The Greater The Concentration Gradient The Faster The Diffusion Rate
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
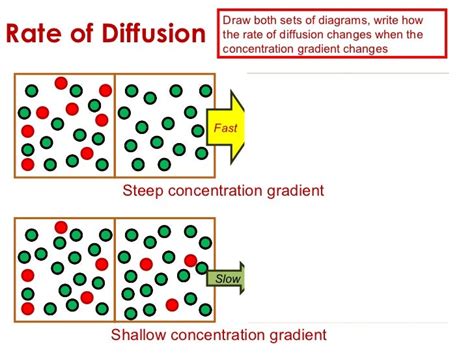
Table of Contents
The Greater the Concentration Gradient, the Faster the Diffusion Rate: A Deep Dive
Diffusion, a fundamental process in biology and chemistry, governs the movement of substances from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. Understanding the factors influencing diffusion rate is crucial in various fields, from medicine and pharmacology to environmental science and materials engineering. This article delves into the relationship between concentration gradient and diffusion rate, exploring the underlying principles and providing real-world examples.
Understanding Concentration Gradients
Before we dive into the relationship between concentration gradient and diffusion rate, let's first clarify what a concentration gradient is. A concentration gradient is simply the difference in the concentration of a substance between two points. Imagine a drop of ink placed in a glass of water. Initially, the ink is highly concentrated at the point of the drop. As time passes, the ink molecules spread out, moving from the region of high concentration (the drop) to the region of low concentration (the surrounding water). This movement is driven by the concentration gradient. The steeper the gradient (i.e., the bigger the difference in concentration), the faster the ink will spread.
Visualizing the Gradient
Think of it like a hill. A steep hill represents a large concentration gradient – a significant difference in concentration between the top and bottom. A gentle slope represents a small concentration gradient – a smaller difference in concentration. The steeper the hill (larger gradient), the faster an object will roll down (faster diffusion). Conversely, on a gentle slope (smaller gradient), the object will roll down more slowly (slower diffusion). This analogy helps visualize the concept of how the magnitude of the concentration gradient directly impacts the rate of diffusion.
The Direct Relationship: Gradient and Diffusion Rate
The core principle is this: the greater the concentration gradient, the faster the diffusion rate. This is because a larger difference in concentration creates a stronger driving force for the movement of molecules. More molecules are "pushing" to move from the high-concentration area to the low-concentration area, resulting in a faster rate of diffusion.
Molecular Dynamics and Kinetic Energy
At a microscopic level, this increased rate is a consequence of the increased kinetic energy of the molecules in the high-concentration region. Molecules are in constant, random motion due to their inherent thermal energy. In a region of high concentration, the molecules collide more frequently, leading to a higher probability of movement towards the region of lower concentration. A steeper concentration gradient simply amplifies this effect.
Factors Influencing Diffusion Beyond Concentration Gradient
While the concentration gradient is a primary factor, it's not the only one. Other factors significantly influence diffusion rates:
1. Temperature
Higher temperatures increase the kinetic energy of molecules, making them move faster and thus increasing the diffusion rate. Imagine heating the glass of water with the ink drop – the ink will spread faster because the water molecules are moving more rapidly, facilitating the dispersal of ink molecules.
2. Molecular Size and Shape
Smaller molecules generally diffuse faster than larger ones. Their smaller size allows them to navigate through spaces more easily. Similarly, the shape of a molecule can influence its ability to move through a medium. A spherical molecule might diffuse faster than a long, elongated one due to its greater maneuverability.
3. Medium of Diffusion
The medium through which diffusion occurs also plays a crucial role. Diffusion is generally faster in gases than in liquids, and faster in liquids than in solids. This is because the molecules in gases are more widely spaced, offering less resistance to movement. The viscosity and density of the medium also impact diffusion rates. A less viscous medium allows for faster diffusion.
4. Distance
The distance over which diffusion must occur is inversely proportional to the rate. The further the molecules need to travel, the longer it takes, and the slower the effective diffusion rate becomes. This is why efficient transport mechanisms are essential in larger organisms to overcome the limitations of diffusion over long distances.
5. Membrane Permeability (Biological Systems)
In biological systems, the permeability of the cell membrane or other barriers significantly impacts diffusion rates. The membrane's structure and composition determine which molecules can pass through and at what rate. For example, a membrane that is permeable to a specific molecule will facilitate faster diffusion compared to a less permeable membrane.
Real-World Applications and Examples
The principle of concentration gradients and their influence on diffusion is fundamental to many processes:
1. Oxygen Uptake in Lungs
Oxygen diffuses from the alveoli (air sacs in the lungs) into the blood capillaries due to the concentration gradient. The alveoli have a high oxygen concentration, while the blood entering the capillaries has a lower concentration. This concentration difference drives oxygen into the bloodstream. Any factors that reduce this gradient, such as lung disease, will decrease the rate of oxygen uptake.
2. Nutrient Absorption in the Intestine
Nutrients from digested food diffuse across the intestinal lining into the bloodstream. The high concentration of nutrients in the intestine creates a concentration gradient that drives their absorption. Malabsorption syndromes can be related to disruptions in this gradient or the efficiency of the absorption process.
3. Waste Removal in Kidneys
The kidneys filter waste products from the blood. The concentration gradient between the blood and the nephrons (functional units of the kidneys) helps drive the filtration process. Kidney diseases can impair this process by affecting the concentration gradients.
4. Perfume Spreading in a Room
When you spray perfume, the fragrance molecules diffuse through the air. The initial high concentration of perfume molecules near the spray creates a gradient that causes the scent to spread throughout the room until a relatively uniform concentration is achieved.
5. Drug Delivery
Pharmaceutical scientists carefully consider concentration gradients when designing drug delivery systems. The rate at which a drug is released and absorbed into the body is influenced by the concentration gradient between the drug formulation and the surrounding tissue.
6. Environmental Science
In environmental science, understanding diffusion is crucial for studying pollutant dispersal in the atmosphere or water bodies. The concentration gradient of pollutants determines how quickly they spread and affect different areas.
Conclusion: Implications and Further Exploration
The relationship between concentration gradient and diffusion rate is a cornerstone of understanding many natural phenomena and technological processes. The steeper the concentration gradient, the faster the diffusion. However, remember that other factors, such as temperature, molecular size, medium of diffusion, distance and membrane permeability, also play crucial roles. Further research and exploration into these intricate interplays will continue to advance our understanding of diffusion and its widespread significance. This knowledge allows us to develop better strategies for optimizing diffusion-based processes across diverse fields. From enhancing drug delivery systems to mitigating environmental pollution, grasping the principles of concentration gradients and diffusion remains a critical aspect of scientific and technological advancement.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Electrical Conductivity Physical Or Chemical Property
Mar 28, 2025
-
Why Do Atoms Want 8 Valence Electrons
Mar 28, 2025
-
Two Angles Whose Measures Have A Sum Of 180 Degrees
Mar 28, 2025
-
Select All Of The Following That Are Characteristics Of Plants
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Resistance And Impedance
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Greater The Concentration Gradient The Faster The Diffusion Rate . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
