What Are All The Multiples Of 6
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
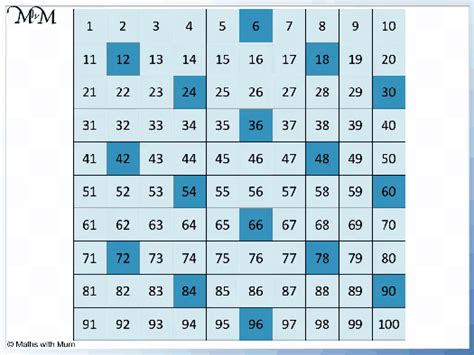
Table of Contents
What Are All the Multiples of 6? An Exploration of Number Theory
The seemingly simple question, "What are all the multiples of 6?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, revealing patterns, relationships, and applications that extend far beyond basic arithmetic. This exploration delves into the concept of multiples, specifically those of 6, examining their properties, identifying methods for finding them, and showcasing their significance in various mathematical contexts.
Understanding Multiples
Before we embark on our journey into the multiples of 6, let's solidify our understanding of the term "multiple." A multiple of a number is the product of that number and any integer (whole number). For example, multiples of 2 are numbers like 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and so on – each being the result of multiplying 2 by another whole number (1 x 2, 2 x 2, 3 x 2, etc.).
Therefore, multiples of 6 are numbers obtained by multiplying 6 by any integer. This includes positive integers, zero, and negative integers.
Generating Multiples of 6
The most straightforward way to generate multiples of 6 is through multiplication. We can start by listing them systematically:
- 6 x 1 = 6
- 6 x 2 = 12
- 6 x 3 = 18
- 6 x 4 = 24
- 6 x 5 = 30
- 6 x 6 = 36
- 6 x 7 = 42
- 6 x 8 = 48
- 6 x 9 = 54
- 6 x 10 = 60
...and so on, infinitely in both positive and negative directions. This list can be extended indefinitely, demonstrating that there are infinitely many multiples of 6.
The Pattern in Multiples of 6
Notice that all multiples of 6 are even numbers. This is because 6 itself is an even number (divisible by 2), and the product of an even number and any integer will always be even. This observation reveals a fundamental property of multiples: they inherit the divisibility properties of the original number.
Furthermore, observe the last digits of the multiples: 6, 2, 8, 4, 0, 6, 2, 8, 4, 0… This sequence repeats every five terms. This cyclical pattern in the units digit is a characteristic feature of multiples and can be used as a quick check to determine if a number is a multiple of 6 (though it's not sufficient on its own).
Identifying Multiples of 6: Divisibility Rules
Instead of manually multiplying 6 by every integer, we can employ divisibility rules to efficiently determine if a given number is a multiple of 6. A number is divisible by 6 if it is divisible by both 2 and 3. This is because 6 = 2 x 3, and the prime factorization of a number reveals its divisors.
Let's break down the divisibility rules for 2 and 3:
-
Divisibility Rule for 2: A number is divisible by 2 if its last digit is an even number (0, 2, 4, 6, or 8).
-
Divisibility Rule for 3: A number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3.
Therefore, to check if a number is a multiple of 6:
-
Check for divisibility by 2: If the last digit is not even, the number is not a multiple of 6.
-
Check for divisibility by 3: If the sum of the digits is not divisible by 3, the number is not a multiple of 6.
-
If both conditions are met: The number is a multiple of 6.
Example: Let's consider the number 132.
-
Divisibility by 2: The last digit is 2 (even), so it's divisible by 2.
-
Divisibility by 3: The sum of the digits is 1 + 3 + 2 = 6, which is divisible by 3.
Therefore, 132 is a multiple of 6 (6 x 22 = 132).
Multiples of 6 in Different Mathematical Contexts
The multiples of 6 are not merely an abstract sequence of numbers; they appear in various mathematical areas and real-world applications:
1. Number Theory:
- Even Numbers: As previously discussed, all multiples of 6 are even, highlighting the connection between even numbers and multiples.
- Arithmetic Progressions: The multiples of 6 form an arithmetic progression with a common difference of 6. An arithmetic progression is a sequence where each term is obtained by adding a constant value (the common difference) to the previous term.
- Prime Factorization: Understanding the prime factorization of 6 (2 x 3) is crucial for understanding its multiples. Any number that contains at least one factor of 2 and one factor of 3 will be a multiple of 6.
2. Geometry:
- Hexagons: The internal angles of a regular hexagon sum to 6 multiples of 180 degrees. This geometrical shape and its properties are directly connected to the number 6 and its multiples.
- Tessellations: Hexagons, with their ability to tessellate (tile a plane without gaps), provide a visual representation of the regular arrangement inherent in the multiples of 6.
3. Algebra:
- Equations: Multiples of 6 can be used to solve equations, especially those involving divisibility or modular arithmetic. For example, solving for 'x' in the equation 6x = 132 directly relates to finding a multiple of 6.
- Sequences and Series: The sequence of multiples of 6 can be analyzed using algebraic techniques to determine patterns, sums, and other properties.
4. Real-World Applications:
- Measurement: Multiples of 6 appear frequently in measurements, particularly those involving inches (e.g., 6 inches, 12 inches, 18 inches, etc.).
- Calendars: The number of days in certain periods (e.g., two weeks) is a multiple of 6.
- Packaging: Items are often packaged in multiples of 6 for ease of handling and distribution.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Multiples of 6
This exploration into the multiples of 6 demonstrates how a seemingly simple concept can lead to rich mathematical insights. From the fundamental principles of divisibility to the intricate patterns found in number theory and geometrical applications, the multiples of 6 showcase the interconnectedness of various mathematical branches. Understanding these multiples goes beyond mere calculation; it helps develop critical thinking, pattern recognition, and a deeper appreciation for the beauty and structure within mathematics. The infinite sequence of multiples of 6, therefore, presents not an end, but a gateway to continued mathematical discovery.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
3 Out Of 7 Is What Percent
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is The Factors Of 126
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is The Average Kinetic Energy
Mar 14, 2025
-
Rusting Of Iron Physical Or Chemical Change
Mar 14, 2025
-
Is Baking Bread A Chemical Or Physical Change
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are All The Multiples Of 6 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
