hexagons in Nature: Honeycomb Structure
- Hexagons in Crystals and Minerals
- Hexagonal Tessellations: Paving the Plane
- Hexagons in Human Design and Engineering
- Architecture and Construction: Hexagonal Buildings
- Engineering and Manufacturing: Hexagonal Nuts and Bolts
- Graphic Design and Art: Hexagonal Patterns
- Games and Puzzles: Hexagonal Grids
- Beyond the Six Sides: Exploring Related Geometric Concepts
- Symmetry and Transformations
- Area and Perimeter Calculations
- Relationship to Other Shapes
- Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of the Hexagon
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
How Many Sides Does a Hexagon Have? A Deep Dive into Hexagonal Geometry
The question, "How many sides does a hexagon have?" might seem deceptively simple. The answer, of course, is six. But a simple answer often belies a deeper, more fascinating exploration. This article will delve into the world of hexagons, examining their properties, applications, and the mathematical concepts that underpin their unique structure. We'll go beyond the basic definition, exploring why hexagons are so prevalent in nature and human design.
Understanding the Hexagon: A Six-Sided Polygon
A hexagon is a polygon, a two-dimensional closed figure composed of straight line segments. The defining characteristic of a hexagon is its possession of six sides. These six sides connect to form six angles. The sum of the interior angles of any hexagon is always 720 degrees. This is a fundamental property that stems from the general formula for the sum of interior angles in an n-sided polygon: (n-2) * 180 degrees. For a hexagon (n=6), this equates to (6-2) * 180 = 720 degrees.
Types of Hexagons: Regular vs. Irregular
Not all hexagons are created equal. They are categorized into two main types:
-
Regular Hexagons: A regular hexagon possesses six sides of equal length and six angles of equal measure (120 degrees each). It exhibits perfect symmetry, meaning it can be divided into identical smaller shapes in multiple ways. Its elegant structure makes it a favorite in design and pattern-making.
-
Irregular Hexagons: Irregular hexagons have sides and angles of varying lengths and measures. They lack the perfect symmetry of their regular counterparts and can take on a wide range of shapes.
The Prevalence of Hexagons in Nature and Design
The hexagon's unique geometric properties make it surprisingly common in both the natural world and human creations. Let's explore some prominent examples:
Hexagons in Nature: Honeycomb Structure
Perhaps the most famous example of hexagonal structures in nature is the honeycomb created by bees. Bees instinctively build their honeycombs using hexagonal cells. This isn't accidental; it's a marvel of natural engineering. The hexagonal shape maximizes space and minimizes material usage, making it the most efficient way to store honey and raise young. This efficiency is a direct result of the hexagon's six equal sides and angles, allowing for optimal packing and structural integrity.
The hexagonal structure of honeycombs isn't limited to the surface. The cells themselves extend downwards, often creating a three-dimensional honeycomb structure. This complexity adds another layer to the already fascinating geometric precision of these natural wonders.
Hexagons in Crystals and Minerals
Hexagonal structures are also prevalent in the world of mineralogy and crystallography. Many crystals, such as quartz and beryl, exhibit hexagonal symmetry in their crystalline structure. This hexagonal arrangement of atoms and molecules results from the underlying forces of chemical bonding and crystal lattice formation. The stability and efficiency of the hexagonal lattice contribute to the formation and growth of these naturally occurring hexagonal crystals.
Hexagonal Tessellations: Paving the Plane
A tessellation is a pattern of shapes that completely covers a surface without overlapping or leaving gaps. The hexagon is one of only three regular polygons (along with the square and equilateral triangle) capable of creating a regular tessellation. This property stems from the fact that the interior angle of a regular hexagon (120 degrees) is a divisor of 360 degrees. This allows multiple hexagons to fit perfectly together, without any gaps or overlaps, to cover a flat surface. This tessellation property is essential in understanding why hexagons are so effective in packing and tiling applications.
Hexagons in Human Design and Engineering
The practicality and aesthetic appeal of hexagons have made them a staple in human design and engineering:
Architecture and Construction: Hexagonal Buildings
While less common than rectangular or circular structures, hexagonal buildings are increasingly present in modern architecture. The unique shape offers structural advantages in some situations, and it can create visually striking and memorable designs. The inherent symmetry of a regular hexagon allows for even weight distribution, and its ability to tessellate can facilitate efficient space planning.
Engineering and Manufacturing: Hexagonal Nuts and Bolts
Hexagonal shapes are ubiquitous in fasteners, specifically nuts and bolts. The six sides of a hexagonal nut provide a solid grip for a wrench, making it easy to tighten and loosen. The hexagonal shape provides both strength and efficiency, making it a reliable standard in engineering and manufacturing.
Graphic Design and Art: Hexagonal Patterns
The visually appealing symmetry and tessellation properties of hexagons make them popular elements in graphic design and art. Hexagonal patterns can create intricate and captivating designs, ranging from simple geometric patterns to complex, multifaceted works of art. The repeating nature of these patterns lends itself well to various applications, from textile design to digital artwork.
Games and Puzzles: Hexagonal Grids
Many games and puzzles utilize hexagonal grids. The ability of hexagons to tessellate perfectly allows for efficient use of space and creates unique strategic possibilities. Board games like Settlers of Catan and various hex-based wargames benefit from the hexagon’s unique geometric features. The hexagonal grid allows for multiple paths and strategic movement options unavailable in a square grid.
Beyond the Six Sides: Exploring Related Geometric Concepts
The study of hexagons opens up avenues to explore broader concepts in geometry:
Symmetry and Transformations
Hexagons, particularly regular hexagons, demonstrate high degrees of symmetry. They exhibit rotational symmetry (rotating by 60-degree increments results in the same shape) and reflectional symmetry (lines of reflection produce mirror images). Understanding these symmetries is crucial in analyzing and manipulating hexagonal shapes.
Area and Perimeter Calculations
Calculating the area and perimeter of a hexagon depends on whether it's regular or irregular. For a regular hexagon with side length 's', the area is given by (3√3/2)s², and the perimeter is 6s. For irregular hexagons, more complex calculations are needed, involving trigonometry and vector methods.
Relationship to Other Shapes
Hexagons are related to other geometric shapes. A regular hexagon can be divided into six equilateral triangles, highlighting its connection to triangular geometry. Furthermore, understanding hexagonal geometry provides a pathway to understanding more complex shapes and patterns.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of the Hexagon
The simple question, "How many sides does a hexagon have?" serves as a gateway to a rich exploration of geometry, nature, and design. The answer – six – is only the beginning. Hexagons, with their unique properties and prevalence in diverse fields, continue to fascinate and inspire, showcasing the beauty and efficiency found within the seemingly simple forms of mathematics. From the intricate honeycomb structures of bees to the precise designs of human engineering, the hexagon stands as a testament to the enduring power of geometric principles. It's a shape that seamlessly bridges the gap between the natural world and human creation, offering insights into efficiency, stability, and the mathematical beauty of the universe.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Tearing Paper A Physical Change
Apr 01, 2025
-
The Movement Of Water Across A Semipermeable Membrane Is Called
Apr 01, 2025
-
Differences Between Primary Data And Secondary Data
Apr 01, 2025
-
Where Glucose Gets Broken Into Pyruvate In The Cell
Apr 01, 2025
-
Find The Inverse Of The Relation
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Side Does A Hexagon Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
