The C Shape Of The Tracheal Cartilages Is Important Because
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
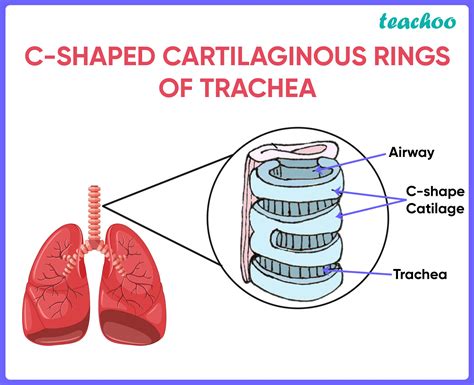
Table of Contents
The C-Shape of Tracheal Cartilages: A Crucial Design for Breathing
The human trachea, or windpipe, is a vital component of the respiratory system, responsible for conducting air to and from the lungs. Its structure is far from simple, with a key feature being the C-shaped hyaline cartilage rings that encircle its circumference. This isn't a random design choice; the incomplete, C-shaped nature of these cartilages is crucial for several important physiological functions. This article will delve into the significance of this unique architecture, exploring its role in breathing mechanics, swallowing, and overall respiratory health.
Why the C-Shape and Not a Full Circle?
The most immediate question is: why aren't the tracheal cartilages complete rings? The answer lies in the intricate interplay between the trachea's function in breathing and its proximity to the esophagus, the tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach.
1. Esophageal Expansion During Swallowing: If the tracheal cartilages were complete rings, they would rigidly encircle the trachea, restricting its flexibility. This would severely impede the esophagus's ability to expand during swallowing. The posterior, open section of the C-shaped cartilage allows the esophageal wall to bulge outward when a food bolus passes through. This prevents compression of the esophagus and the risk of choking or aspiration of food into the trachea.
2. Facilitating Tracheal Movement During Breathing: The trachea isn't a static structure; it moves and flexes with each breath. The incomplete cartilaginous rings provide the necessary flexibility to accommodate these movements. The soft tissue membrane connecting the ends of the C-shaped cartilages, called the trachealis muscle, plays a significant role in this flexibility. It can contract and relax, adjusting the diameter of the trachea and influencing airflow. This adaptability is essential for regulating the volume of air entering and leaving the lungs. A rigid, fully circular structure would restrict this essential movement.
3. Protection Against Collapse: While allowing flexibility, the C-shaped cartilages still provide crucial structural support. Their rigid nature prevents the trachea from collapsing under the internal pressure changes that occur during breathing. This is especially important during forceful exhalation, where the pressure within the airways can become significantly lower than atmospheric pressure. The incomplete rings maintain the patency (openness) of the airway, ensuring a continuous flow of air.
The Role of the Trachealis Muscle: Fine-Tuning Airflow
The posterior gap in the tracheal cartilages is bridged by the trachealis muscle, a smooth muscle that plays a crucial role in regulating airflow. Its actions are largely involuntary, meaning they happen without conscious control.
1. Cough Reflex: During a cough, the trachealis muscle contracts forcefully, narrowing the trachea. This increases the velocity of the expelled air, helping to clear irritants or mucus from the airways. The coordinated action of the trachealis muscle with other respiratory muscles allows for a powerful and effective cough.
2. Breathing Regulation: During normal breathing, the trachealis muscle's activity is more subtle. It can subtly adjust the tracheal diameter, contributing to the fine-tuning of airflow resistance. This subtle regulation plays a crucial role in maintaining efficient gas exchange within the lungs. In situations of increased airway resistance (e.g., during exercise or respiratory illness), the trachealis muscle can further adjust to optimize airflow.
3. Protective Mechanisms: The trachealis muscle, along with the surrounding connective tissue, plays a vital role in protecting the delicate tracheal mucosa (the inner lining of the trachea). Its contractions can help protect the mucosa from damage by reducing stress during coughing and other forceful respiratory maneuvers.
Clinical Significance of Tracheal Cartilage Structure
Understanding the structure and function of the tracheal cartilages is vital for diagnosing and treating various respiratory conditions. Abnormalities in the shape, number, or composition of these cartilages can lead to significant respiratory problems.
1. Tracheomalacia: This condition involves abnormal softening or weakness of the tracheal cartilages, leading to tracheal collapse, particularly during exhalation. This can cause wheezing, shortness of breath, and recurrent respiratory infections. The incomplete C-shaped rings, while generally beneficial, can also make individuals more susceptible to this condition if there are congenital defects or acquired weakening of the cartilage.
2. Tracheostenosis: This involves a narrowing of the trachea, which can be caused by various factors, including congenital abnormalities, injury, or inflammation. The rigid nature of the cartilaginous rings, while normally supportive, can exacerbate the problem by limiting the trachea's ability to expand and compensate for the narrowing.
3. Intubation and Tracheostomy: Medical procedures like intubation (inserting a tube into the trachea) and tracheostomy (creating an opening in the trachea) require a thorough understanding of the tracheal anatomy. The placement of these tubes must carefully consider the location and structure of the C-shaped cartilages to avoid damage and complications.
4. Age-Related Changes: The tracheal cartilages, like other cartilaginous structures in the body, are subject to age-related changes. Calcification and loss of elasticity can occur with aging, impacting the flexibility and function of the trachea. This can contribute to age-related decline in respiratory function.
The Interplay of Structure and Function: A Holistic Perspective
The C-shape of the tracheal cartilages is not just a random anatomical feature; it's a testament to the elegance and efficiency of biological design. The interplay between the rigid support of the cartilages and the flexibility provided by the trachealis muscle ensures that the trachea can effectively fulfill its vital role in respiration while coexisting peacefully with the esophagus. Any deviation from this optimized design can lead to significant respiratory complications.
Furthermore, the intricate relationship between the trachea, esophagus, and surrounding structures highlights the interconnectedness of bodily systems. The efficient functioning of one system often relies on the proper function of others. The C-shaped cartilages stand as a remarkable example of this interconnectedness, illustrating how a seemingly simple anatomical feature plays a critical role in maintaining overall health and well-being.
Beyond the Basics: Further Research and Understanding
While much is known about the function of tracheal cartilages, ongoing research continues to refine our understanding of their role in respiratory health. Advanced imaging techniques allow for detailed visualization of tracheal structure and function, aiding in the diagnosis and management of respiratory disorders. Studies are also exploring the impact of various factors, including aging, environmental pollutants, and genetic predisposition, on the health and integrity of tracheal cartilage.
Understanding the intricate mechanics of breathing and the crucial role played by the C-shaped tracheal cartilages is vital for improving the diagnosis and treatment of respiratory diseases. Further research will undoubtedly unveil more about this fascinating and critical aspect of human anatomy and physiology. The seemingly simple C-shape holds the key to a complex and crucial system, underscoring the remarkable ingenuity of biological design.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Square Root Of 625
Mar 17, 2025
-
Speed Of Light In Terms Of Permittivity And Permeability
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Does T Stand For In Physics
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Electron Does Oxygen Have
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Percentage And Percentile
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The C Shape Of The Tracheal Cartilages Is Important Because . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
