What Is Prime Factorization Of 58
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
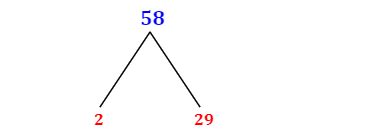
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization of 58? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
Prime factorization, a cornerstone of number theory, is the process of breaking down a composite number into its prime number components. Understanding prime factorization is crucial not only for academic pursuits but also for various applications in cryptography, computer science, and other fields. This article will delve into the concept of prime factorization, explain how to find the prime factorization of 58, and explore the broader significance of this mathematical process.
Understanding Prime Numbers and Composite Numbers
Before we dive into the prime factorization of 58, let's clarify the fundamental terms:
Prime Numbers: A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself. Examples include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and so on. The number 2 is the only even prime number.
Composite Numbers: A composite number is a positive integer that has at least one positive divisor other than 1 and itself. Essentially, it's a number that can be factored into smaller whole numbers. Examples include 4 (2 x 2), 6 (2 x 3), 9 (3 x 3), and so on. The number 1 is neither prime nor composite.
The Prime Factorization Process
Prime factorization involves expressing a composite number as a product of its prime factors. This process is unique for every composite number; there's only one way to express it as a product of primes (disregarding the order of the factors). This uniqueness is fundamental to many mathematical applications.
The process typically involves:
-
Finding a small prime factor: Begin by dividing the composite number by the smallest prime number, 2. If it divides evenly, record the 2 as a factor and continue with the quotient. Repeat this process until the quotient is no longer divisible by 2.
-
Trying subsequent prime numbers: If the quotient is not divisible by 2, move on to the next prime number, 3. Repeat the division process until you find a prime factor. Continue this process, progressing through prime numbers (5, 7, 11, and so on), until you arrive at a prime quotient.
-
Expressing as a product: Once you've reached a prime quotient, you have found all the prime factors of the original composite number. Express the result as a product of these prime factors.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 58
Now, let's apply this process to find the prime factorization of 58:
-
Check for divisibility by 2: 58 is an even number, so it's divisible by 2. 58 ÷ 2 = 29
-
Check the quotient: The quotient is 29.
-
Is 29 prime?: Yes, 29 is a prime number. It's only divisible by 1 and itself.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 58 is 2 x 29. We can't break it down any further because both 2 and 29 are prime numbers.
Applications of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple process of prime factorization has far-reaching applications in various fields:
1. Cryptography:
Prime numbers form the bedrock of many modern encryption algorithms. The difficulty of factoring very large composite numbers into their prime factors is the foundation of the RSA encryption system, which is widely used to secure online communications and transactions.
2. Computer Science:
Prime factorization plays a role in optimizing algorithms and data structures. Understanding prime numbers helps in efficiently managing memory and processing data.
3. Number Theory:
Prime factorization is fundamental to numerous theorems and concepts within number theory, impacting various mathematical fields.
4. Other Applications:
Prime factorization also finds applications in areas such as coding theory, error correction, and even some aspects of physics.
Exploring Related Concepts
Understanding prime factorization also leads to understanding related concepts:
-
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): The GCD of two numbers is the largest number that divides both without leaving a remainder. Prime factorization helps efficiently calculate the GCD.
-
Least Common Multiple (LCM): The LCM of two numbers is the smallest number that is a multiple of both. Prime factorization aids in determining the LCM.
-
Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic: This theorem states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers (ignoring the order of the factors). This is a cornerstone of number theory.
Beyond the Basics: More Advanced Techniques for Factorization
While the method we used for 58 is straightforward, larger numbers require more sophisticated techniques. These include:
-
Trial Division: Systematically testing prime numbers as potential divisors. This becomes less efficient for very large numbers.
-
Pollard's Rho Algorithm: A probabilistic algorithm that efficiently factors composite numbers, especially those with smaller prime factors.
-
General Number Field Sieve (GNFS): The most efficient known algorithm for factoring very large numbers, used in breaking RSA encryption (though breaking currently used key sizes remains computationally infeasible).
These advanced algorithms are crucial for tackling the computational challenges associated with factoring incredibly large numbers used in advanced cryptography.
Conclusion: The Significance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of 58, seemingly a simple calculation (2 x 29), reveals a glimpse into a vast and intricate mathematical world. The process itself, and the underlying concepts of prime and composite numbers, are fundamental to various fields, impacting our daily lives in ways we may not even realize. From securing online transactions to optimizing computer algorithms, the power of prime factorization extends far beyond the classroom. Understanding this concept provides a solid foundation for exploring more complex mathematical ideas and applications. While the factorization of 58 is easily solved, the principles involved underpin far more complex mathematical computations and applications that shape modern technology and security.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Difference Between Nerve And Neuron
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is The Sum Of The Angles Of A Hexagon
Mar 25, 2025
-
Rectangular Oyramid Labeling Of The Length Width And Hiegh Base
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Type Of Cell Has Large Vacuoles
Mar 25, 2025
-
Light Microscope And Electron Microscope Differences
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Prime Factorization Of 58 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
