What Is Advantage Of Ac Over Dc
Juapaving
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
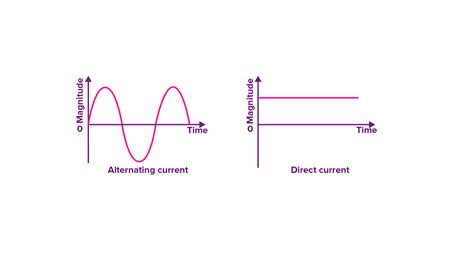
Table of Contents
What are the Advantages of AC Over DC?
The ongoing debate between AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) electricity has a long and fascinating history, shaping the development of our modern world. While DC might seem simpler—current flowing in one consistent direction—AC's widespread adoption speaks volumes about its advantages. This article delves deep into the key benefits of AC over DC, exploring the technical reasons behind its dominance in power transmission and distribution.
The Reign of AC: Why It Won the "Current Wars"
The "War of the Currents" in the late 19th century pitted Thomas Edison's DC system against George Westinghouse's AC system. While Edison championed DC, arguing for its safety and simplicity, Westinghouse's AC ultimately prevailed due to several crucial advantages:
1. Efficient Long-Distance Transmission: The Transformer's Role
This is arguably the most significant advantage of AC. AC voltage can be easily stepped up and down using transformers. This is crucial for long-distance power transmission. High-voltage transmission lines minimize power loss (due to resistance) over long distances. Once the electricity reaches its destination, transformers reduce the voltage to safe levels for domestic and industrial use. DC, on the other hand, lacks this inherent ability for efficient voltage transformation. While DC-DC converters exist, they are significantly less efficient than AC transformers, particularly at high power levels.
In simpler terms: Imagine trying to send water through a narrow pipe over a long distance. A lot of water (power) would be lost due to friction. Now imagine increasing the water pressure (voltage) before sending it, and then reducing the pressure at the destination. This is analogous to AC transmission, minimizing energy loss. DC would struggle with this efficient pressure (voltage) adjustment.
2. Ease of Generation and Distribution: Alternators' Superiority
Alternators, the machines that generate AC, are inherently simpler and more robust than DC generators. They require less maintenance and are more efficient in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. The rotating magnetic field in an alternator naturally produces AC, while generating DC requires complex commutators that are prone to wear and tear.
This difference in generator design and maintenance translates to significant cost savings for power companies. The simpler design of alternators and the inherent ability of transformers to manipulate AC voltage have been instrumental in building the vast and efficient power grids that power our world.
3. Reduced Transmission Losses: Minimizing Energy Waste
As mentioned, AC's ability to be transformed to high voltages significantly reduces transmission losses. High voltage means lower current for the same power, and lower current minimizes the resistive heating (I²R losses) in the transmission lines. This translates to less energy wasted as heat, resulting in greater efficiency and significant cost savings. DC transmission, without the benefit of easy voltage transformation, suffers from far greater energy losses over long distances.
4. Multiple-Phase AC Systems: Enhanced Power Delivery and Efficiency
Modern power grids utilize three-phase AC systems. This means three separate AC currents are generated and transmitted, each slightly out of phase with the others. This configuration results in a more balanced and efficient power delivery compared to single-phase AC or DC systems. Three-phase systems are crucial for driving large industrial motors and other high-power equipment. The smoother power delivery minimizes fluctuations and improves overall efficiency.
Addressing the Perceived Drawbacks of AC
While AC's advantages are undeniable, some perceived drawbacks are often cited:
-
Higher Risk of Electric Shock: This is a valid concern, but safety regulations and proper insulation mitigate this risk significantly. High-voltage lines are meticulously designed to prevent accidental contact, and domestic voltages are kept relatively low. Moreover, DC shocks can also be dangerous, especially at higher voltages.
-
More Complex Circuitry: This is true to some extent, but the complexity is mostly confined to the high-voltage transmission and distribution infrastructure. Domestic AC circuits are relatively simple and well understood.
Specific Applications Where AC Shines
AC's advantages are particularly prominent in several key areas:
1. Power Grids and Long-Distance Transmission: The Backbone of Modern Infrastructure
The vast majority of the world's power grids utilize AC. The ability to efficiently transmit power over hundreds or even thousands of kilometers makes AC the clear choice for connecting power generation sources to consumers.
2. Industrial Applications: Driving Large Motors and Machinery
Three-phase AC power is ideal for driving large induction motors, which are widely used in industrial settings. These motors are robust, reliable, and require less maintenance than their DC counterparts.
3. Household Appliances: Powering Everyday Devices
While many household appliances internally convert AC to DC, the widespread availability of AC makes it the most convenient choice for powering homes and businesses.
The Resurgence of DC: HVDC Transmission and Specialized Applications
While AC dominates the long-distance transmission landscape, there's a resurgence of DC in specific niche applications:
1. High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Transmission: Long-Distance, Underground, and Submarine Cables
HVDC transmission is becoming increasingly important for very long distances, submarine cables, and underground transmission lines. While it requires more complex converter stations at both ends, HVDC offers some advantages in specific situations, particularly where minimizing reactive power losses is crucial.
2. Electronics and Microelectronics: DC's Role in Smaller Devices
DC remains the preferred choice for powering most electronic devices, from smartphones to computers. However, this is primarily due to the nature of the electronic components, not a fundamental advantage of DC over AC in general power distribution.
Conclusion: AC Remains King, but DC Plays a Vital Role
The advantages of AC over DC for large-scale power transmission and distribution are overwhelming. The efficiency of transformers, the ease of generation, and the effectiveness of three-phase systems have cemented AC's dominance. While DC has specific applications, particularly in high-voltage long-distance transmission and electronics, AC's reign as the king of power continues, shaping our modern world's infrastructure and technological capabilities. The "War of the Currents" may be over, but the contrasting roles of AC and DC remain a fascinating aspect of electrical engineering.
Keywords:
AC, DC, Alternating Current, Direct Current, power transmission, power distribution, transformer, alternator, generator, high voltage, low voltage, three-phase AC, HVDC, High-Voltage Direct Current, electricity, energy efficiency, power loss, War of the Currents, Thomas Edison, George Westinghouse, electrical engineering.
Semantic Keywords:
Efficient energy transmission, long-distance power delivery, electrical grid infrastructure, industrial motor control, household appliance power supply, advantages of AC over DC in transmission, comparing AC and DC power systems, benefits of using AC electricity, AC vs DC applications, evolution of electrical power systems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which One Of The Following Compound Is Aromatic
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is A Common Multiple Of 3 4 And 5
Mar 28, 2025
-
31 Inches Is How Many Feet
Mar 28, 2025
-
Is Clockwise Moment Positive Or Negative
Mar 28, 2025
-
44 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Advantage Of Ac Over Dc . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
