Sum Of Even And Odd Numbers
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
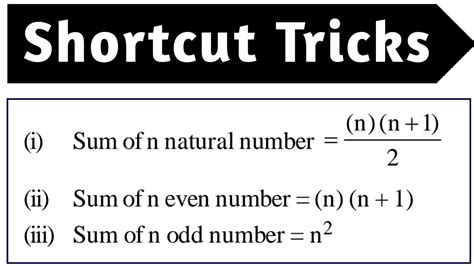
Table of Contents
The Fascinating World of Even and Odd Numbers: Sums, Patterns, and Properties
The seemingly simple concepts of even and odd numbers form the bedrock of number theory. Understanding their properties, particularly how their sums behave, unlocks a deeper appreciation for mathematical patterns and structures. This exploration delves into the fascinating world of even and odd numbers, examining their sums, revealing underlying patterns, and highlighting their applications in various mathematical contexts. We'll unravel the seemingly simple yet surprisingly rich mathematics behind these fundamental number types.
Defining Even and Odd Numbers
Before diving into the intricacies of sums, let's establish clear definitions:
-
Even Numbers: An even number is any integer that is perfectly divisible by 2, leaving no remainder. Mathematically, we can represent an even number as 2k, where k is any integer (0, 1, 2, 3, ...). Examples include 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, and so on.
-
Odd Numbers: An odd number is any integer that leaves a remainder of 1 when divided by 2. We can express an odd number as 2k + 1, where k is again any integer. Examples are 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, and so forth.
These seemingly simple definitions are crucial for understanding the behavior of even and odd numbers when added together.
Sum of Two Even Numbers
The sum of two even numbers is always even. This is easily demonstrable:
Let's take two even numbers, represented as 2a and 2b, where 'a' and 'b' are integers. Their sum is:
2a + 2b = 2(a + b)
Since 'a' and 'b' are integers, their sum (a + b) is also an integer. Let's call this integer 'c'. Therefore, the sum becomes:
2c
This is clearly an even number, confirming that the sum of any two even numbers is always even. This principle extends to the sum of any number of even numbers – the result will always be even.
Sum of Two Odd Numbers
The sum of two odd numbers is always even. Let's prove this:
Let's represent two odd numbers as 2a + 1 and 2b + 1. Their sum is:
(2a + 1) + (2b + 1) = 2a + 2b + 2 = 2(a + b + 1)
Again, (a + b + 1) is an integer, let's call it 'd'. The sum simplifies to:
2d
This is, once again, an even number. This holds true for any two odd numbers. Similarly, the sum of an even number of odd numbers will always be even.
Sum of an Even and an Odd Number
The sum of an even and an odd number is always odd. This is the most straightforward case:
Let's take an even number (2a) and an odd number (2b + 1). Their sum is:
2a + (2b + 1) = 2a + 2b + 1 = 2(a + b) + 1
(a + b) is an integer, let's call it 'e'. The sum becomes:
2e + 1
This is the representation of an odd number. This demonstrates that the sum of an even and an odd number will always result in an odd number.
Patterns and Properties in Sums of Even and Odd Numbers
These simple rules about the sums of even and odd numbers reveal interesting patterns and properties:
-
Parity: The concept of "parity" refers to whether a number is even or odd. The parity of a sum depends solely on the parity of the numbers being added. The sum of two numbers with the same parity is always even, while the sum of numbers with opposite parity is always odd.
-
Modular Arithmetic: These rules are deeply connected to modular arithmetic, particularly modulo 2. Even numbers are congruent to 0 (mod 2), and odd numbers are congruent to 1 (mod 2). The rules of even and odd number sums are essentially the rules of addition modulo 2.
-
Predictability: The predictability of these sums makes them invaluable in various mathematical proofs and algorithms. Knowing the parity of a result without explicitly calculating it can significantly simplify complex computations.
Applications in Mathematics and Computer Science
The properties of even and odd number sums find applications in diverse areas:
-
Number Theory: Many number-theoretic proofs rely heavily on the properties of even and odd numbers. For example, proving certain theorems about prime numbers or divisibility often involves analyzing the parity of numbers involved.
-
Cryptography: Cryptographic algorithms often leverage the properties of even and odd numbers for security. Some encryption schemes rely on the difficulty of determining the parity of a very large number.
-
Computer Science: In computer science, bitwise operations frequently utilize the concept of even and odd numbers. Checking the least significant bit (LSB) of a number effectively determines whether the number is even or odd. This is used in algorithms for efficient data manipulation and error checking.
-
Combinatorics: Combinatorial problems often involve counting scenarios that can be simplified by considering the parity of numbers.
-
Game Theory: Certain games and puzzles involve strategies based on the parity of numbers. Winning or losing might depend on whether the total score is even or odd.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
While the basic sums of even and odd numbers are straightforward, delving deeper reveals more complex and interesting mathematical concepts:
-
Sums of Sequences: Examining the sums of sequences of even or odd numbers reveals interesting patterns. For instance, the sum of the first 'n' even numbers is n(n+1), while the sum of the first 'n' odd numbers is n².
-
Infinite Series: Infinite series involving even and odd numbers can lead to surprising results and connections to other mathematical concepts.
-
Parity of Factorials: Determining the parity of factorials (n!) is another interesting application. Factorials of numbers greater than 1 are always even.
-
Parity in Graphs: Graph theory also uses parity concepts. For instance, Eulerian paths and circuits in a graph are closely related to the parity of the degrees of the vertices.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple world of even and odd numbers and their sums hides a wealth of mathematical richness and practical applications. From the fundamental properties of parity to their advanced applications in number theory, cryptography, and computer science, understanding these concepts provides a strong foundation for further mathematical exploration. The predictability of their sums makes them an essential tool for simplifying complex computations and solving various problems in different fields. Further exploration into advanced concepts related to sequences, infinite series, and graph theory will only deepen one's appreciation for the profound implications of these fundamental building blocks of arithmetic. The elegant simplicity and far-reaching consequences of even and odd numbers serve as a compelling example of the beauty and utility found at the heart of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Lcm Of 5 10 And 3
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Are The Least Common Multiples Of 8 And 12
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Psychology And Philosophy
Mar 24, 2025
-
Square Root Of 112 In Radical Form
Mar 24, 2025
-
How Many Electrons Are In Carbons Valence Shell
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sum Of Even And Odd Numbers . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
