Vapor Pressure Of Water At 23c
Juapaving
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
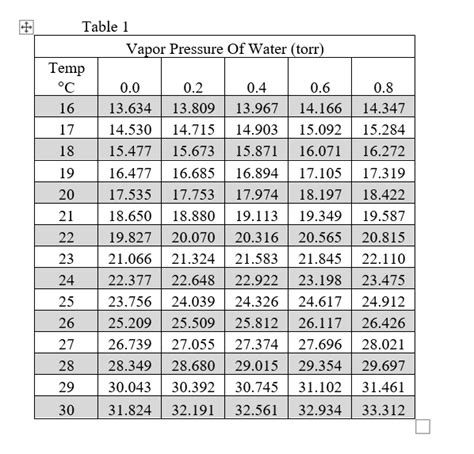
Table of Contents
Vapor Pressure of Water at 23°C: A Deep Dive
The vapor pressure of water, a fundamental concept in chemistry and meteorology, represents the pressure exerted by water vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its liquid or solid phase at a given temperature. Understanding this property is crucial in numerous applications, from predicting weather patterns to designing industrial processes. This article delves into the vapor pressure of water specifically at 23°C, exploring its significance, calculation methods, influencing factors, and practical applications.
What is Vapor Pressure?
At any temperature above absolute zero, water molecules possess kinetic energy, causing them to constantly move and collide. Some molecules near the surface possess enough energy to overcome the intermolecular forces holding them in the liquid phase and escape into the gaseous phase, a process known as vaporization or evaporation. These escaped water molecules exert a pressure known as vapor pressure.
In a closed system, an equilibrium is eventually established where the rate of evaporation equals the rate of condensation (gas molecules returning to the liquid phase). At this equilibrium, the pressure exerted by the water vapor is the equilibrium vapor pressure. This equilibrium vapor pressure is solely dependent on the temperature of the water and the nature of the water itself (pure water versus a solution).
Vapor Pressure of Water at 23°C: The Value and Its Significance
The vapor pressure of water at 23°C (73.4°F) is approximately 21.07 mmHg (millimeters of mercury) or 2.81 kPa (kilopascals). This seemingly simple value has profound implications across various scientific disciplines and real-world applications.
The significance of knowing this precise value is multifaceted:
-
Meteorology and Climate Science: Understanding the vapor pressure of water at different temperatures is fundamental to predicting humidity, dew point, and cloud formation. At 23°C, a relatively comfortable temperature, the vapor pressure directly relates to the amount of water vapor present in the air. Higher vapor pressure indicates higher humidity. This influences weather patterns and climate modeling.
-
Chemical Engineering and Industrial Processes: Many industrial processes involve evaporation, drying, or distillation. Accurate knowledge of the vapor pressure of water at the operating temperature is critical for designing efficient and effective equipment and predicting process outcomes. For instance, in drying processes, the vapor pressure dictates the rate at which water will evaporate from a material.
-
Biology and Environmental Science: The vapor pressure of water plays a key role in various biological processes, such as transpiration in plants and water loss from living organisms. Understanding this value aids in ecological studies and agricultural practices. For example, understanding water vapor pressure helps explain how plants control water loss in hot and dry environments.
Calculating Vapor Pressure: Methods and Equations
Several methods can be used to determine the vapor pressure of water at 23°C.
1. Antoine Equation:
The Antoine equation is an empirical equation that accurately predicts the vapor pressure of various substances over a range of temperatures. The equation is:
log₁₀(P) = A - (B / (T + C))
where:
- P is the vapor pressure in mmHg
- T is the temperature in °C
- A, B, and C are empirical constants specific to the substance.
For water, a common set of Antoine constants is:
- A = 8.07131
- B = 1730.63
- C = 233.426
Substituting T = 23°C into the Antoine equation yields a vapor pressure value very close to the accepted value of 21.07 mmHg.
2. Clausius-Clapeyron Equation:
The Clausius-Clapeyron equation relates the vapor pressure of a substance to its enthalpy of vaporization (the energy required to convert liquid to gas) and temperature. This equation is more theoretical and requires knowledge of the enthalpy of vaporization, which can be obtained from thermodynamic tables. While less precise for a single point calculation, it provides a more fundamental understanding of the relationship between vapor pressure and temperature.
3. Vapor Pressure Tables:
Pre-calculated vapor pressure tables are readily available in many chemistry and engineering handbooks. These tables provide vapor pressure values at various temperatures, offering a quick and convenient method for determining the vapor pressure of water at 23°C.
4. Advanced Software and Simulations:
Sophisticated thermodynamic software packages and computational simulations can accurately predict vapor pressures based on complex models, considering various factors influencing the equilibrium. These methods offer high precision but are often more resource-intensive.
Factors Affecting Vapor Pressure
While temperature is the primary determinant of vapor pressure, other factors can subtly influence the value:
-
Presence of solutes: Dissolving substances in water lowers its vapor pressure, a phenomenon known as Raoult's Law. The vapor pressure reduction is proportional to the mole fraction of the solute. This is crucial in many applications involving solutions, such as saline solutions or industrial process streams.
-
Atmospheric pressure: While typically having a negligible effect, very large variations in atmospheric pressure can minutely affect vapor pressure. This effect is often only significant at high altitudes or in specialized experimental settings.
-
Isotopic composition: The isotopic composition of water (e.g., the ratio of deuterium to hydrogen) can slightly influence the vapor pressure. This effect is very small but can be important in certain scientific studies involving isotopic fractionation.
Practical Applications of Understanding Vapor Pressure at 23°C
The knowledge of water's vapor pressure at 23°C has numerous practical applications across diverse fields:
-
HVAC Systems: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems rely on accurate vapor pressure data to control humidity levels and ensure optimal comfort and energy efficiency. The vapor pressure at 23°C dictates the dew point, helping engineers to design systems that avoid condensation issues.
-
Food Processing: In food processing, understanding vapor pressure is vital for efficient drying and preservation techniques. Dehydration processes often occur at controlled temperatures near 23°C, and the vapor pressure aids in predicting drying rates and preserving food quality.
-
Weather Forecasting: Meteorologists utilize vapor pressure data, including the value at 23°C as a reference point, to predict weather patterns, including the likelihood of precipitation and humidity levels. This information helps in accurate weather forecasts and early warning systems for extreme weather conditions.
-
Medical Applications: Vapor pressure plays a role in various medical applications such as respiration, where understanding humidity levels, related to water vapor pressure, is crucial for maintaining respiratory health. Also, in drug delivery systems, vapor pressure is significant in formulations involving aerosols.
-
Environmental Monitoring: Environmental monitoring often requires precise measurements of humidity and vapor pressure. This data is essential in assessing air quality, predicting the impact of climate change, and managing environmental resources. Understanding the vapor pressure at typical ambient temperatures like 23°C is crucial for this aspect.
Conclusion
The vapor pressure of water at 23°C, while a seemingly small and specific value (approximately 21.07 mmHg or 2.81 kPa), holds immense practical and theoretical significance. This fundamental property underpins many natural phenomena and industrial processes, impacting everything from weather forecasting and climate modeling to the design of HVAC systems and food preservation techniques. A comprehensive understanding of vapor pressure and its influencing factors is crucial for numerous scientific, engineering, and industrial applications. By employing various calculation methods and considering the impacting factors, we can accurately determine and utilize this vital thermodynamic property in a wide variety of fields. The continued research and refinement of our understanding of vapor pressure will undoubtedly lead to further advancements and innovations across these areas.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Write The Chemical Formula For The Dichromate Ion
Mar 31, 2025
-
Step By Step Implicit Differentiation Calculator
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Are Cold Blooded And Warm Blooded Animals
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Is The Prime Factorization Of 216
Mar 31, 2025
-
Suez Canal Connects Which Two Bodies Of Water
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Vapor Pressure Of Water At 23c . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
