What Are Rows On The Periodic Table Called
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
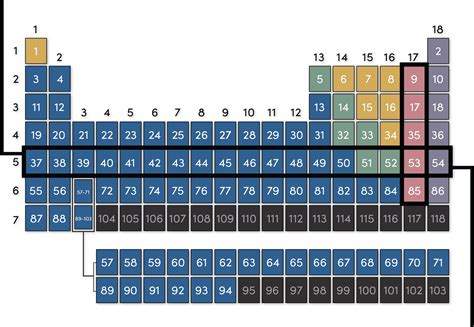
Table of Contents
What Are Rows on the Periodic Table Called? Understanding Periods and Their Significance
The periodic table, a cornerstone of chemistry, organizes chemical elements based on their atomic number, electronic configuration, and recurring chemical properties. While many are familiar with the columns (groups), understanding the rows is equally crucial to grasping the fundamental principles of chemistry. So, what are rows on the periodic table called? They're called periods. This seemingly simple answer opens the door to a wealth of information about the organization and behavior of elements.
Understanding Periods: A Deeper Dive
Each period represents a principal energy level or electron shell. As you move across a period from left to right, the atomic number increases, indicating an increase in the number of protons and electrons. This systematic addition of electrons results in predictable changes in elemental properties. Let's explore these changes in more detail.
Period 1: The Simplest Beginnings
The first period is the shortest, containing only two elements: hydrogen (H) and helium (He). These elements fill the first principal energy level (n=1), which has only one electron shell. This shell can hold a maximum of two electrons, hence the limited number of elements in this period.
Period 2 and 3: The Rise of Blocks
Periods 2 and 3, with eight elements each, introduce the concept of 'blocks' within the periodic table. These periods start with alkali metals and end with noble gases, showcasing a transition in properties. The alkali metals (Group 1) are highly reactive, while the noble gases (Group 18) are exceptionally unreactive due to their complete valence electron shells. This regular pattern of properties begins to emerge, setting the stage for the understanding of the trends in the periodic table. Within these periods, we also see the introduction of alkaline earth metals (Group 2) and halogens (Group 17), further highlighting the varied characteristics within a single period. The filling of the s and p subshells defines the properties of elements in these periods.
Period 4 and Beyond: The Emergence of Transition Metals
Periods 4 and beyond are longer due to the filling of the d subshell, resulting in the introduction of transition metals. These metals exhibit a complex array of properties due to the involvement of d electrons in bonding. This introduces a significant increase in the number of elements in these periods, adding complexity to the periodic trends. The filling of the d orbitals influences the behavior of these metals, leading to variable oxidation states and colored compounds, often associated with catalytic properties. These periods show a clear progression from left to right, reflecting the changes in electronic configuration.
Period 6 and the Lanthanides
Period 6 is significantly longer due to the filling of the f subshell, leading to the lanthanides (rare earth elements). These elements, situated below the main body of the periodic table, display similar chemical properties due to the similarities in their electronic configurations. Their f electron configurations account for the similarities between these elements and contribute to their specific applications. The physical and chemical properties of these elements are influenced by this unique configuration.
Period 7 and the Actinides
Similarly, period 7 houses the actinides, also placed below the main table, further demonstrating the role of f subshells. This series consists of radioactive elements, many of which are synthetically created. The actinides show a wide range of properties, impacted by their radioactive nature and unique electron configurations.
Periodicity and Trends: Why Periods Matter
The organization of elements by periods highlights important periodic trends. These are predictable changes in properties as you move across a period (left to right) or down a group (top to bottom). Understanding these trends is crucial for predicting chemical behavior and interpreting experimental data.
Atomic Radius: A Decreasing Trend Across Periods
As you move across a period, the atomic radius generally decreases. This is because the number of protons increases, resulting in a stronger positive charge that pulls the electrons closer to the nucleus. While additional electrons are added, they are also added to the same principal energy level, not significantly shielding the increased nuclear charge.
Ionization Energy: An Increasing Trend Across Periods
Ionization energy, the energy required to remove an electron from an atom, generally increases across a period. This is a direct consequence of the increasing nuclear charge mentioned above. The stronger attraction between the nucleus and electrons makes it more difficult to remove an electron, thus requiring higher ionization energy.
Electronegativity: Following a Similar Trend
Electronegativity, the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond, also tends to increase across a period. This is because of the same reasons as the increasing ionization energy. Atoms with higher electronegativity tend to attract electrons more strongly, affecting the bonding characteristics of the element.
Metallic Character: A Decreasing Trend
Metallic character, reflecting properties like conductivity and malleability, generally decreases across a period. This is related to the increasing ionization energy and electronegativity. As you move across, elements become less likely to lose electrons, shifting towards non-metallic behavior.
Predicting Properties Based on Period
The periodic table’s organization by periods allows for predictions about the properties of elements based on their position. Knowing the period of an element gives insights into its electron shell configuration, valence electrons, and ultimately its reactivity and bonding behavior. For example, an element in period 3 will have three principal energy levels occupied by electrons, influencing its chemical and physical properties compared to an element in period 2.
Beyond the Basics: Further Applications
The understanding of periods goes beyond basic chemical principles. It extends into various fields, including:
- Material Science: The periodic table guides the development of new materials with desired properties. By understanding the trends in periods, scientists can predict the potential behavior of alloys and compounds.
- Catalysis: Many transition metals, found in various periods, are excellent catalysts due to their variable oxidation states. Understanding their position on the periodic table aids in the selection and design of catalysts for various chemical reactions.
- Nuclear Chemistry: The actinides, located in period 7, play a critical role in nuclear reactions and applications. Their properties, directly influenced by their period, inform the development of nuclear technologies.
Conclusion: The Significance of Periods in Chemistry
The rows on the periodic table, or periods, are fundamental to understanding the organization and behavior of chemical elements. Each period represents a principal energy level, leading to predictable trends in atomic radius, ionization energy, electronegativity, and metallic character. Understanding these trends is vital for predicting chemical behavior, designing new materials, and exploring applications in diverse fields. The periodic table, organized by periods and groups, is a powerful tool for comprehending the fundamental principles of chemistry and predicting the behavior of elements, offering a glimpse into the intricacies of the chemical world. The significance of periods, therefore, extends far beyond a simple label; they form the backbone of our understanding of the elemental landscape.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple Of 9 12 And 15
Mar 16, 2025
-
Energy That An Object Has Due To Its Motion
Mar 16, 2025
-
How Many Centimeters Are In 3 Inches
Mar 16, 2025
-
Examples Of Pulling And Pushing Forces
Mar 16, 2025
-
Refraction Causes The Bottom Of A Swimming Pool To Appear
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are Rows On The Periodic Table Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
