What Are The Factors Of 73
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
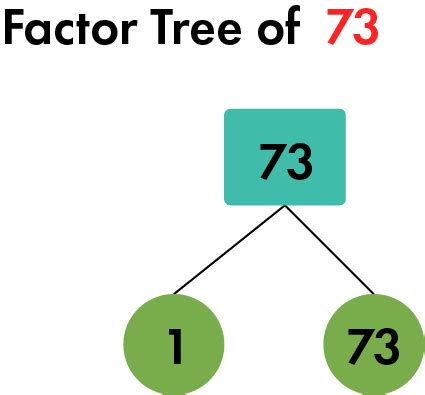
Table of Contents
Unraveling the Factors of 73: A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Divisibility
The seemingly simple question, "What are the factors of 73?", opens a door to a fascinating exploration of number theory, prime numbers, and the fundamental building blocks of mathematics. While the immediate answer might seem straightforward, delving deeper reveals a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts and their practical applications. This article will not only answer the question directly but also explore the broader context of factors, prime numbers, and their significance in various fields.
What are Factors?
Before we delve into the specifics of 73, let's establish a clear understanding of what factors are. In mathematics, a factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides that number exactly, leaving no remainder. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 because each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder. Finding factors is a fundamental operation in arithmetic and forms the basis for many more advanced mathematical concepts.
Identifying the Factors of 73
Now, let's address the core question: what are the factors of 73? The process of finding factors often involves trial division, systematically checking each whole number to see if it divides the target number evenly. However, in this case, we can significantly simplify the process by considering the nature of the number 73.
73 is a prime number. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two distinct positive divisors: 1 and itself. This means that the only numbers that divide 73 without leaving a remainder are 1 and 73.
Therefore, the factors of 73 are 1 and 73.
Prime Numbers: The Building Blocks of Numbers
The identification of 73 as a prime number highlights the importance of prime numbers in number theory. Prime numbers are considered the fundamental building blocks of all other whole numbers. This is because of the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, which states that every whole number greater than 1 can be uniquely expressed as a product of prime numbers (ignoring the order of the factors). This theorem is crucial in various areas of mathematics, including cryptography and computer science.
For example, consider the number 12. Its prime factorization is 2 x 2 x 3 (or 2² x 3). This means that 12 can be constructed solely by multiplying the prime numbers 2 and 3. This unique factorization is essential for many mathematical operations and algorithms.
Why is the Primality of 73 Significant?
The fact that 73 is a prime number has significant implications in several fields:
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers form the backbone of many modern cryptographic systems, such as RSA encryption. These systems rely on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime components. The larger the prime numbers used, the more secure the encryption becomes. While 73 is relatively small, its prime nature illustrates the fundamental principle underlying these systems.
-
Number Theory: The study of prime numbers is a central theme in number theory, a branch of mathematics that explores the properties and relationships of numbers. Questions about the distribution of prime numbers, the existence of infinitely many primes, and the search for larger and larger primes have captivated mathematicians for centuries.
-
Computer Science: Prime numbers are used in various algorithms and data structures in computer science, such as hash tables and random number generators. Efficient algorithms for primality testing and prime factorization are essential for optimizing these applications.
Exploring Related Concepts: Divisibility Rules and Prime Factorization
Understanding the factors of 73 provides a stepping stone to explore related concepts:
-
Divisibility Rules: Divisibility rules are shortcuts to determine whether a number is divisible by another number without performing long division. While there isn't a specific divisibility rule for 73 (as it's a prime number), understanding divisibility rules for smaller prime numbers (like 2, 3, 5, 7, 11) is crucial for efficient factorization.
-
Prime Factorization: Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. For instance, the prime factorization of 12 is 2 x 2 x 3. This process is fundamental in simplifying fractions, solving algebraic equations, and understanding the structure of numbers. Since 73 is prime, its prime factorization is simply 73.
-
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM): The GCD is the largest number that divides two or more numbers without leaving a remainder. The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of two or more numbers. Understanding prime factorization is essential for efficiently calculating GCD and LCM.
The Significance of Small Prime Numbers
Although 73 might seem like a relatively small prime number in the vast landscape of numbers, it plays a crucial role in demonstrating fundamental mathematical concepts. Its simplicity makes it an ideal example for learning about factors, prime numbers, and their significance. Moreover, small prime numbers are often used as building blocks in more complex mathematical structures and algorithms.
Applications in Real-World Scenarios
The concepts discussed here, while seemingly abstract, have practical applications in various fields:
-
Cryptography: As mentioned earlier, prime numbers are essential for securing online transactions and protecting sensitive data.
-
Coding Theory: Prime numbers are used in error-correcting codes, ensuring reliable data transmission.
-
Computer Graphics: Prime numbers are used in generating textures and patterns in computer graphics.
-
Music Theory: Surprisingly, prime numbers have applications in music theory, influencing musical scales and harmonies.
Conclusion: Beyond the Simple Answer
The factors of 73 are simply 1 and 73. However, this seemingly simple answer opens a window to a rich world of mathematical concepts, including prime numbers, divisibility, prime factorization, and their widespread applications. By understanding these concepts, we gain a deeper appreciation for the underlying structure of numbers and their crucial role in various scientific and technological fields. The seemingly simple question about the factors of 73, therefore, serves as a gateway to a fascinating exploration of the fundamental building blocks of mathematics and their impact on our world. Further exploration into the realm of number theory reveals even greater depths and complexities, emphasizing the unending beauty and power of mathematical discovery. The journey into understanding numbers, beginning with the seemingly simple question of the factors of 73, is a journey well worth undertaking.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are Rows On The Periodic Table Called
Mar 16, 2025
-
Is Carbon Tetrachloride Ionic Or Covalent
Mar 16, 2025
-
Write The Formula For Sulfurous Acid
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Are The Raw Materials Required For Photosynthesis
Mar 16, 2025
-
How Many Protons Electrons And Neutrons Are In Sodium
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors Of 73 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
