Triangle That Has 2 Equal Sides
Juapaving
Mar 04, 2025 · 6 min read
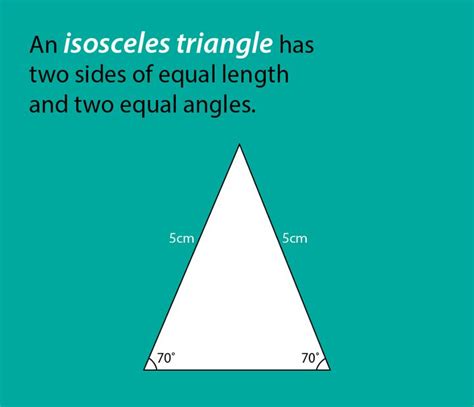
Table of Contents
Delving Deep into Isosceles Triangles: Properties, Theorems, and Applications
An isosceles triangle, a geometric shape familiar to many, holds a special place in mathematics due to its unique properties and diverse applications. Characterized by having two sides of equal length, this seemingly simple triangle unlocks a wealth of mathematical concepts and finds its way into various real-world scenarios. This comprehensive exploration will delve into the intricacies of isosceles triangles, examining their key properties, significant theorems associated with them, and practical examples of their application across different fields.
Defining an Isosceles Triangle: More Than Just Equal Sides
At its core, an isosceles triangle is defined as a triangle with at least two sides of equal length. These sides are referred to as the legs of the triangle, while the third side, which can be either shorter or longer than the legs, is called the base. The angles opposite the equal sides are known as base angles, and they are always equal to each other. This equality of base angles is a crucial property, forming the foundation for many theorems and problem-solving techniques involving isosceles triangles.
It's important to note that while the definition mentions at least two equal sides, an equilateral triangle, with all three sides equal, is also considered a special case of an isosceles triangle. This highlights the inclusive nature of the definition and the interconnectedness within geometric shapes.
Key Properties and Theorems of Isosceles Triangles
The unique nature of isosceles triangles leads to several significant properties and theorems that are instrumental in understanding their behavior and solving related problems:
1. Base Angles Theorem: The Cornerstone of Isosceles Triangles
The Base Angles Theorem states that if two sides of a triangle are congruent (equal in length), then the angles opposite those sides are also congruent. This theorem is fundamental to understanding the symmetry inherent in isosceles triangles. Conversely, if two angles of a triangle are congruent, then the sides opposite those angles are also congruent – this is the converse of the Base Angles Theorem. These theorems form a powerful pair, allowing us to deduce information about either sides or angles based on the known information.
Proof (Base Angles Theorem): Various methods exist to prove the Base Angles Theorem, often involving constructing an altitude from the vertex angle to the midpoint of the base. This creates two congruent right-angled triangles, leading to the conclusion that the base angles are equal.
2. The Isosceles Triangle Theorem and its Implications
The Isosceles Triangle Theorem is simply another name for the Base Angles Theorem and its converse. Understanding this theorem is crucial for tackling many geometric problems. For instance, knowing that the base angles are equal often allows us to solve for unknown angles within the triangle or in related geometrical figures.
3. Altitude from the Vertex Angle: A Line of Symmetry
The altitude drawn from the vertex angle (the angle between the two equal sides) to the base of an isosceles triangle has a special property: it bisects both the vertex angle and the base. This means the altitude acts as a line of symmetry, dividing the isosceles triangle into two congruent right-angled triangles. This property is invaluable in solving various problems involving areas, lengths, and angles within the triangle.
4. Medians and Angle Bisectors: Further Properties
The median drawn from the vertex angle to the base also coincides with the altitude and angle bisector in an isosceles triangle. This confluence of lines simplifies many geometric constructions and calculations. This property highlights the inherent symmetry and regularity of isosceles triangles.
Solving Problems Involving Isosceles Triangles
Understanding the properties of isosceles triangles is crucial for effectively solving various geometric problems. Here are some examples illustrating how the theorems and properties discussed above are applied:
Example 1: Finding Unknown Angles
Consider an isosceles triangle with base angles of 40°. To find the vertex angle, we use the fact that the sum of angles in a triangle is 180°. Since the base angles are equal, the vertex angle is 180° - 40° - 40° = 100°.
Example 2: Determining Side Lengths
An isosceles triangle has two equal sides of length 5cm and a base of 6cm. Using the Pythagorean theorem (applicable when the altitude is drawn), we can calculate the altitude and various other segments within the triangle.
Example 3: Area Calculation
To find the area of an isosceles triangle, we can use the standard formula: Area = (1/2) * base * height. The height can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem, as mentioned earlier.
Example 4: Proof-based problems
Many geometry problems require using the properties of isosceles triangles to prove other statements. For example, one could prove that two triangles are congruent using the Side-Angle-Side (SAS) postulate, where the equal sides of the isosceles triangle form part of the congruent sides.
Applications of Isosceles Triangles in Real World
Beyond theoretical mathematics, isosceles triangles find practical applications across diverse fields:
1. Architecture and Engineering: Structural Integrity
The inherent stability and symmetry of isosceles triangles make them a preferred choice in architecture and engineering. Many roof structures, bridges, and other constructions utilize isosceles triangles to distribute weight efficiently and ensure structural integrity. The symmetrical load distribution leads to better stability and resistance to stress.
2. Design and Art: Aesthetics and Balance
Isosceles triangles frequently appear in artistic designs and various aesthetic applications. Their symmetrical nature contributes to visual balance and harmony in compositions. This symmetrical appeal is seen in logos, artwork, and even in the design of everyday objects.
3. Surveying and Navigation: Triangulation Techniques
Surveying and navigation often use triangulation techniques, which involve creating a network of triangles to accurately measure distances and locate points. Isosceles triangles can be part of these networks, simplifying calculations and improving accuracy.
4. Computer Graphics and Game Development: Geometric Modeling
In computer graphics and game development, isosceles triangles are essential building blocks for creating more complex shapes and models. The simplicity of their mathematical representation and their ability to tessellate efficiently makes them suitable for creating various 3D models and textures.
Exploring Beyond the Basics: Advanced Concepts
While the core properties of isosceles triangles are relatively straightforward, more advanced concepts can deepen our understanding:
-
Isosceles Triangle Theorems in Higher Dimensions: The concepts of isosceles triangles can be extended to higher-dimensional spaces, leading to more complex geometrical considerations.
-
Isosceles Triangles in Non-Euclidean Geometry: Examining isosceles triangles within non-Euclidean geometries (like spherical or hyperbolic geometry) reveals intriguing differences from their Euclidean counterparts.
-
Relationship to other geometric figures: Isosceles triangles are closely linked to other geometric shapes, such as kites, rhombuses, and certain types of quadrilaterals. Understanding these connections further enriches our geometric knowledge.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Isosceles Triangles
This detailed exploration reveals the depth and significance of isosceles triangles, extending far beyond their simple definition. From fundamental theorems to practical applications, isosceles triangles play a vital role in mathematics, engineering, art, and other fields. Their inherent symmetry and properties continue to inspire mathematical curiosity and drive innovation across diverse disciplines. This detailed understanding empowers problem-solving capabilities within geometry and provides a solid foundation for exploring more advanced mathematical concepts. The seemingly simple isosceles triangle holds a remarkable complexity and significance that deserves continued exploration and appreciation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple Of 8 And 7
Mar 04, 2025
-
1 Universal Mass Unit Eual To
Mar 04, 2025
-
Name 3 Ways To Dissolve Something Faster
Mar 04, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 10 And 12
Mar 04, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between A Solute And Solvent
Mar 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Triangle That Has 2 Equal Sides . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
