What Is The Factor Of 200
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
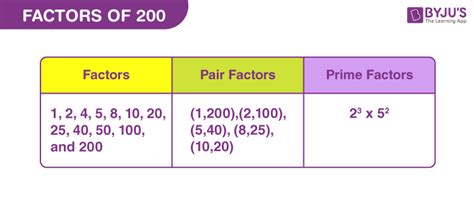
Table of Contents
What are the Factors of 200? A Comprehensive Guide to Prime Factorization and Divisibility
Finding the factors of a number is a fundamental concept in mathematics, crucial for understanding divisibility, prime factorization, and various other arithmetic operations. This article delves deep into determining the factors of 200, exploring the methods involved and expanding on the broader mathematical principles behind factorization. We'll cover prime factorization, finding all factors (both prime and composite), and explore practical applications of this knowledge.
Understanding Factors and Divisibility
Before jumping into the factors of 200, let's clarify the basic concepts. A factor of a number is any integer that divides that number without leaving a remainder. In other words, if 'a' is a factor of 'b', then b/a results in a whole number. Divisibility is the ability of one number to be divided evenly by another. Therefore, understanding factors is intrinsically linked to understanding divisibility.
For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder.
Prime Factorization of 200
Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. Prime numbers are whole numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, etc.). Prime factorization provides a unique representation of any composite number (a number that is not prime).
Let's find the prime factorization of 200:
- Start with the smallest prime number, 2: 200 is an even number, so it's divisible by 2. 200 ÷ 2 = 100.
- Continue with 2: 100 is also even, so it's divisible by 2. 100 ÷ 2 = 50.
- Again with 2: 50 is even, divisible by 2. 50 ÷ 2 = 25.
- Now, move to the next prime number, 5: 25 is divisible by 5. 25 ÷ 5 = 5.
- Finally, 5 is a prime number: The process ends here.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 200 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 5 x 5, which can be written as 2³ x 5². This means 200 can be expressed as the product of three 2's and two 5's.
Finding All Factors of 200
Now that we have the prime factorization (2³ x 5²), we can systematically find all the factors of 200. This involves considering all possible combinations of the prime factors.
Here's how to approach this:
- Start with the factors of 2³: The factors of 2³ (or 8) are 1, 2, 4, and 8.
- Consider the factors of 5²: The factors of 5² (or 25) are 1, 5, and 25.
To find all the factors of 200, we combine these factors:
- Combine the factors of 2³ with 1 from 5²: 1 x 1 = 1; 2 x 1 = 2; 4 x 1 = 4; 8 x 1 = 8
- Combine the factors of 2³ with 5 from 5²: 1 x 5 = 5; 2 x 5 = 10; 4 x 5 = 20; 8 x 5 = 40
- Combine the factors of 2³ with 25 from 5²: 1 x 25 = 25; 2 x 25 = 50; 4 x 25 = 100; 8 x 25 = 200
Therefore, the complete list of factors of 200 is: 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 20, 25, 40, 50, 100, and 200.
Practical Applications of Factorization
Understanding factors and prime factorization has numerous applications in various areas of mathematics and beyond:
-
Simplifying fractions: Finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of the numerator and denominator allows for simplification of fractions to their lowest terms. For example, to simplify 200/300, finding the GCF (100) helps reduce the fraction to 2/3.
-
Solving algebraic equations: Factorization is crucial in solving quadratic equations and other polynomial expressions.
-
Cryptography: Prime factorization plays a significant role in modern cryptography, particularly in public-key cryptosystems like RSA, where the security relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components.
-
Number theory: Factorization is a fundamental concept in number theory, a branch of mathematics dealing with the properties of integers.
-
Computer science: Efficient algorithms for factorization are essential in various computer science applications, including cryptography and database management.
Beyond the Factors of 200: Exploring Further
This exploration of the factors of 200 provides a foundation for understanding more complex concepts in number theory and mathematics. Here are some avenues for further exploration:
-
Greatest Common Factor (GCF): Finding the GCF of multiple numbers is a valuable skill used in many mathematical operations, including fraction simplification.
-
Least Common Multiple (LCM): The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of two or more given numbers. It’s crucial in operations involving fractions and least common denominators.
-
Divisibility rules: Understanding divisibility rules for different numbers (e.g., divisibility by 2, 3, 5, 9, 11) can significantly speed up the process of determining factors.
-
Euclidean Algorithm: This algorithm provides an efficient method for computing the GCF of two integers.
Conclusion
Determining the factors of 200, starting with its prime factorization (2³ x 5²), allows us to systematically identify all its divisors – 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 20, 25, 40, 50, 100, and 200. This seemingly simple exercise underpins many complex mathematical operations and has far-reaching applications across various disciplines. By understanding the fundamental concepts of factors, divisibility, and prime factorization, we open doors to a deeper understanding of the world of numbers and their intricate relationships. Further exploration into related concepts such as GCF, LCM, and divisibility rules will enhance mathematical proficiency and broaden your problem-solving skills.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are The Function Of Petals
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is The Molar Mass Of Calcium Nitrate
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is The Positively Charged Particle Of An Atom
Mar 16, 2025
-
Is Photosynthesis An Endergonic Or Exergonic Reaction
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is 36 Inches In Feet
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Factor Of 200 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
