What Is The Factors Of 126
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
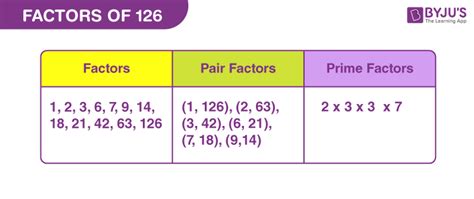
Table of Contents
Unraveling the Factors of 126: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
The seemingly simple question, "What are the factors of 126?" opens a door to a fascinating exploration of number theory, prime factorization, and the fundamental building blocks of mathematics. While finding the factors of 126 might seem trivial at first glance, understanding the process and its implications provides a solid foundation for more complex mathematical concepts. This article will delve into the various methods of determining the factors of 126, explore the related concepts of prime numbers and divisibility rules, and touch upon the broader significance of factorization in mathematics and beyond.
Understanding Factors and Divisibility
Before we tackle the specific case of 126, let's establish a clear understanding of what factors are. A factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides evenly into that number without leaving a remainder. In other words, if 'a' is a factor of 'b', then b/a results in a whole number. Divisibility, therefore, is the key concept here. A number is divisible by another number if the division results in a whole number quotient with no remainder.
This concept underlies many mathematical operations and is crucial for simplifying fractions, solving equations, and understanding more complex number theory problems.
Finding the Factors of 126: A Systematic Approach
There are several methods to determine the factors of 126. Let's explore these methods, starting with the most straightforward:
Method 1: Trial Division
This is the most basic method, involving testing each whole number sequentially to see if it divides 126 without leaving a remainder. We start with 1 and continue until we reach the square root of 126 (approximately 11.2). This is because factors always come in pairs; if 'a' is a factor, then 126/a is also a factor. Once we pass the square root, we'll have already found all the pairs.
Let's try it:
- 1 divides 126 (126/1 = 126)
- 2 divides 126 (126/2 = 63)
- 3 divides 126 (126/3 = 42)
- 6 divides 126 (126/6 = 21)
- 7 divides 126 (126/7 = 18)
- 9 divides 126 (126/9 = 14)
- 14 divides 126 (126/14 = 9)
- 18 divides 126 (126/18 = 7)
- 21 divides 126 (126/21 = 6)
- 42 divides 126 (126/42 = 3)
- 63 divides 126 (126/63 = 2)
- 126 divides 126 (126/126 = 1)
Therefore, the factors of 126 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 9, 14, 18, 21, 42, 63, and 126.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
A more elegant and efficient method involves finding the prime factorization of 126. Prime numbers are numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, etc.). Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors.
Let's find the prime factorization of 126:
- Start by dividing 126 by the smallest prime number, 2: 126 = 2 x 63
- Now, 63 is divisible by 3: 63 = 3 x 21
- 21 is also divisible by 3: 21 = 3 x 7
- 7 is a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 126 is 2 x 3 x 3 x 7 or 2 x 3² x 7.
From Prime Factorization to All Factors
Once we have the prime factorization, we can systematically find all the factors. We do this by considering all possible combinations of the prime factors and their powers. In the case of 126 (2 x 3² x 7):
- Combinations with only one prime factor: 2, 3, 7
- Combinations with two prime factors: 2 x 3 = 6, 2 x 7 = 14, 3 x 7 = 21, 3 x 3 = 9
- Combinations with three prime factors: 2 x 3 x 3 = 18, 2 x 3 x 7 = 42, 3 x 3 x 7 = 63
- Combination with all four prime factors: 2 x 3 x 3 x 7 = 126
- Also remember the factor 1
This method neatly generates all the factors we found using trial division: 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 9, 14, 18, 21, 42, 63, 126.
Divisibility Rules: Shortcuts to Factor Finding
Understanding divisibility rules can significantly speed up the process of finding factors. Divisibility rules are shortcuts to determine if a number is divisible by a particular prime number without performing the actual division. Some useful rules include:
- Divisibility by 2: A number is divisible by 2 if its last digit is even (0, 2, 4, 6, 8).
- Divisibility by 3: A number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3. (1 + 2 + 6 = 9, which is divisible by 3, so 126 is divisible by 3)
- Divisibility by 5: A number is divisible by 5 if its last digit is 0 or 5.
- Divisibility by 7: There's no easy rule, but we can use long division or trial division.
- Divisibility by 9: A number is divisible by 9 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 9. (1+2+6 = 9, so 126 is divisible by 9)
Using these rules can help you quickly identify some of the factors before resorting to more involved methods.
The Significance of Factorization
The seemingly simple act of finding factors has profound implications across various areas of mathematics and beyond:
1. Simplifying Fractions:
Factorization is essential for simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. Finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of the numerator and denominator allows for simplification.
2. Solving Equations:
In algebra, factorization is a crucial tool for solving polynomial equations.
3. Cryptography:
Prime factorization plays a critical role in modern cryptography, particularly in public-key cryptosystems like RSA. The difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components forms the basis of the security of these systems.
4. Number Theory:
Factorization is a fundamental concept in number theory, with many theorems and conjectures revolving around the properties of prime numbers and factorization.
5. Computer Science:
Efficient algorithms for prime factorization are actively researched in computer science, with applications in cryptography and other areas.
Conclusion: Beyond the Factors of 126
While finding the factors of 126 might seem like a basic exercise, it serves as a gateway to understanding fundamental concepts in number theory and their far-reaching applications. The process of factorization, whether through trial division or prime factorization, underscores the importance of understanding divisibility rules and the unique properties of prime numbers. This knowledge is crucial not only for mathematical problem-solving but also for appreciating the deeper structures and patterns that underpin our numerical world. The seemingly simple number 126, therefore, holds a wealth of mathematical significance, revealing the intricate beauty and power of number theory.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Cold Air Go Up Or Down
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 20 And 3
Mar 17, 2025
-
Function Of The Motor End Plate
Mar 17, 2025
-
A Push Or A Pull Is Called
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Factors Of 126 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
