What Does T Stand For In Physics
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
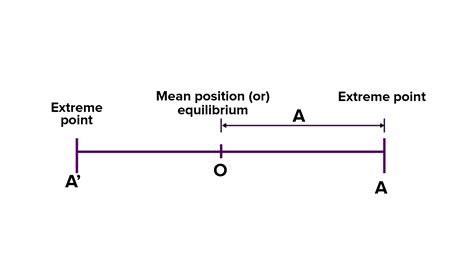
Table of Contents
What Does T Stand For in Physics? A Comprehensive Guide
Physics, a vast and intricate field, employs a multitude of symbols and abbreviations. One such symbol, 'T', appears frequently, often representing different quantities depending on the context. This comprehensive guide will delve into the various meanings of 'T' in physics, exploring its significance in different branches of the field. We'll examine its usage in mechanics, thermodynamics, electromagnetism, and more, ensuring a clear and comprehensive understanding for students and enthusiasts alike.
T as a Unit of Measurement: Tesla
Perhaps the most widely recognized meaning of 'T' in physics is its representation of the Tesla, the SI unit of magnetic flux density. Named after the brilliant Serbian-American inventor Nikola Tesla, this unit measures the strength of a magnetic field.
Understanding Magnetic Flux Density
The magnetic flux density, often denoted by B, quantifies the force a magnetic field exerts on a moving charged particle. A stronger magnetic field corresponds to a higher Tesla value. One Tesla is a significant magnetic field; powerful electromagnets might generate fields of several Tesla, whereas the Earth's magnetic field is measured in microteslas (µT).
Applications of Tesla
The Tesla unit finds applications across numerous areas, including:
-
Medical Imaging: MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) machines utilize powerful magnetic fields, measured in Tesla, to generate detailed images of the human body's internal structures. Higher Tesla MRI scanners offer superior image resolution and clarity.
-
Particle Accelerators: High-energy particle accelerators like the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) rely on incredibly strong magnetic fields to guide and accelerate charged particles. These fields are also measured in Tesla.
-
Industrial Applications: Maglev (magnetic levitation) trains utilize strong magnetic fields to levitate above the tracks, enabling high-speed travel. The magnetic fields responsible for this levitation are measured in Tesla.
T as Time: A Fundamental Quantity
In numerous physics equations and contexts, 'T' signifies time. Time, alongside mass and length, forms one of the fundamental dimensions in physics, playing a critical role in many physical phenomena.
Time in Kinematics and Dynamics
In classical mechanics, time is an independent variable, essential for understanding motion. Kinematics equations, describing motion without considering the forces involved, frequently feature 'T' to represent the elapsed time. Similarly, dynamics equations, which incorporate forces, also utilize 'T' to represent time.
Time in Oscillations and Waves
'T' also represents the period of an oscillation or wave. The period is the time it takes for one complete cycle to occur. For example, in simple harmonic motion (SHM), the period 'T' is inversely proportional to the frequency 'f' (T = 1/f).
Time in Relativity
In Einstein's theory of special relativity, time is not absolute but is relative to the observer's frame of reference. Time dilation, a consequence of special relativity, shows that time passes slower for objects moving at high speeds relative to a stationary observer. This relativistic time is still represented by 'T' within the relevant equations.
T in Thermodynamics: Temperature and Tension
In the context of thermodynamics, 'T' commonly represents temperature, a fundamental property of matter related to the average kinetic energy of its particles.
Temperature Scales
Different temperature scales exist, including Celsius (°C), Fahrenheit (°F), and Kelvin (K). The Kelvin scale is the absolute temperature scale, where 0 K represents absolute zero, the theoretical lowest temperature possible. While sometimes shown as °T or other representations, 'T' is frequently used to refer to the Kelvin temperature in thermodynamic equations.
Tension in Thermodynamics
Although less frequent, 'T' can also represent tension in certain thermodynamic contexts, particularly when dealing with stretched materials or systems under stress. This usage is context-dependent and less common than its use for temperature.
T in Other Contexts: Torque, Transmission Coefficient, and More
Beyond the established usages, 'T' can represent various other quantities in specialized physics branches:
-
Torque: In rotational mechanics, 'T' is often used to denote torque, the rotational equivalent of force. Torque is the measure of a force's effectiveness at causing rotational acceleration.
-
Transmission Coefficient: In quantum mechanics, 'T' can symbolize the transmission coefficient, a quantity representing the probability that a particle will pass through a potential barrier. This coefficient plays a critical role in understanding quantum tunneling.
-
Period of a Wave: As mentioned earlier, T frequently denotes the period of a wave in oscillations and wave phenomena. This is crucial for characterizing wave properties like frequency and wavelength.
Distinguishing the Meanings of 'T'
The various meanings of 'T' in physics highlight the importance of carefully examining the context. The surrounding equations, figures, and discussion usually provide clear clues about the intended meaning. Consulting textbooks, scientific papers, or lecture notes related to the specific topic often resolves any ambiguity.
Tips for Understanding Physics Notation
Physics often uses concise notation, and understanding these conventions is essential. Here are a few tips:
- Context is key: Always pay close attention to the context in which a symbol is used. The surrounding text and equations will usually provide clarification.
- Units of Measurement: The units associated with a symbol often give clues to its meaning (e.g., Tesla for magnetic flux density, seconds for time).
- Refer to Standard Texts: Consulting reliable physics textbooks or reference materials can clarify any uncertainties regarding symbols and their meanings.
- Seek Clarification: If the meaning remains unclear, don't hesitate to seek help from instructors, colleagues, or online forums dedicated to physics.
Conclusion: The Versatility of 'T' in Physics
'T' serves as a versatile symbol in physics, representing various essential quantities depending on the context. While its most common meanings are Tesla (magnetic flux density) and time, it can also stand for temperature, torque, transmission coefficient, and the period of a wave. Understanding the different meanings of 'T' and the context in which it's used is vital for comprehending physics concepts and equations accurately. By carefully considering the surrounding information and using the recommended tips, students and enthusiasts can confidently navigate the multifaceted use of 'T' in the fascinating world of physics. Remember to always prioritize understanding the context for accurate interpretation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Find An Area Of A Triangle
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 6 9 And 12
Mar 17, 2025
-
Write 80 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Is A Better Conductor Of Electricity Metal Or Water
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Minutes Are There In A Day
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Does T Stand For In Physics . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
