The Sum Of All Body Chemistry
Juapaving
Mar 21, 2025 · 7 min read
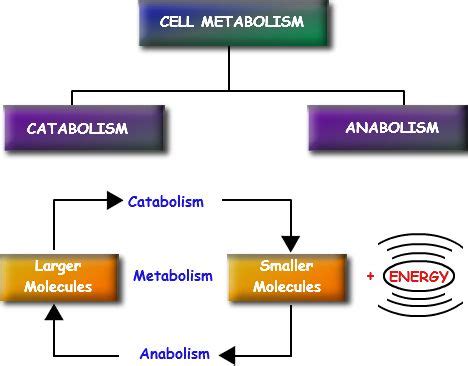
Table of Contents
The Sum of All Body Chemistry: A Deep Dive into Human Biochemistry
The human body is a marvel of intricate biological machinery, a complex ecosystem operating at a breathtaking scale. At its core lies biochemistry, the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. Understanding the sum of all body chemistry is not merely an academic pursuit; it's fundamental to comprehending health, disease, and the very essence of what it means to be human. This article delves deep into the multifaceted world of human biochemistry, exploring its key components and their interconnectedness.
The Building Blocks: Macromolecules and Metabolism
Our bodies are primarily composed of four major classes of macromolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. These molecules, along with water and various inorganic ions, participate in a dynamic network of metabolic pathways.
Carbohydrates: The Body's Primary Energy Source
Carbohydrates, ranging from simple sugars like glucose to complex polysaccharides like starch and glycogen, serve as the body's primary energy source. Glucose, a monosaccharide, is crucial for cellular respiration, the process that generates ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the cell's energy currency. Glycogen, a storage form of glucose, is stored in the liver and muscles, providing a readily available energy reserve. The metabolism of carbohydrates involves intricate pathways, including glycolysis, the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation, all tightly regulated to maintain energy homeostasis. Understanding carbohydrate metabolism is vital for managing conditions like diabetes, where glucose regulation is impaired.
Lipids: More Than Just Fat
Lipids, encompassing fats, oils, phospholipids, and steroids, play diverse roles beyond energy storage. Fats provide a concentrated energy source, while phospholipids form the structural basis of cell membranes. Steroids, like cholesterol, are crucial components of cell membranes and precursors to hormones like testosterone and estrogen. Lipid metabolism involves complex processes like lipogenesis (fat synthesis) and lipolysis (fat breakdown), influenced by factors like diet and hormonal regulation. Disruptions in lipid metabolism contribute to conditions like obesity, cardiovascular disease, and certain types of cancer.
Proteins: The Workhorses of the Cell
Proteins are the workhorses of the cell, performing a vast array of functions. They act as enzymes, catalyzing biochemical reactions; as structural components, providing support and shape; as transporters, moving molecules across cell membranes; and as hormones and receptors, mediating cellular communication. Protein synthesis, governed by the genetic code, involves transcription (DNA to RNA) and translation (RNA to protein). Protein structure, determined by the amino acid sequence, dictates its function. Protein deficiencies can lead to numerous health problems, affecting everything from growth and development to immune function.
Nucleic Acids: The Blueprint of Life
Nucleic acids, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid), carry the genetic information that dictates the structure and function of all living organisms. DNA stores the genetic blueprint, while RNA plays crucial roles in protein synthesis and gene regulation. The replication of DNA ensures the faithful transmission of genetic information during cell division, while mutations in DNA can lead to genetic disorders and cancer. Understanding nucleic acid structure and function is fundamental to genetic engineering, gene therapy, and the diagnosis and treatment of genetic diseases.
The Interplay of Systems: Maintaining Homeostasis
The body's biochemical processes don't operate in isolation. Instead, they are intricately interconnected and regulated to maintain homeostasis, a state of internal balance. Several key systems contribute to this intricate orchestration:
The Endocrine System: Hormonal Regulation
The endocrine system, composed of glands that secrete hormones, plays a pivotal role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development. Hormones, acting as chemical messengers, travel through the bloodstream to target cells, influencing various biochemical processes. Insulin, for example, regulates blood glucose levels, while thyroid hormones influence metabolic rate. Hormonal imbalances can lead to a wide range of disorders, from diabetes and hypothyroidism to growth disorders and reproductive problems.
The Nervous System: Rapid Communication
The nervous system facilitates rapid communication between different parts of the body, influencing biochemical processes through neural signals. Neurotransmitters, released at synapses, transmit signals between neurons, affecting processes like muscle contraction, sensory perception, and cognitive function. Neurological disorders can disrupt these delicate signaling pathways, leading to a variety of debilitating conditions.
The Immune System: Defense Mechanisms
The immune system defends the body against pathogens (disease-causing organisms) and harmful substances. Immune cells, such as lymphocytes and macrophages, recognize and eliminate foreign invaders through complex biochemical interactions. Antibodies, proteins produced by immune cells, specifically target and neutralize pathogens. Immune dysfunction can result in autoimmune diseases, immunodeficiencies, and increased susceptibility to infections.
The Digestive System: Nutrient Absorption
The digestive system breaks down food into smaller molecules, facilitating nutrient absorption. Enzymes secreted by the digestive tract catalyze the hydrolysis of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids, converting them into forms that can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Digestive disorders can impair nutrient absorption, leading to nutritional deficiencies and other health problems.
Beyond the Basics: Specialized Biochemical Processes
Beyond the fundamental macromolecules and metabolic pathways, numerous other specialized biochemical processes contribute to the sum of all body chemistry.
Cellular Respiration: Energy Production
Cellular respiration, the process by which cells extract energy from nutrients, is central to energy production. This complex multi-step process involves glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation, generating ATP, the cell's primary energy currency. Mitochondrial dysfunction, impacting cellular respiration, can contribute to various diseases.
DNA Replication and Repair: Maintaining Genetic Integrity
DNA replication ensures the faithful transmission of genetic information during cell division, while DNA repair mechanisms correct errors and damage to the DNA molecule. Failures in DNA repair can lead to mutations and genomic instability, contributing to cancer and other genetic disorders.
Signal Transduction: Cellular Communication
Signal transduction pathways allow cells to respond to external stimuli, such as hormones and neurotransmitters. These pathways involve intricate networks of proteins and other molecules that transmit signals from the cell surface to the nucleus, influencing gene expression and cellular behavior. Disruptions in signal transduction can lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and metabolic disorders.
The Impact of External Factors: Diet, Environment, and Lifestyle
The sum of all body chemistry is not solely determined by internal factors. External factors, including diet, environment, and lifestyle, significantly influence biochemical processes and overall health.
Diet: Providing Essential Nutrients
A balanced diet provides essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and essential amino acids and fatty acids, which are crucial for various biochemical processes. Nutritional deficiencies can impair metabolic pathways, leading to various health problems. Adopting a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein is vital for maintaining optimal health.
Environment: Exposure to Toxins
Exposure to environmental toxins, including pollutants and heavy metals, can disrupt biochemical processes, leading to various health problems. These toxins can damage cells, interfere with enzyme activity, and disrupt hormonal balance. Minimizing exposure to environmental toxins is crucial for protecting health.
Lifestyle: Exercise and Stress
Lifestyle factors, such as exercise and stress, significantly impact biochemistry. Regular exercise improves metabolic health, while chronic stress can disrupt hormonal balance and increase the risk of various diseases. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and stress management techniques, is crucial for overall well-being.
The Future of Biochemistry: Unraveling Complexity
The study of human biochemistry continues to evolve, with advancements in technology and research methods revealing ever greater complexities. Techniques such as genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics allow scientists to analyze the entire genome, proteome (the complete set of proteins), and metabolome (the complete set of metabolites) of an organism, providing a comprehensive view of its biochemical makeup. This deeper understanding promises to revolutionize diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases, leading to more personalized and effective healthcare.
In conclusion, the sum of all body chemistry is a vast and intricate network of biochemical processes, constantly interacting and adapting to maintain homeostasis. Understanding this complex interplay is fundamental to comprehending health and disease, and the ongoing research in this field promises to unlock new possibilities for improving human health and well-being. From the basic building blocks of life to the sophisticated regulatory mechanisms that govern cellular processes, the study of biochemistry offers a profound insight into the miraculous complexity of the human body.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
An Atom Gets An Overall Positive Charge By
Mar 28, 2025
-
Hydrogen Metal Or Nonmetal Or Metalloid
Mar 28, 2025
-
List The First 5 Multiples Of 2
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Liters In 2 Gallons
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Reciprocal Of A Mixed Fraction
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Sum Of All Body Chemistry . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
